Background Services Overview Protocols Related Products Published Data Q&A Resources
To support the complement system clinical and pre-clinical research, Creative Biolabs provides
rapid hemolytic assay and hemolytic inhibition assays for complement function or activity assessment.
Background
Mechanism of Hemolytic Assay
Generally, the complement system mainly functions by cracking the target cells through the formation of the
cytolytic membrane attack complex (MAC). Based on this property, the hemolysis assay has been developed as the major
approach for total complement system activity assessment.
Usually, serum isolated from immunized rabbits and SRBC is used in vitro for hemolytic assay.
Specific antibodies, namely hemolysin, will be produced after the sheep red blood cells (SRBC) are injected
into rabbits as antigens. When SRBC is added to the tube with isolated serum, the hemolysin immediately
reacts with the antigen on the surface of SRBC forming antigen-antibody complex. If a complement sample with
normal activity is added to the tube, the complement will attack the antigen-antibody complex on the surface of
SRBC, leading to the SRBC lysis and hemolysis. Common hemolysis assays are CH50 and
AH50 (i.e., diluted serum complement concentration at 50% lysis of SRBC), which are respectively used
for assessment activities of complement classic pathway and complement alternative pathway.
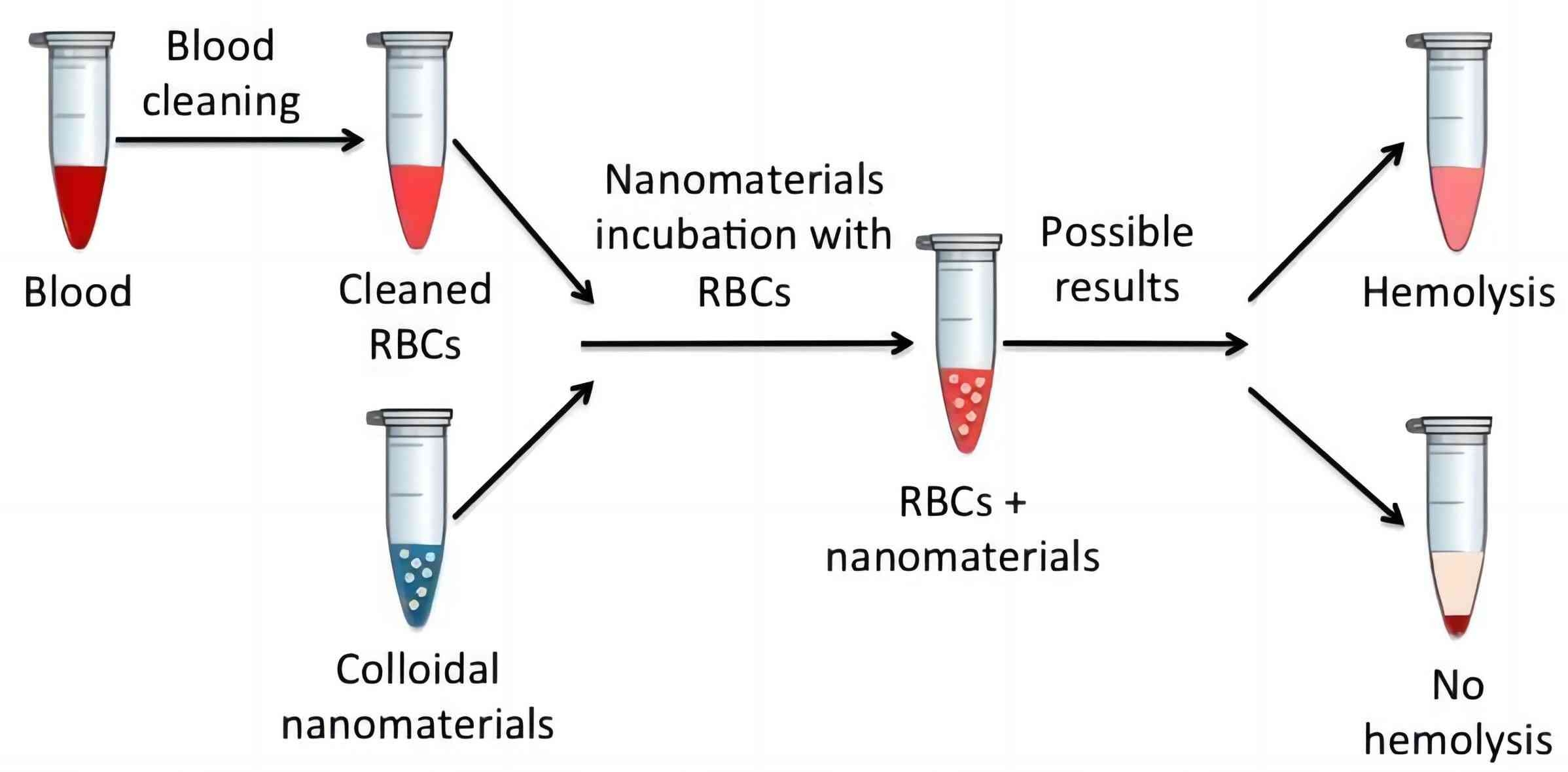
Fig. 1 Hemolysis assay process.1, 3
Hemolytic Inhibition Assay for Complement Activity Assessment
With the deepening of research and the development of complement therapeutics, a variety of complement inhibitors, such
as CD55, CD59, anti-C5 antibody, C1 inhibitor, have been approved and developed for human disease
treatment. This requires a method to evaluate the inhibitory activity of these inhibitors, namely hemolysis
inhibition assay. The inhibition activities can be determined by comparison of the hemolysis inhibition between
normal complement samples with that of complement samples with inhibitors. Two references can be used as a measure
of the activity of complement inhibition, one is the value of CH50 or AH50, the other is the hemolysis inhibition
curve of complement samples with gradient dilution.
Besides, hemolytic assay or hemolytic inhibition also can be applied for the detection and identification of
