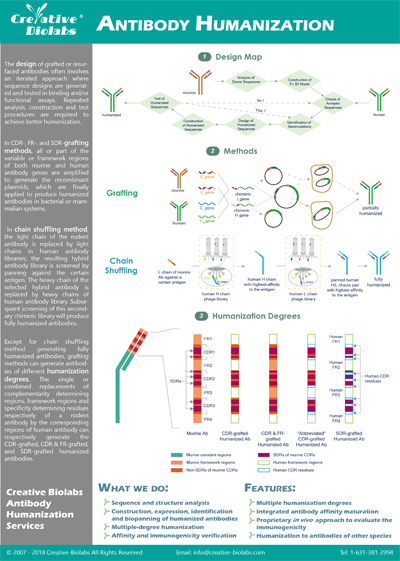
Single Domain Antibody (SdAb) Humanization Service
Advantage of HuSdL™ VHHs HuSdL™ Platform Case Study Published Data FAQ Resources
Creative Biolabs is a leading service provider in the field of VHH development and downstream engineering. Based on our extensive experience with VHH humanization, our scientists provide best-fit solutions to generate novel humanized VHHs for customers all over the world.
Due to their small size, excellent stability, high affinity, and improved solubility, VHHs that selectively bind to specific antigens have shown great potential for biotechnological and medical applications, especially in molecular imaging and therapeutic purposes. However, despite camelid VHHs having a high sequence similarity with human family III VH, their non-human origin raises concerns about immunogenicity in therapeutic applications. Therefore, VHH humanization remains a critical step for therapeutic VHH drug candidates to enter clinical stages.
To address this practical need, Creative Biolabs has developed the novel HuSdL™ humanization platform, which can nearly eliminate the immunogenicity of VHHs in humans while retaining their specificity and affinity. Compared to conventional VHH humanization strategies, our HuSdL™ platform better mitigates the various risks of immunogenicity in clinical applications.
Advantages of HuSdL™ VHHs
-
Smallest antibody fragment with high affinity and specificity
-
Minimally immunogenic in humans
-
Effective human therapeutics with reduced risk of side effects and toxicity
-
Recognizes hidden/cleft epitopes that conventional antibodies cannot
-
High stability with the ability to reversibly refold and exist under extreme conditions
-
Easy to clone and manufacture with high production yields
HuSdL™ Platform
As an innovative platform for VHH humanization, HuSdL™ retains the stability and antigen-binding characteristics of the parental VHH to the maximum extent possible while reducing its immunogenicity in humans. Moreover, this platform is compatible with other innovative approaches, such as in silico modeling and site-specific optimization.
With the HuSdL™ platform, several features and calculated biophysical properties of VHHs can be predicted, including conserved amino acid residues in antibody structures, antigenic sites, and structural properties. Our scientists can then design and develop stable, low-immunogenic VHH backbones that accommodate antigen-specific paratopes. A variety of strategies are available at Creative Biolabs to allow the epitope specificity of the original VHH is retained, especially when specific framework residues are directly or indirectly involved in the antigen interaction. The additional screening process helps minimize to reducing unacceptable affinity loss and non-functional expression risk. Additionally, we assist our clients in evolving desired candidates that can adapt to specified conditions or exhibit particularly requested characteristics.

Based on our advanced platforms and powerful technologies, Creative Biolabs is confident in offering the best VHH humanization service to meet the specific needs of human therapeutic agents with excellent prospects in clinical stages. If you are interested in VHH humanization, please feel free to contact us for more details.
