All products and services are For Research Use Only and CANNOT be used in the treatment or diagnosis of disease.
Creative Biolabs is committed to advancing the field of MM treatment through the development of state-of-the-art anti-BCMA CAR T-cell therapies. Our comprehensive suite of anti-BCMA CAR related products and sophisticated in vitro and in vivo assays underscore our dedication to providing effective and lasting therapeutic solutions.
B cell maturation antigen (BCMA), also known as CD269 or TNFRSF17, is a member of the tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily. It plays a crucial role in B-cell maturation and differentiation into plasma cells. Structurally, BCMA comprises three major domains: an extracellular domain, a transmembrane domain, and a cytoplasmic domain. Notably, BCMA is almost exclusively found on plasma cells and is overexpressed during malignant transformations, making it a specific and compelling target for multiple myeloma (MM) treatments.
Associated Disease
Creative Biolabs offers a range of BCMA-targeting CAR constructs to assist customers' projects.
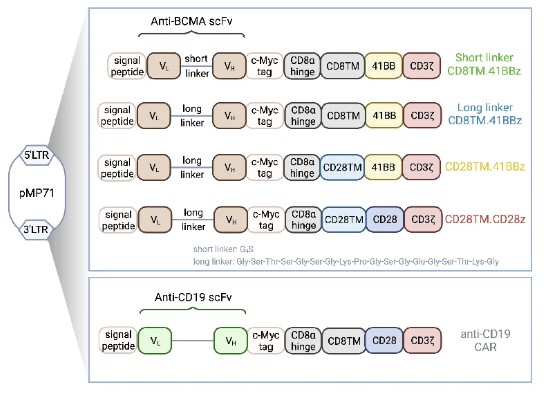 Fig.1 Schematic of different Anti-BCMA constructs.1
Fig.1 Schematic of different Anti-BCMA constructs.1
CAR expression test is an essential test for CART development, which can verify specific CAR expression levels to facilitate subsequent development processes. Creative Biolabs provides robust CAR expression tests by various methods, such as WB, FACS, and qPCR.
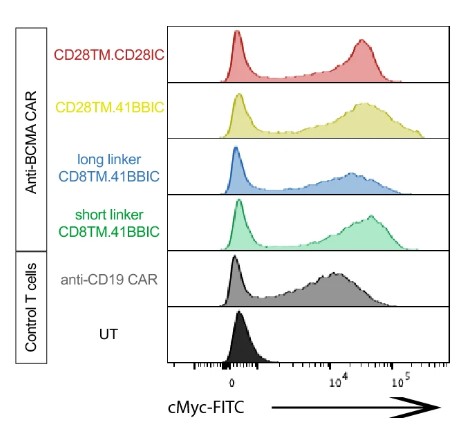 Fig.2 The anti-BCMA CAR expression was detected by flow cytometry.1
Fig.2 The anti-BCMA CAR expression was detected by flow cytometry.1
In vitro characterization of CAR-T cells is critical to evaluate their potential efficacy before clinical application. Creative Biolabs has launched several phenotype tests to assess the performance of CART cells, such as T cells subpopulation analysis, exhaustion marker test, activation marker test, etc.
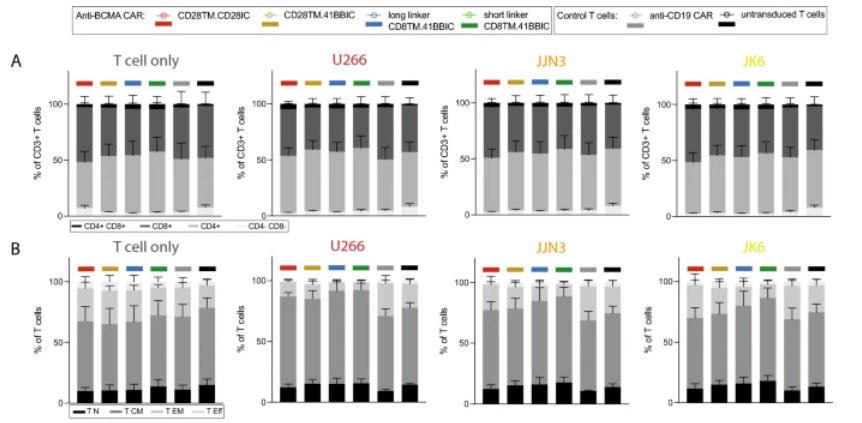 Fig.3 Phenotypic analysis of different anti-BCMA CAR T cells after activation. (Panel A: CD8+ and CD4+ T cell subtypes, panel B: T cell subpopulations for T cell differentiation status).1
Fig.3 Phenotypic analysis of different anti-BCMA CAR T cells after activation. (Panel A: CD8+ and CD4+ T cell subtypes, panel B: T cell subpopulations for T cell differentiation status).1
Creative Biolabs specializes in comprehensive cytokine production assays to measure the release of various cytokines, such as IFN-γ, IL-2, and TNF-α, following CAR-T cell activation. Enhanced cytokine production is indicative of robust CAR-T cell activation and anti-tumor efficacy.
