To maintain its integrity, the human ocular surface (cornea and conjunctiva) has an absolute requirement for vitamin A and its active derivatives, the retinoic acids (RAs). These RAs regulate transcriptional levels of target genes through the activation of members of a superfamily of nuclear receptors that feature retinoic acid receptors (RARs) α, β, and γ as well as retinoid X receptors (RXRs) α, β, and γ. Creative Biolabs is dedicated to establishing the most exquisite service platform and offering one-stop nuclear receptors modeling services to support our clients’ projects.
The studies dealing with the effects of dietary vitamin A deficiency have demonstrated that vitamin A is required for eye morphogenesis. Lack of vitamin A causes abnormal differentiation of the ocular surface that results in keratinization, ulceration, epithelial squamous metaplasia, and a deficiency of conjunctival goblet cells. The pleiotropic effects of RAs are mediated by RARs and RXRs, which are ligand-activated transcription factors. Members of the RARs are activated by most of the physiologically-occurring RAs (all-trans RA, 9-cis RA, 4-oxo RA, and 3,4di-hydro RA). In contrast, members of the RXRs are only activated by 9-cis RA. The transcriptional regulation of the target genes relies on the recognition and cooperative assembly of RAR-RXR heterodimers in short DNA sequences in their promoter regions.
RARs and RXRs have a modular structure common to all nuclear receptors composed of six conserved regions designated A-F (Fig.1). The highly conserved C region harbors the DNA-binding domain (DBD) which consists of two cysteine-rich zinc-finger motifs and confers sequence-specific DNA recognition. Region E is the second most conserved region and corresponds to the ligand-binding domain (LBD). The LBD is formed by 12 conserved α-helices and a β-turn which are folded into a three-layered, antiparallel helical sandwich. The D region harbors nuclear localization signals and serves as a hinge between the DBD and the LBD, allowing rotation of the DBD. AF region is present in RARs but absent in RXRs.
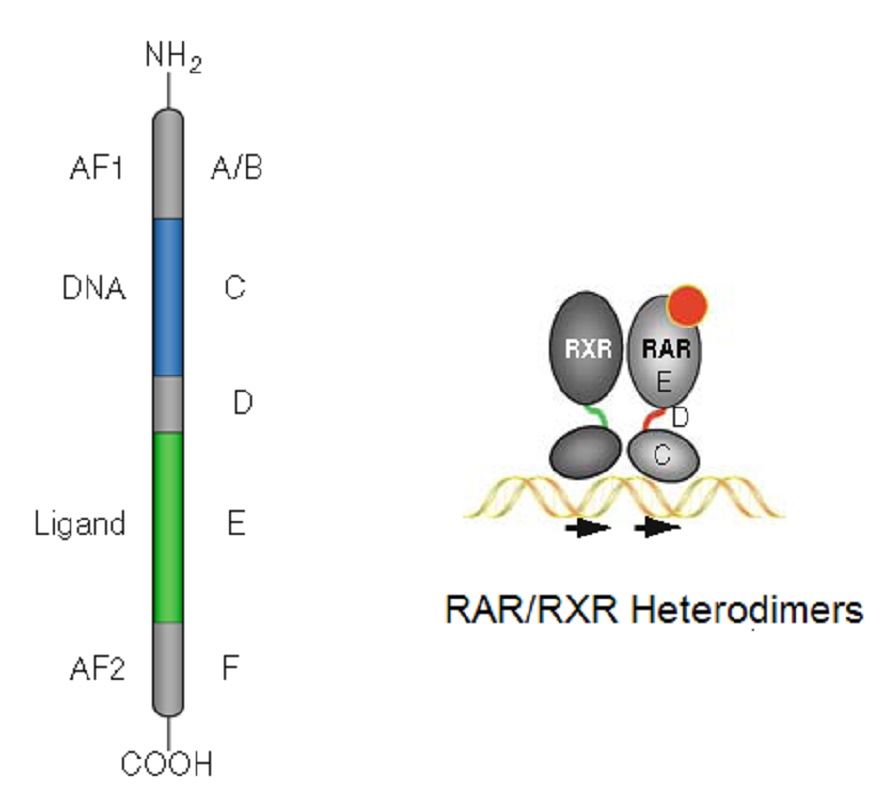 Fig.1 Schematic representation of RAR-RXR heterodimers.
Fig.1 Schematic representation of RAR-RXR heterodimers.
Topical retinoids have been tested as pharmacological agents for the treatment of ocular surface diseases involving wound healing, squamous metaplasia or dry eye. Most of the retinoids that are currently in clinical use are RAR or RXR agonists/antagonists. However, in the desire to generate new retinoids/rexinoids that may exhibit fewer side-effects, an ideal goal is to develop RAR- and RXR-specific ligands. The generation of these agents has been made possible by progress in crystallographic studies on nuclear receptor LBDs that have enabled useful information on ligand-receptor interactions at the molecular level. Taken together all crystal structures confirm the existence of a common fold, the so-called helical sandwich fold for LBDs and show that ligands induce major structural changes upon binding. Thus, various ligands have been developed by computer-assisted procedures using virtual libraries and/or molecular modeling. We can provide a variety of structure-based nuclear receptors modeling approaches to meet customers’ specific requirements.
Creative Biolabs is passionate about acquiring and using cutting-edge tools to advance drug development and is always looking for ways to improve our capabilities. We whole-heartedly cooperate with you to accomplish our shared goals. Our team provides you with outstanding support and meets your specific needs with a professional technology platform. If you are interested in our services, please contact us for more details.
All listed services and products are For Research Use Only. Do Not use in any diagnostic or therapeutic applications.