complement system deficiency as well as deficiency or function verification of a single complement component.
These kinds of assay usually are based on the depleted serum of individual components. By adding the missing
individual component, the complement activity can recover.
Services Overview
Hemolytic Inhibition Assay in Creative Biolabs
As a leading diagnostic service biotech company, Creative Biolabs has armed with a powerful and
standardized complement assay platform, aiming to offer the best and convenient complement related services. At
present, we provide custom hemolytic inhibition assays for the rapid complement activity assessment. For the samples
that are not suitable for mailing, we also provide ready-to-use hemolytic assay products and guidance. So what you
need to do is just feel free to contact us or send us your specific demands. Our professional scientist will reply
to you as soon as possible.
Our hemolytic inhibition assay service includes an array of advanced features designed to meet the unique needs of our clients.
-
Comprehensiveness: We offer a full range of testing, including activity analysis of novel agents, potential toxicity evaluation, and immune response measurement.
-
Customization: We understand that every client may have different needs and requirements. Therefore, our HIA services are easily customizable to meet your specific needs.
-
Accurate and Rapid Results: We aim to deliver precise results in the shortest span of time without compromising the quality of the tests. Our standard turnaround time is among the best in the industry.
-
Quality Control: We adhere strictly to the international quality norms for biotechnological testing. All assays are performed under strictly controlled conditions to ensure the highest accuracy.
Our team consists of highly qualified scientists and professionals with specialized training and experience in conducting such tests. The laboratory is equipped with state-of-the-art equipment and software to ensure reliable and detailed results.
We end up providing detailed and easy-to-understand reports of laboratory results, highlighting key findings and explaining their potential impact. A dedicated team is available to answer any questions you may have about the testing procedure, results or next steps.
