Introduction of CD3
CD3 is a complex of three type 1 transmembrane proteins, namely CD3γ, CD3δ, and CD3ε, that are expressed on T cells and possibly some neurons. CD3ζ is another component of the CD3 complex, but it is described in a separate chapter due to its significant differences from the other CD3 subunits. The CD3γ and CD3δ chains are glycoproteins that form heterodimers with the non-glycosylated CD3ε chain. These heterodimers associate with the T cell receptor (TCR) αβ and a CD3ζζ dimer to form the TCR complex in αβ T cells. The TCR complex is responsible for the activation of T cells upon antigen recognition and initiation of the immune response. In addition, the CD3 and CD3ζ subunits facilitate the assembly and transport of the TCR to the cell surface. Because CD3 is essential for T cell activation, drugs that target it are being investigated as immunosuppressant therapies for type 1 diabetes and other autoimmune diseases. Moreover, BsAbs that target CD3 and another tumor-associated antigen can redirect T cells to kill tumor cells, providing a novel strategy for cancer immunotherapy.
Introduction of GPC3
GPC3 is a member of the glypican family of heparan sulfate proteoglycans, which are attached to the cell membrane by a glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI) anchor. The full name of GPC3 is glypican 3, and it is also known as MXR7 or OCI-5. The GPC3 gene encodes a protein that consists of two domains: an N-terminal core protein domain and a C-terminal GPI anchor domain. GPC3 is involved in the regulation of cell growth, differentiation, migration, and signaling, by interacting with various growth factors and receptors. GPC3 can bind to Wnt proteins and inhibit the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway, which promotes cell proliferation and invasion. GPC3 can also bind to Hedgehog proteins and enhance the Hedgehog signaling pathway, which promotes cell survival and angiogenesis. GPC3 is a potential target for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and other solid tumors because it is almost not expressed in normal liver cells, but highly expressed in HCC cells, and correlates with HCC occurrence, progression, and prognosis. GPC3 can be detected in serum and tissue samples of HCC patients, and thus it can be used as a diagnostic and prognostic biomarker for HCC.
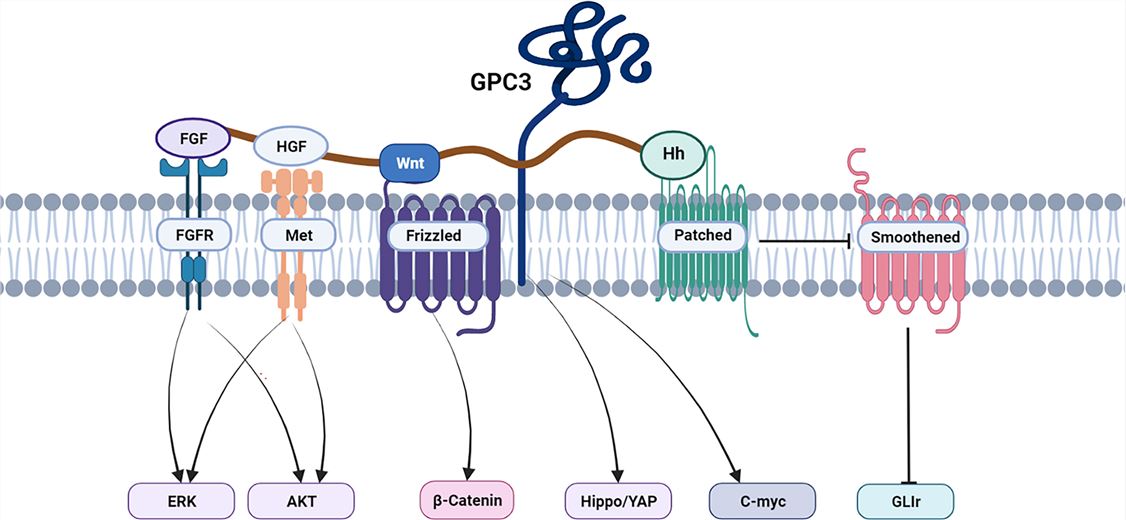
Fig.1 GPC3 Associated Signaling Pathways in HCC (Zheng X, 2022)
Signaling Pathways Involved in Bispecific Antibodies Targeting CD3 and GPC3
BsAbs targeting CD3 and GPC3 can exert antitumor effects through two mechanisms: one is by activating T cells to kill GPC3-positive tumor cells; the other is by blocking the interaction of GPC3 with its ligands or receptors, affecting the growth and survival of tumor cells. BsAbs targeting CD3 and GPC3 can activate several signaling pathways, including the TCR signaling pathway, the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway, and the Hedgehog signaling pathway.
The TCR signaling pathway is the main signaling pathway for T cell activation and effector functions, triggered by the recognition of antigen by the TCR, leading to the phosphorylation of CD3 subunits and the activation of downstream signaling molecules3. BsAbs targeting CD3 and GPC3 can mimic the antigen recognition by the TCR, inducing T cells to produce cytokines, proliferate, and kill GPC3-positive tumor cells.
The Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway is an important signaling pathway that regulates cell fate, activated by the interaction of Wnt proteins with their receptors Frizzled and LRP, leading to the stabilization of β-catenin and the activation of transcription factors4. GPC3 can bind to Wnt proteins and inhibit the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway, promoting cell proliferation and invasion. BsAbs targeting CD3 and GPC3 can interfere with the binding of GPC3 to Wnt proteins, restoring the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway, and inhibiting tumor cell growth and metastasis.
The Hedgehog signaling pathway is an important signaling pathway that regulates cell differentiation and development, activated by the interaction of Hedgehog proteins with their receptors Patched and Smoothened, leading to the release of Gli proteins and the activation of transcription factors. GPC3 can bind to Hedgehog proteins and enhance the Hedgehog signaling pathway, promoting cell survival and angiogenesis. BsAbs targeting CD3 and GPC3 can interfere with the binding of GPC3 to Hedgehog proteins, inhibiting the Hedgehog signaling pathway, and inducing tumor cell apoptosis and vascular regression.
Clinic Status of Bispecific Antibodies Targeting CD3 and GPC3
BsAbs targeting CD3 and GPC3 are a novel type of tumor immunotherapy strategy, and currently, several candidate drugs have entered clinical trial stages, mainly for HCC and other solid tumors with high expression of GPC3. To date, no bispecific antibodies targeting CD3 and GPC3 have been approved for marketing. However, there are several BsAbs targeting CD3 and GPC3 in clinical trial stages. For example, a ERY974, fully humanized IgG-like antibody developed by Chugai Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. in Japan, has received conditional approval in Japan for the treatment of unresectable or recurrent HCC. This means that ERY974 can be used for clinical treatment under limited conditions, but further data is still needed to prove its effectiveness and safety. Currently, ERY974 is also undergoing clinical trials in other countries and regions to evaluate its application in other types of solid tumors.
Table 1. Summary of ERY974 (a bispecific antibody targeting CD3 and GPC3)
|
Item
|
Description
|
|
Developer
|
Chugai Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. in Japan
|
|
Structure
|
A fully humanized IgG-like antibody with two scFv fragments, targeting CD3 and GPC3 respectively
|
|
Mechanism of action
|
Redirects T cells to kill GPC3-positive tumor cells and blocks the interaction of GPC3 with its ligands or receptors
|
|
Indication
|
Unresectable or recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC)
|
|
Approval status
|
Conditionally approved in Japan in December 2021 for the treatment of HCC in adult patients who are ineffective or intolerant to standard therapy
|
|
Clinical trials
|
Ongoing in other countries and regions for HCC and other solid tumors, such as gastric cancer, esophageal cancer, and ovarian cancer
|
|
Adverse events
|
The most common treatment-related adverse events were cytokine release syndrome (CRS) and pyrexia
|
References
1. Zheng X, et al. Glypican-3: A Novel and Promising Target for the Treatment of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Front Oncol. 2022 Feb 16;12:824208.
2. Crawford A, Chiu D. Targeting Solid Tumors Using CD3 Bispecific Antibodies. Mol Cancer Ther. 2021 Aug;20(8):1350-1358.
3. Zhang Y, et al. Mechanisms and Clinical Trials of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Immunotherapy Based on Glypican-3. Front Genet. 2021 Jul 8;12:691391.
4. Ishiguro T, et al. An anti-glypican 3/CD3 bispecific T cell-redirecting antibody for treatment of solid tumors. Sci Transl Med. 2017 Oct 4;9(410):eaal4291.
5. Nakajima K, et al. ERY974, a novel bispecific antibody targeting GPC3 and CD3 for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma: A case report of a patient with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma treated with ERY974 in a phase I clinical trial. Hepatol Res. 2020 Nov;50(11):1374-1380.
6. Sano Y, et al. Combination of T cell-redirecting bispecific antibody ERY974 and chemotherapy reciprocally enhances efficacy against non-inflamed tumours. Nat Commun. 2022 Sep 7;13(1):5265.
7. Waaijer SJ, et al. Preclinical PET imaging of bispecific antibody ERY974 targeting CD3 and glypican 3 reveals that tumor uptake correlates to T cell infiltrate. J Immunother Cancer. 2020 Mar;8(1):e000548.
8. Iwata Y, et al. Priming treatment with T-cell redirecting bispecific antibody ERY974 reduced cytokine induction without losing cytotoxic activity in vitro by changing the chromatin state in T cells. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2022 Apr 15;441:115986.
9. Komatsu SI, et al. Determination of starting dose of the T cell-redirecting bispecific antibody ERY974 targeting glypican-3 in first-in-human clinical trial. Sci Rep. 2022 Jul 19;12(1):12312.
10. Shiraiwa H, et al. Engineering a bispecific antibody with a common light chain: Identification and optimization of an anti-CD3 epsilon and anti-GPC3 bispecific antibody, ERY974. Methods. 2019 Feb 1;154:10-20.
Our products and services are for research use only, and not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
Welcome! For price inquiries, we will get back to you as soon as possible.
To order, please email
INQUIRY