Published Data
The Development and Application of an Anti-HER2 Humanized VHH named NM-02
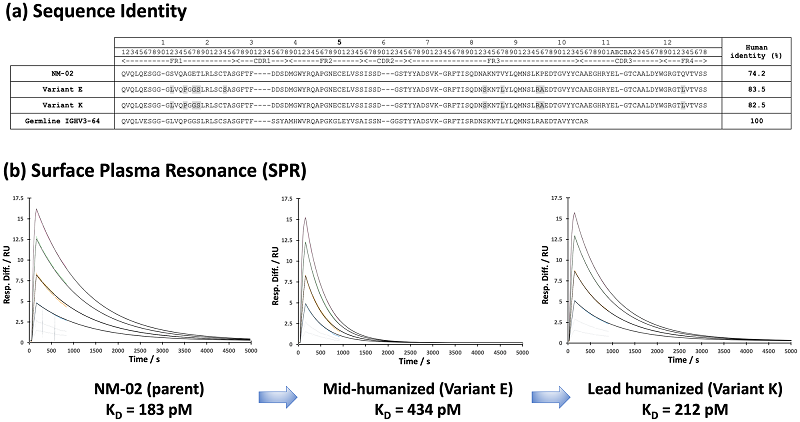 Fig. 1 Sequence Comparison and Binding Kinetics of Humanized NM-02 Candidates.1,2
Fig. 1 Sequence Comparison and Binding Kinetics of Humanized NM-02 Candidates.1,2
HER2, intimately linked with a multitude of cancers like breast cancer, is a promising target for medical diagnosis and clinical treatment of various malignancies. This article focused on developing a theranostic tool for HER2-positive breast cancer and identified a novel anti-HER2 single-domain antibody, designated NM-02. Using phage display technology, NM-02 was selected, and its binding site with HER2 was determined by X-ray crystallography, revealing high affinity and specificity for special binding sites. To minimize immunogenicity potential, the research team proceeded to humanize NM-02 and confirmed that the humanized NM-02 exhibited comparable binding characteristics to the original. Moreover, a series of developability analyses, including thermal stability, freeze-thaw stability, and serum stability tests, were conducted to verify the excellent drug-like properties of humanized NM-02. In a breast cancer mouse model, NM-02 demonstrated great in vivo efficacy in imaging, offering new possibilities for the diagnosis and treatment of HER2-positive breast cancer.
References
-
Sawmynaden, Kovilen, et al. "Co-crystallisation and humanization of an anti-HER2 single-domain antibody as a theranostic tool." Plos one 18.7 (2023): e0288259.
-
under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
FAQ
1. What is VHH humanization?
VHH humanization means modifying camelid-derived VHHs to be compatible with the human immune system. This approach changes their amino acid sequences to mimic human antibody structures, aiming to reduce the immunogenicity of VHHs utilized in therapeutic applications while maintaining their high specificity and affinity, thereby enhancing their safety and efficacy in human therapy.
2. What are the primary strategies commonly used in VHH humanization?
Several common methods are used to humanize VHHs, including sequence alignment, grafting, and computational modeling. Sequence alignment involves identifying camelid-specific residues in VHH sequences and replacing them with sequences similar to human antibodies. Grafting can transfer the complementarity-determining regions (CDRs) of VHHs to human antibody frameworks. Computational modeling helps predict the structural and functional consequences of these changes, ensuring that the humanized VHHs retain their binding affinity and specificity.
3. How can the immunogenicity of humanized VHHs be assessed?
The immunogenicity of humanized VHHs can be assessed using in silico prediction methods, in vitro experiments, and in vivo research. In silico technologies predict potential T-cell epitopes by evaluating the sequence and structure. In vitro tests, such as T-cell proliferation and cytokine release assays, help evaluate the immunological response to humanized VHHs. In vivo studies in animal models can also assess immunogenicity and safety profiles, providing comprehensive insights into how the humanized VHHs may function in humans.
4. What potential therapeutic areas can benefit from VHH humanization?
VHH humanization can be beneficial for neurodegenerative diseases, infectious diseases, autoimmune disorders, and cancer. In oncology, humanized VHHs are designed to target tumor-specific antigens, improving the specificity and efficacy of cancer immunotherapies. Autoimmune diseases can be treated with humanized VHHs that regulate immune responses. Humanized VHHs can also be used to neutralize infectious pathogens or their toxins, as well as to target pathogenic proteins involved in neurodegenerative diseases, providing novel therapeutic options.
5. What future advancements are expected in the field of VHH humanization?
Future improvements in VHH humanization are expected to concentrate on enhancing computational and AI-based methodologies for better prediction and design of humanized antibodies. Enhanced high-throughput screening techniques will enable faster and more efficient selection of the best-humanized candidates. Additionally, advances in synthetic biology and gene editing technologies could facilitate the development of novel VHHs with improved characteristics. Collaborative, multidisciplinary approaches are likely to accelerate the development of next-generation humanized VHHs, increasing their therapeutic potential and clinical applications.
Resources
We are offering highly customized CRO services to assist your Single Domain Antibody (sdAb) related projects. Please Contact Us for more details.


 Fig. 1 Sequence Comparison and Binding Kinetics of Humanized NM-02 Candidates.1,2
Fig. 1 Sequence Comparison and Binding Kinetics of Humanized NM-02 Candidates.1,2