Protocols
Complement Function Analysis Protocols
Related Products
Published Data
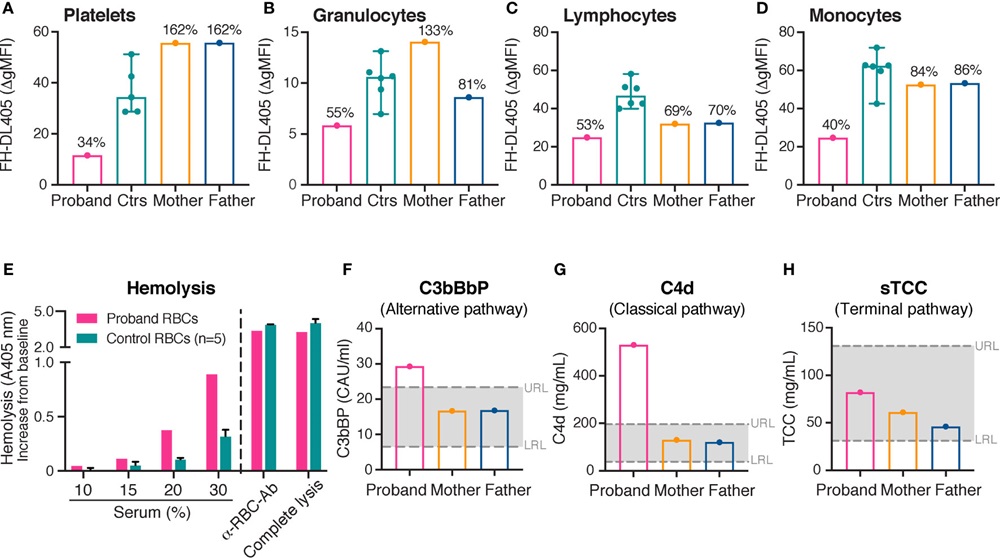 Fig.2 Complement inhibitor FH binding on platelets and leukocytes, with hemolytic assay and complement activation analysis.2,3
Fig.2 Complement inhibitor FH binding on platelets and leukocytes, with hemolytic assay and complement activation analysis.2,3
Hereditary thrombocytopenias are a genetically diverse cause of heightened bleeding risk. Sialic acid serves as a crucial ligand for complement factor H (FH), a key regulator that shields host cells from unintended complement attack. FH binding to erythrocytes was indirectly assessed by measuring complement-mediated hemolysis rates. The proband showed significantly reduced sialic acid expression on platelets and leukocytes, resulting in markedly diminished FH binding and moderate activation of both alternative and classical/lectin complement pathways, along with increased erythrocyte lysis. Reduced sialylation on platelets, leukocytes, and erythrocytes diminishes FH binding, prompting moderate complement activation and higher hemolysis rates.
Resources
References
-
Fornaguera, Cristina, and Conxita Solans. "Methods for the in vitro characterization of nanomedicines—biological component interaction." Journal of personalized medicine 7.1 (2017): 2.
-
Smolag, Karolina I., et al. "Severe congenital thrombocytopenia characterized by decreased platelet sialylation and moderate complement activation caused by novel compound heterozygous variants in GNE." Frontiers in Immunology 12 (2021): 777402.
-
Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
Questions & Answer
A: In hemolytic inhibition assay, the test sample, typically serum or plasma, is mixed with red blood cells and complement proteins. If the complement system is functional, it will cause lysis of the red blood cells. The addition of an inhibitory substance, such as an antibody or drug, can prevent or inhibit this lysis, which can be quantified to determine the level of inhibition.
A: Hemolytic inhibition assay has various applications, including assessing complement deficiencies, diagnosing autoimmune disorders such as systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), evaluating the effectiveness of complement-targeting drugs, and researching the role of complement in various diseases.
A: Some limitations of the hemolytic inhibition assay include the need for specialized laboratory equipment and technical expertise. It requires careful handling of complement proteins, which are heat-labile and can be affected by storage conditions. Interfering substances present in the test sample, such as hemolysis inhibitors or complement inhibitors, can impact the assay results and should be considered. Standardization and quality control measures are important to ensure reproducibility and accuracy of the assay results. Our services can meet these requirements.
A: Proper storage and transport of samples are crucial to maintain their integrity. Generally, you should freeze your samples at a recommended temperature (usually -80°C) if they're not being sent immediately. For transportation, samples should be well-packed in a leak-proof, insulated container with ice packs. However, specific storage and shipping instructions may vary depending on the nature of your samples.
A: The turnaround time depends on the nature of the study and the total volume of samples. Depending on these factors, it could vary from a few days to a couple of weeks. Rest assured, we prioritize providing high-quality, accurate results in a timely manner.
A: The raw data from the assay is typically analyzed using statistical techniques to distinguish significant results. Parameters such as percent hemolysis and concentration of inhibiting antibodies are used for quantification. Our team of experts will analyze the data and provide you with a detailed report.
A: We follow strict quality control guidelines for our hemolytic inhibition assays. Protocols are meticulously followed and each step gets validated and recorded. Known positive and negative controls are run alongside unknown samples to validate the accuracy of results. We also regularly participate in proficiency testing to ensure our assay performance remains at its peak.
For Research Use Only.
Related Sections:


 Fig.2 Complement inhibitor FH binding on platelets and leukocytes, with hemolytic assay and complement activation analysis.2,3
Fig.2 Complement inhibitor FH binding on platelets and leukocytes, with hemolytic assay and complement activation analysis.2,3

