Using autologous T-cell therapies for cancer treatment presents several challenges. These challenges include factors related to prior chemotherapies or allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation (HCT), which can affect the quantity and quality of the initial material. Additionally, there is uncontrollable variability between patients and prolonged waiting times due to global manufacturing processes. To solve the challenges in scalability and timely availability, Creative Biolabs offers allogeneic TCR-T therapy development services to accelerate your program.
TCR-T cell therapy is a type of cellular immunotherapy for cancer that entails genetically modifying T cells to produce T cell receptors (TCRs) capable of recognizing specific tumor-associated antigens. This therapy enables T cells to identify and destroy cancer cells expressing these antigens, providing a promising treatment option for solid tumors. TCR-T cell therapy offers advantages such as recognition of multiple tumor antigens, independence from surface antigen limitations, enhanced specificity, potential for personalized treatment, and improved anti-tumor activity. At the same time, TCR-T cell therapy is facing some challenges including:
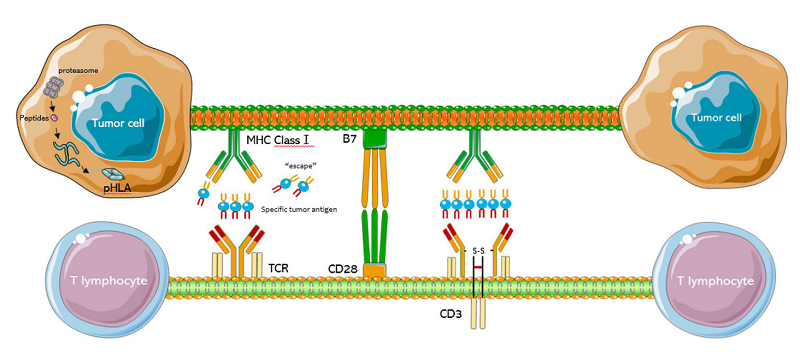 Fig 1. The structure of TCR-T cell.1
Fig 1. The structure of TCR-T cell.1
To enhance the effectiveness of TCR-T cell therapy, we may consider the following aspects:
Creative Biolabs has established dedicated platforms aimed at enhancing your TCR-T cell therapy protocols. We are pleased to offer assistance in allogeneic TCR-T cell therapy. For more details, please explore:
Please contact us and we would be pleased to help you improve your program through allogeneic TCR-T cell therapy.
Reference
For any technical issues or product/service related questions, please leave your information below. Our team will contact you soon.
All products and services are For Research Use Only and CANNOT be used in the treatment or diagnosis of disease.
 NEWSLETTER
NEWSLETTER
The latest newsletter to introduce the latest breaking information, our site updates, field and other scientific news, important events, and insights from industry leaders
LEARN MORE NEWSLETTER NEW SOLUTION
NEW SOLUTION
CellRapeutics™ In Vivo Cell Engineering: One-stop in vivo T/B/NK cell and macrophage engineering services covering vectors construction to function verification.
LEARN MORE SOLUTION NOVEL TECHNOLOGY
NOVEL TECHNOLOGY
Silence™ CAR-T Cell: A novel platform to enhance CAR-T cell immunotherapy by combining RNAi technology to suppress genes that may impede CAR functionality.
LEARN MORE NOVEL TECHNOLOGY NEW SOLUTION
NEW SOLUTION
Canine CAR-T Therapy Development: From early target discovery, CAR design and construction, cell culture, and transfection, to in vitro and in vivo function validation.
LEARN MORE SOLUTION