Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor (AHR) Nuclear Receptor Assay Service
Unlocking Insights into AHR Biology
The aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AHR) is a ligand-activated transcription factor involved in various biological processes, including xenobiotic metabolism and immune response modulation.
-
AHR Nuclear Receptor Assay: A Gateway to ADME Profiling
By utilizing our AHR nuclear receptor assay, you gain crucial insights into how your compounds interact with AHR, influencing the metabolic pathways:
-
Activation and Enzyme Induction: The assay helps determine whether your compounds activate AHR, leading to the induction of metabolizing enzymes such as CYP1A1 and CYP1B1. This activation can significantly impact the metabolic stability and clearance of drugs.
-
Modulation of Metabolic Enzymes: Understanding AHR interactions can predict alterations in the metabolism of co-administered drugs, providing foresight into potential drug-drug interactions.
Creative Biolabs offers a specialized AHR nuclear receptor assay service to assess functional responses of AHR to agonists or antagonists in a cell-based context. This assay utilizes robust methodologies to quantify IC50 values, providing critical insights into AHR activation or inhibition dynamics.
|
Receptor
|
Assay Type
|
Subtype
|
Functional Mode
|
Detection
|
|
Human AHR
|
Functional
|
Cell-based
|
Agonist
|
IC50
|
|
Functional
|
Cell-based
|
Antagonist
|
IC50
|
|
Rat AHR
|
Functional
|
Cell-based
|
Agonist
|
IC50
|
|
Functional
|
Cell-based
|
Antagonist
|
IC50
|
At Creative Biolabs, we are committed to supplying top-tier assay services, leveraging our tremendous expertise and advanced technology. Our AHR nuclear receptor assay provider is designed to deliver unique, dependable, and extremely good effects, assisting your research and development efforts with professionalism and excellence. Whether you are investigating the agonistic or antagonistic activities of compounds on the AHR receptor, our service is tailored to meet your specific desires.
Technical Procedure
-
Cell Culture Preparation: Cell lines engineered to express human or rat AHR are cultured under optimized conditions.
-
Treatment with Compounds: Cells are exposed to varying concentrations of test compounds, including agonists or antagonists of AHR.
-
Detection of AHR Activation: After compound exposure, cells are processed to measure AHR activation through luciferase reporter gene assays or other suitable readouts.
-
Data Analysis: IC50 values are determined to assess the efficiency of tested compounds in modulating AHR activity.
-
Validation and Quality Control: Perform replicate assays using independent cell batches to ensure robustness and reproducibility.
Published Data
