Retinoid X receptors (RXRs), a member of the nuclear receptor superfamily activated by binding of 9-cis-retinoic acid, comprise three different gene isoforms: RXRα, RXRβ, and RXRγ. Ligand activation of RXRs has potentially pleiotropic effects on numerous biological pathways and therapeutic opportunities for the treatment of respiratory diseases. Creative Biolabs is dedicated to establishing the most exquisite service platform for our clients and our one-stop nuclear receptor modeling services can provide comprehensive technical support to advance our clients’ projects.
RXR is widely expressed in several tissues and cells including adipose tissue, liver, kidneys, small intestine, cardiac myocytes and monocytes/macrophages. Recent investigations have demonstrated that RXRs are related to the development of asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Mice lacking PPARγ were reported to exhibit enhanced cigarette smoke (CS)-induced airway inflammation and emphysematous changes in the lungs. Gene expression of LXR in the lungs was increased in COPD patients, and an LXR agonist exerted anti-inflammatory effects on IL-10 production by alveolar macrophages. These data suggest that RXRs may be potential targets for the prevention and management of COPD.
In vitro studies demonstrated that RXRs heterodimers (with the retinoic acid receptor, RAR) act as ligand-dependent transcriptional regulators by binding to specific DNA-response elements found into the promoter region of target genes and the interaction of RXR increases the DNA-binding efficiency of its partner. For example, the crystal structure of a heterodimer between the ligand-binding domains (LBDs) of the human RAR and the constitutively active mouse RXR mutant shows that pushed by a bulky extension of the ligand, RAR helix H12 adopts an antagonist position, which is advantageous for the combination of DNA. RXRs are obligate heterodimerization partners for some nuclear receptors, and the number of their potential target genes is tremendous. RXRs can also form homodimers in vitro that can bind to DNA through DR-1 elements, suggesting the existence of RXR-specific signaling.
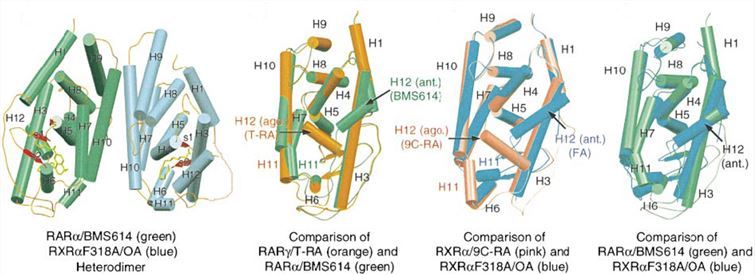 Fig.1 The RXR-RAR LBD heterodimer and its component monomers.
Fig.1 The RXR-RAR LBD heterodimer and its component monomers.
RXRs activation promotes the expression of anti-inflammatory mediators, including IL-10 and LXRs, and contributes to the phenotype of alternatively activated macrophages that exert suppressive effects on inflammation. RXRs are novel targets for respiratory disease and continued work with these ligands may result in a potential new treatment for chronic inflammatory respiratory diseases. Structure-based modeling remains one of the most important techniques for obtaining a rational 3D structural model to use in ligand design. We can offer a variety of nuclear receptors modeling services to meet specific requirements.
Creative Biolabs is able to apply a range of computational techniques to help you gain a deep understanding of your drug target and to complement any biological validation. We whole-heartedly cooperate with you to accomplish our shared goals. Our team provides you with outstanding support and meets your specific needs through a professional technology platform. If you are interested in our services, please contact us for more details.
All listed services and products are For Research Use Only. Do Not use in any diagnostic or therapeutic applications.