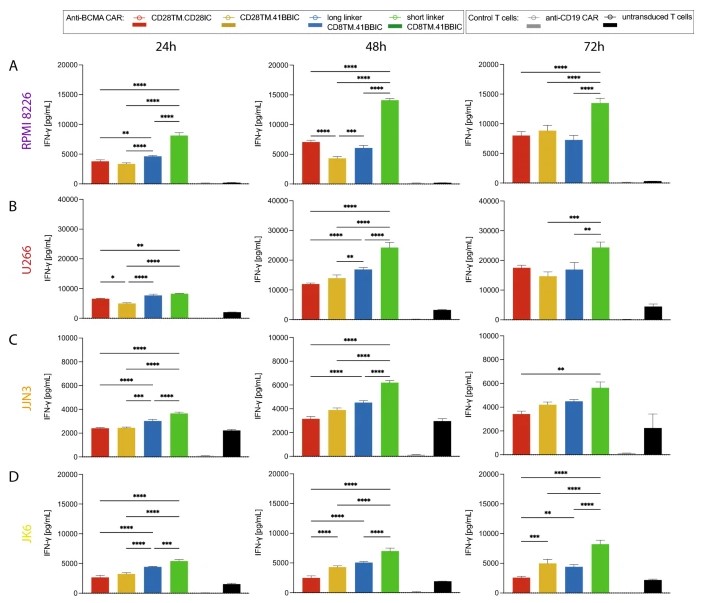 Fig.4 IFN-γ secretion detection of different anti-BCMA CART cells against target cells.1
Fig.4 IFN-γ secretion detection of different anti-BCMA CART cells against target cells.1
Cytotoxicity assays are performed using MM cell lines expressing BCMA as target cells. These assays assess the ability of CAR-T cells to recognize and lyse BCMA-expressing tumor cells, providing pivotal data on the therapeutic potential of CAR-T constructs.
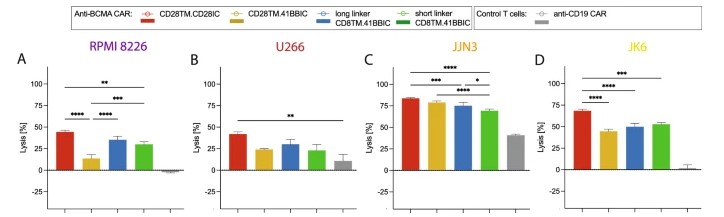 Fig.5 Cytotoxic assay of different anti-BCMA CART cells against target cells.1
Fig.5 Cytotoxic assay of different anti-BCMA CART cells against target cells.1
The efficacy of anti-BCMA CAR-T cells is evaluated in vivo using mouse models engrafted with human MM cell lines. These studies are pivotal in demonstrating tumor reduction and assessing the long-term persistence of CAR-T cells post-administration. Creative Biolabs provides several in vivo models that are designed to mimic clinical scenarios, providing relevant insights into the potential clinical performance of CAR-T therapies.
Safety and toxicity are paramount considerations in CAR-T cell therapy development. Creative Biolabs conducts comprehensive toxicity assessments to monitor potential adverse effects, such as off-target activity and cytokine release syndrome (CRS). These evaluations ensure that anti-BCMA CAR-T cells are not only effective but also safe for clinical application, adhering to regulatory standards.