This study illustrates the mechanism by which ligand binding induces conformational modifications in each of the AHR receptors and the AHR-Arnt complicated. This conformational change is essential in determining whether or not the ligands act as agonists or antagonists of the AHR pathway. Agonists usually stabilize the lively conformation of AHR, main to its nuclear translocation and next gene transcription. In comparison, antagonists prevent this activation using inhibiting ligand-prompted conformational changes. These insights are vital for understanding how one-of-a-kind compounds can selectively modulate AHR hobby, influencing diverse organic techniques and capacity healing packages.
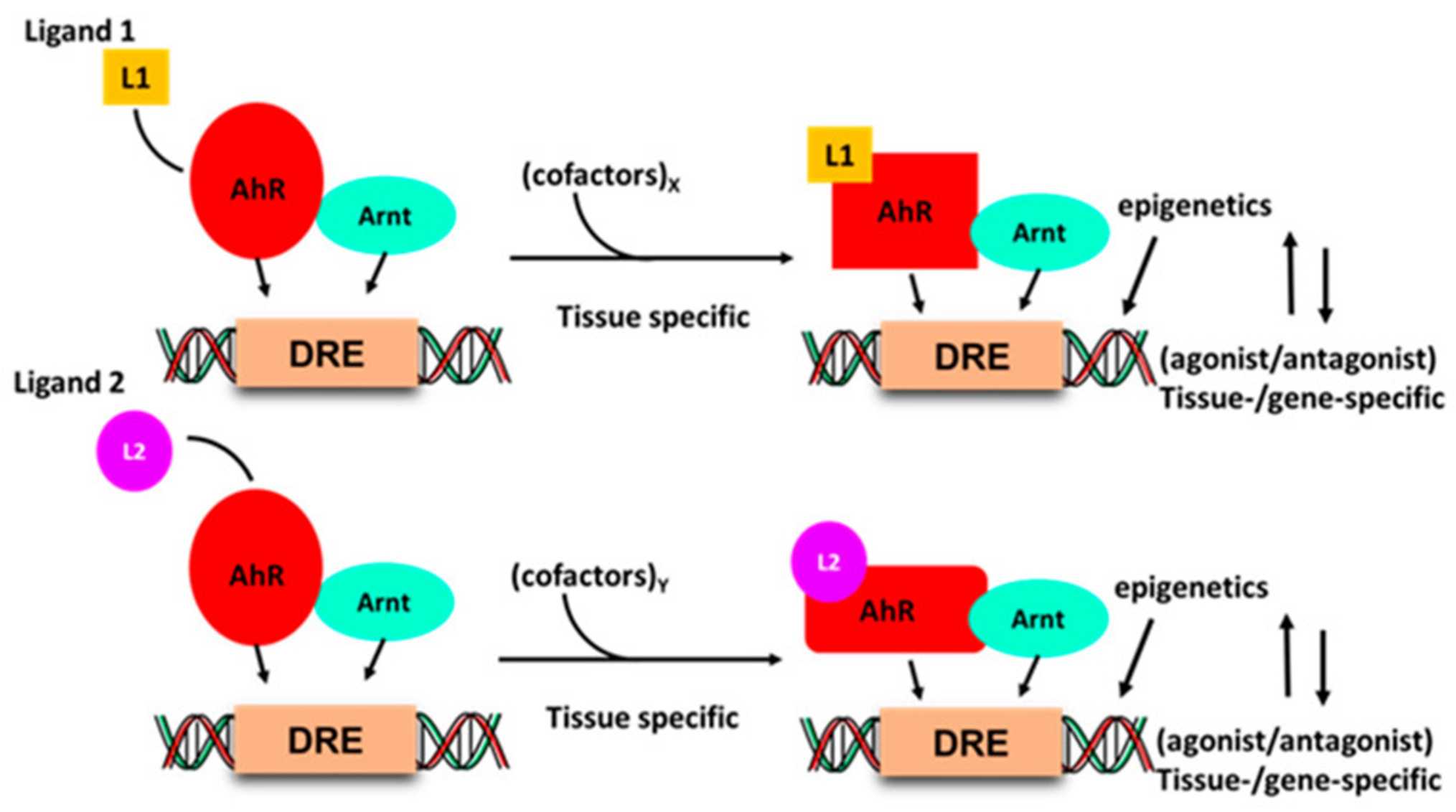 Fig.1 Ligand–AHR binding induces conformational changes in the AHR and AHR–Arnt complex.1
Fig.1 Ligand–AHR binding induces conformational changes in the AHR and AHR–Arnt complex.1
Integration with ADME Services
Our AHR nuclear receptor assay is an essential issue of our complete absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion (ADME) services. Our AHR nuclear receptor assay enhances and enhances our full range of ADME offerings, which include:
Applications
-
Drug Discovery: Screening for potential drug applicants focused on the AHR receptor.
-
Toxicology Studies: Evaluating the toxicological impact of environmental compounds on AHR receptor activity.
-
Pharmacological Research: Investigating the pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics of compounds affecting AHR signaling pathways.
Advantages
-
High Sensitivity: Our assay detects low levels of AHR activation with immoderate sensitivity.
-
Flexibility: We provide assays for both human and rat AHR, tailored to your precise research needs.
-
Accuracy: Our cell-based assays offer accurate measurements of AHR activation mode (agonist or antagonist).
-
IC50 Determination: We determine IC50 values to quantify the potency of agonists or antagonists.
Our AHR nuclear receptor assay is not just an isolated test but an important part of our holistic ADME profiling offerings. By leveraging this assay, you gain in-depth knowledge of your compound's metabolic pathways and interactions, blanketed seamlessly with our entire ADME testing. This approach ensures that you have all the important information to make informed choices, optimizing your drug development manner. Contact Creative Biolabs to examine the way our incorporated AHR nuclear receptor assay and ADME services assist your research.
Reference
-
Safe, Stephen, et al. "Aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AHR) ligands as selective AHR modulators (SAhRMs)." International journal of molecular sciences 21.18 (2020): 6654.
For Research Use Only | Not For Clinical Use


 Fig.1 Ligand–AHR binding induces conformational changes in the AHR and AHR–Arnt complex.1
Fig.1 Ligand–AHR binding induces conformational changes in the AHR and AHR–Arnt complex.1
 Download our brochure
Download our brochure