Introduction of CAV1
Avelin-1 is a cytoskeletal protein encoded by the CAV1 gene, which is a major component of the caveolae of the cell membrane. Aveolin-1 can be complexed with integrin and tyrosine kinase FYN, and is closely related to physiological processes such as cell signal transduction, intracellular substances and membrane transport. Not only that, aveolin-1 interacts with G proteins and then interacts with other molecules via the caveolin-scaffolding domain (CSD), such as SCP2, PLD2, estrogen receptor alpha, androgen receptor, TRAF2, PTGS2, PDGFRA, PDGFRB, endothelin receptor type B, epidermal growth factor receptor, nitric oxide synthase 2A, gap junction protein, amyloid precursor protein, endothelial NOS, TGFβ receptor 1, cholesterol, etc.
| Basic Information of CAV1 | |
| Protein Name | Caveolin-1 |
| Gene Name | CAV1 |
| Aliases | / |
| Organism | Homo sapiens (Human) |
| UniProt ID | Q03135 |
| Transmembrane Times | 0 |
| Length (aa) | 178 |
| Sequence | MSGGKYVDSEGHLYTVPIREQGNIYKPNNKAMADELSEKQVYDAHTKEIDLVNRDPKHLNDDVVKIDFEDVIAEPEGTHSFDGIWKASFTTFTVTKYWFYRLLSALFGIPMALIWGIYFAILSFLHIWAVVPCIKSFLIEIQCISRVYSIYVHTVCDPLFEAVGKIFSNVRINLQKEI |
Function of CAV1 Membrane Protein
Caveolae are a major membrane domain common to most cells. One of the defining features of this domain is the protein caveolin. The exact function of caveolin, however, is not clear. One possible function is to attract adapter molecules to caveolae in a manner similar to how clathrin attracts molecules to coated pits. At steady state, most caveolin-1 is either at the cell surface associated with invaginated caveolae or near the centrosome in caveosomes. Live cell fluorescence imaging indicates that while much of the caveolin-1 in caveolae at the cell surface is relatively sessile, numerous, highly motile caveolin-1-positive vesicles are present within the cell interior. These vesicles move at speeds ranging from 0.3-2 microm/second and movement is abolished when microtubules are depolymerized with nocodazole. In the absence of microtubules, cell surface invaginated caveolae increases more than two-fold and they become organized into linear arrays.
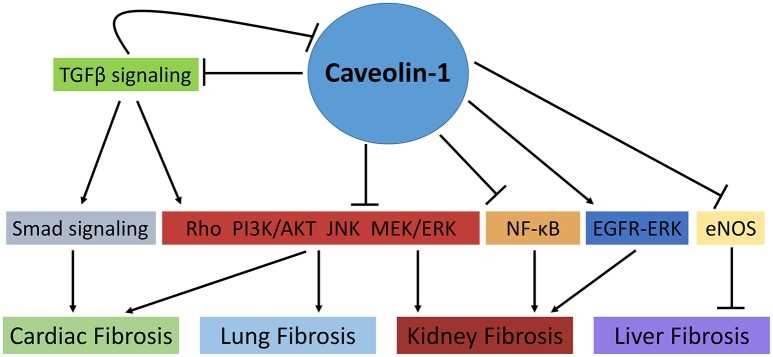 Fig.2 The role of Caveolin-1 in cellular signaling mechanisms involved in fibrosis. (Shihata, 2017)
Fig.2 The role of Caveolin-1 in cellular signaling mechanisms involved in fibrosis. (Shihata, 2017)
Application of CAV1 Membrane Protein in Literature
In this article, the author believes that syntenin may act as an important positive regulator of TGF-β signaling by regulating caveolin-1-mediated internalization of TβRI; thus, providing a novel function for syntenin that is linked to cancer progression.
This article indicates that SRBC (sdr-related gene product that binds to c-kinase) and two other family members [PTRF (Pol I and transcription release factor) and SDPR] function as caveolin adapter molecules that regulate caveolae function.
In this article, the authors observe the fluorescent fusion protein in caveolae and the caveosome, and in constitutively motile vesicles and tubules that evidently serve as transport intermediates between them. Furthermore, as perturbation of either microtubules or actin filaments cause rapid and profound changes in the dynamics and localization of caveolin-1, they conclude that these two structurally distinct components of the cytoskeleton act coordinately to regulate trafficking of the caveolar membrane system.
This article suggests that the main regulatory mechanism for TGF-β signal transduction is that the endocytosis is regulated by Cav-1-associated lipid rafts and early endosomal antigen-1 (EEA-1) non-lipid rafts. The interaction between Cav-1 and TβRI impairs the phosphorylation process, and in turn inhibits the heteromerization with Smad4, which is essential for the initiation of transcriptional changes
This report suggests that the autophagic degradation of Cav-1 contributes to PA-induced apoptosis and inflammation of astrocytes. Therefore, Cav-1 may be a potential therapeutic target for central nervous system injuries caused by PA accumulation.
CAV1 Preparation Options
We provide custom membrane protein preparation services for worldwide customers. Leveraging by our advanced Magic™ membrane protein production platform, we are able to present target membrane protein in multiple active formats. Our professional scientists are happy to help you find an ideal method and make your project a success. Aided by our versatile Magic™ anti-membrane protein antibody discovery platform, we also provide customized anti-CAV1 antibody development services.
Creative Biolabs provides high-quality membrane protein preparation service to facilitate the development of worldwide customer’s research. During the past years, we have successfully established a powerful Magic™ membrane protein platform which enables us to provide a series of membrane protein preparation services. For more detailed information, please feel free to contact us.
Reference
All listed services and products are For Research Use Only. Do Not use in any diagnostic or therapeutic applications.