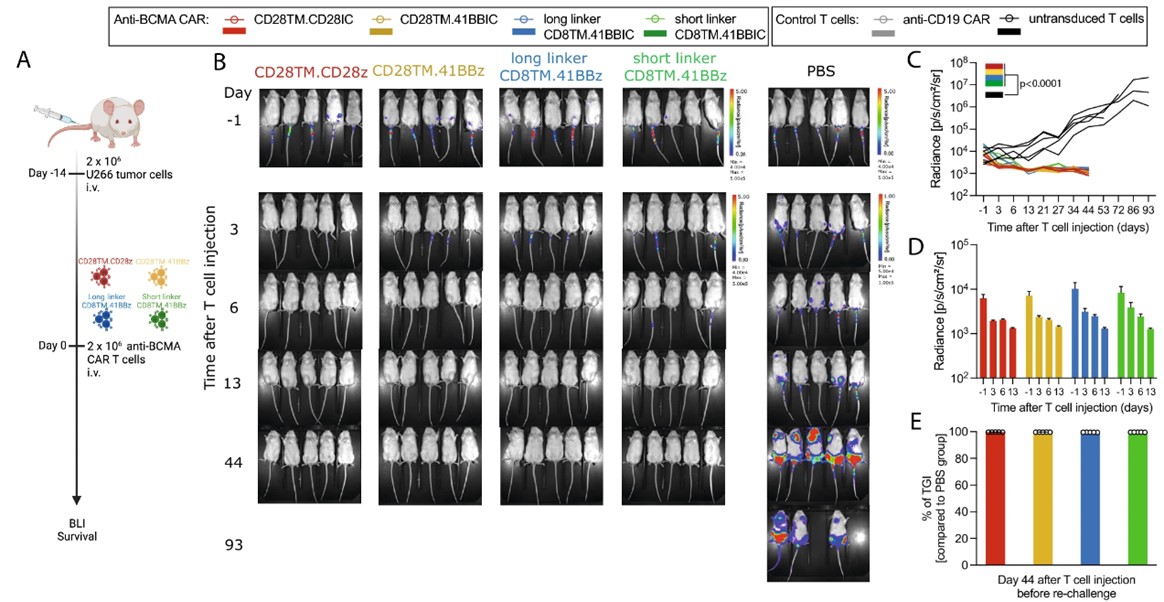 Fig.6 In vivo antitumor activity of anti-BCMA CAR T cells in U266 xenograft model.1
Fig.6 In vivo antitumor activity of anti-BCMA CAR T cells in U266 xenograft model.1
Reference
 Loading...
Loading...
| CAT | Product Name | Target Species | Antibody Clone | Antibody Host | Receptor Construction | Vector Type | Targeting Cell Type | CAR Vector Type | Inquiry & Datasheet |
| XS-0922-ZP1303 | Anti-BCMA (PMC306) h(4-1BB-CD3ζ) CAR, pCDCAR1 | Human | PMC306 | Humanized | scFv-4-1BB-CD3ζ | Lentiviral vector | T cell | ||
| XS-0922-ZP1304 | Anti-BCMA (4C8A4) h(4-1BB-CD3ζ) CAR, pCDCAR1 | Human | 4C8A4 | Mouse | scFv-4-1BB-CD3ζ | Lentiviral vector | T cell | ||
| XS-1122-YF2698 | Anti-BCMA TCR-ABR (scFv-TCRβ, XW-858) CAR Plasmid, pCDCAR1 | Human | XW-858 | Humanized | scFv-TCRβ | Lentiviral vector | T Cell | ||
| XS-1122-YF2699 | Anti-BCMA TCR-ABR (scFv-TCRβ, XW-859) CAR Plasmid, pCDCAR1 | Human | XW-859 | Humanized | scFv-TCRβ | Lentiviral vector | T Cell | ||
| XS-1122-YF2700 | Anti-BCMA TCR-ABR (scFv-TCRβ, XW-860) CAR Plasmid, pCDCAR1 | Human | XW-860 | Mouse | scFv-TCRβ | Lentiviral vector | T Cell | ||
| XS-1122-YF2701 | Anti-BCMA TCR-ABR (scFv-TCRβ, XW-861) CAR Plasmid, pCDCAR1 | Human | XW-861 | Mouse | scFv-TCRβ | Lentiviral vector | T Cell | ||
| XS-1122-YF2702 | Anti-BCMA TCR-ABR (scFv-TCRβ, XW-862) CAR Plasmid, pCDCAR1 | Human | XW-862 | Mouse | scFv-TCRβ | Lentiviral vector | T Cell | ||
| XS-1122-YF2703 | Anti-BCMA TCR-ABR (scFv-TCRβ, XW-863) CAR Plasmid, pCDCAR1 | Human | XW-863 | Mouse | scFv-TCRβ | Lentiviral vector | T Cell | ||
| XS-1122-YF2704 | Anti-BCMA TCR-ABR (scFv-TCRβ, 11D5-3) CAR Plasmid, pCDCAR1 | Human | 11D5-3 | Mouse | scFv-TCRβ | Lentiviral vector | T Cell | ||
| XS-1122-YF2705 | Anti-BCMA TCR-ABR (scFv-TCRβ, XW-865) CAR Plasmid, pCDCAR1 | Human | XW-865 | Mouse | scFv-TCRβ | Lentiviral vector | T Cell | ||
| XS-1122-YF2706 | Anti-BCMA TCR-ABR (scFv-TCRβ, XW-866) CAR Plasmid, pCDCAR1 | Human | XW-866 | Mouse | scFv-TCRβ | Lentiviral vector | T Cell | ||
| XS-1122-YF2707 | Anti-BCMA TCR-ABR (scFv-TCRβ, XW-867) CAR Plasmid, pCDCAR1 | Human | XW-867 | Mouse | scFv-TCRβ | Lentiviral vector | T Cell | ||
