Background Services Overview Protocols Related Products Published Data Q&A Resources
Creative Biolabs is one of the well-recognized expert professionals in the field of complement
therapeutics and related services. Our technical experts are looking forward to offering high-quality and custom
complement inhibitor validation services for our clients.
Background
Complement Inhibitor Overview
The complement system is a cascade reaction playing a pivotal function in recognition and eliminating of
invading pathogens, which serves as a regulator of multiple human diseases. About 40 components (proteins and
enzymes) form the complement cascade, all of which are indispensable and tightly coordinate with each other to
play a normal complement activity. Some of these components positively regulate the complement system so that
the complement cascade can be activated to function properly, whereas, others act as inhibitors to regulate the
complement system in a negative way to prevent its spontaneous or over-activation.
Until now, a diversity of complement inhibitors has been described, including natural proteins in the complement system and those developed by biotechnology. Complement factor I (CFI), complement factor H (CFH), C4 binding protein (C4BP), decay-accelerating factor (DAF), CD35 (CR1), membrane cofactor protein (MCP), etc., are natural inhibitors regulating complement pathways in different ways. Several complement inhibitors have been approved by Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the treatment of related diseases, including anti-C5 monoclonal antibody, and C1 esterase inhibitor.

Fig. 1 Complement system and its targeted modulation.1,3
Services Overview
Complement Inhibitor Validation Services
As the revealing of the relationship between the complement system and diseases, increasing complement inhibitors
are currently developed and evaluated in clinical trials for the related disease therapy. Therefore, complement
inhibition test or complement inhibitor validation is necessary to measure the effect of complement inhibitors.
As an experienced expert in complement therapeutics, Creative Biolabs provides comprehensive custom validation
services for the efficient identification of potential complement inhibitors. Based on the principle of combining
the individual component activity test with the whole complement cascade activity assessment, our scientists verify
or screen complement inhibitors mainly through the following approaches:
-
Hemolytic inhibition assay: for validation of both individual
inhibition and total complement activity inhibition assessment;
-
Cell imaging-based high-throughput screening: for fast and efficient screening potential complement inhibitors
on a large scale;
-
Immunochemical assays for individual components determination: mainly for individual component determination,
such as immunoprecipitation (IP), enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), radial immunodiffusion (RID). This
method also can be used to measure complement autoantibodies.
-
Receptor ligand binding assay: for complement receptor binding
inhibition mainly by competition ELISA, other sensitive binding tests are also available if the ligand-receptor
samples are purified.
-
Quantitative chromogenic assays: for C1 inhibitor activity evaluation.
With over a decade of experience and the state-of-the-art drug development platforms, Creative
Biolabs provides highly custom solutions for complement inhibitors validation to effectively support
your anti-complement therapeutics development.
If you are interested, please directly contact us for more information.
Protocols
Hemolytic Assay Protocols for Individual Component
Assay Protocols for Complement Regulators
Related Products
Published Data
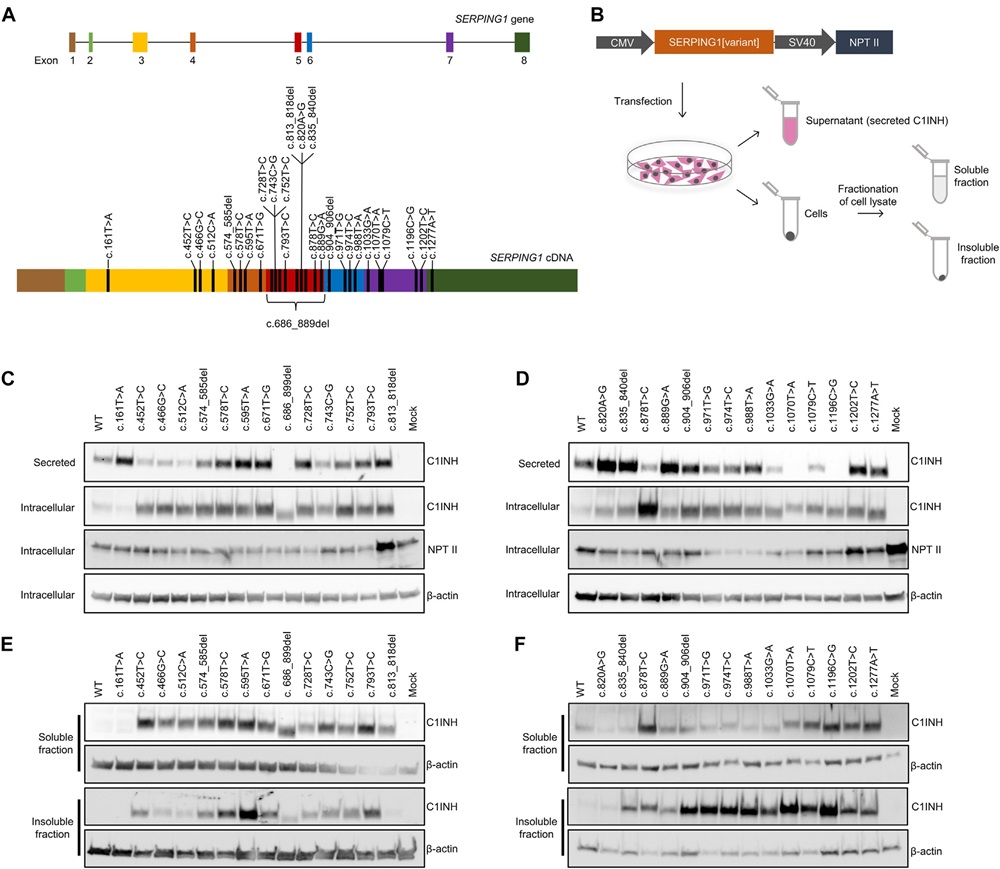 Fig.2 Western-blot assessment of C1INH protein expression and secretion from SERPING1 gene variants linked to HAE.2,3
Fig.2 Western-blot assessment of C1INH protein expression and secretion from SERPING1 gene variants linked to HAE.2,3
Hereditary angioedema (HAE) is marked by recurrent and potentially severe edema episodes and exhibits genetic and clinical variability. It is primarily linked to
SERPING1 gene mutations that result in insufficient plasma levels of C1 inhibitor (C1INH). To investigate distinct C1INH proteins from these
SERPING1 mutations without normal C1INH interference, expression plasmids for each variant were transfected into HeLa cells. Subsequent western blot analysis revealed both intracellular and secreted C1INH. Findings confirmed that post-transfection, HAE-related
SERPING1 variants produce C1INH, which is secreted, albeit less efficiently than the normal protein, aligning with previous studies.
Resources
References
-
Yarmoska, Steven K., et al. "Modulation of the complement system by neoplastic disease of the central nervous system." Frontiers in Immunology 12 (2021): 689435.
-
Ryø, Laura Barrett, et al. "Restriction of C1-inhibitor activity in hereditary angioedema by dominant-negative effects of disease-associated SERPING1 gene variants." Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology 152.5 (2023): 1218-1236.
-
Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
Questions & Answer
A: Complement inhibitor validation typically involves several steps, including: (a) In vitro Testing: Assessing the inhibitor's effect on complement activation in controlled cell-based assays or plasma samples. (b) In vivo Studies: Evaluating the inhibitor's impact in animal models, measuring complement inhibition and potential therapeutic effects. (c) Pharmacokinetics (PK) and Pharmacodynamics (PD): Determining how the inhibitor is absorbed, distributed, metabolized, and excreted, as well as its impact on complement activity. (d)Toxicity and Safety Assessment: Investigating potential adverse effects, such as immunogenicity or interference with other physiological processes. (e) Clinical Trials: Conducting controlled human trials to validate safety, efficacy, and dosing regimens.
A: Yes, complement inhibitor validation can be tailored to specific diseases. The choice of assays, models, and endpoints may vary based on the disease's underlying mechanisms and manifestations. Personalized validation approaches may enhance the inhibitor's effectiveness and safety for a particular condition.
A: Technologies, such as ELISA, hemolytic assay, and specific functional experiments. These assay methods allow researchers to study complement dynamics at a finer resolution, enabling more accurate assessments of the inhibitor's effects.
A: We typically require purified complement inhibitors for validation including small molecules, peptides, antibodies, and other therapeutic agents. However, the sample type may vary depending on your specific research objectives and the design of the experiment. In some cases, we might need plasma or serum samples from animal or human sources.
A: The duration of the validation process can vary depending on factors such as the complexity of the inhibitor, the scope of the experiments, and the availability of resources, but a typical timeline for our complement inhibitor validation service is 4-6 weeks. Our team works efficiently to minimize turnaround time while ensuring thorough validation.
A: The final report will outline the objectives of the study, the methodologies we used, and the results of the validation process. This would include a robust data analysis, interpretation of results in context of the study objectives, along with suggestions on any subsequent steps or studies that might be required. Additionally, our team provides ongoing support and consultation to address any questions or concerns related to the validation process or results.
For Research Use Only.
Related Sections:


 Fig.2 Western-blot assessment of C1INH protein expression and secretion from SERPING1 gene variants linked to HAE.2,3
Fig.2 Western-blot assessment of C1INH protein expression and secretion from SERPING1 gene variants linked to HAE.2,3