| XS-1122-YF2708 | Anti-BCMA TCR-ABR (scFv-TCRβ, XW-868) CAR Plasmid, pCDCAR1 | Human | XW-868 | Mouse | scFv-TCRβ | Lentiviral vector | T Cell | ||
| XS-1122-YF2709 | Anti-BCMA TCR-ABR (scFv-TCRβ, XW-869) CAR Plasmid, pCDCAR1 | Human | XW-869 | Mouse | scFv-TCRβ | Lentiviral vector | T Cell | ||
| XS-1122-YF2710 | Anti-BCMA TCR-ABR (scFv-TCRβ, XW-870) CAR Plasmid, pCDCAR1 | Human | XW-870 | Human | scFv-TCRβ | Lentiviral vector | T Cell | ||
| XS-1122-YF2711 | Anti-BCMA TCR-ABR (scFv-TCRβ, XW-871) CAR Plasmid, pCDCAR1 | Human | XW-871 | Human | scFv-TCRβ | Lentiviral vector | T Cell | ||
| XS-1122-YF2712 | Anti-BCMA TCR-ABR (scFv-TCRβ, XW-872) CAR Plasmid, pCDCAR1 | Human | XW-872 | Mouse | scFv-TCRβ | Lentiviral vector | T Cell | ||
| XS-1122-YF2713 | Anti-BCMA TCR-ABR (scFv-TCRβ, XW-873) CAR Plasmid, pCDCAR1 | Human | XW-873 | Humanized | scFv-TCRβ | Lentiviral vector | T Cell | ||
| XS-1122-YF2714 | Anti-BCMA TCR-ABR (scFv-TCRβ, XW-874) CAR Plasmid, pCDCAR1 | Human | XW-874 | Mouse | scFv-TCRβ | Lentiviral vector | T Cell | ||
| XS-1122-YF2715 | Anti-BCMA TCR-ABR (scFv-TCRβ, XW-875) CAR Plasmid, pCDCAR1 | Human | XW-875 | Mouse | scFv-TCRβ | Lentiviral vector | T Cell | ||
| XS-0823-LX2 | Anti-hBCMA (AB) ICD(CD28-OX40-CD3ζ) CAR-MA, pAd5f35 Vector | Human | AB | Adenoviral vectors |
 NEWSLETTER
NEWSLETTER
The latest newsletter to introduce the latest breaking information, our site updates, field and other scientific news, important events, and insights from industry leaders
LEARN MORE NEWSLETTER NEW SOLUTION
NEW SOLUTION
CellRapeutics™ In Vivo Cell Engineering: One-stop in vivo T/B/NK cell and macrophage engineering services covering vectors construction to function verification.
LEARN MORE SOLUTION NOVEL TECHNOLOGY
NOVEL TECHNOLOGY
Silence™ CAR-T Cell: A novel platform to enhance CAR-T cell immunotherapy by combining RNAi technology to suppress genes that may impede CAR functionality.
LEARN MORE NOVEL TECHNOLOGY NEW SOLUTION
NEW SOLUTION
Canine CAR-T Therapy Development: From early target discovery, CAR design and construction, cell culture, and transfection, to in vitro and in vivo function validation.
LEARN MORE SOLUTION