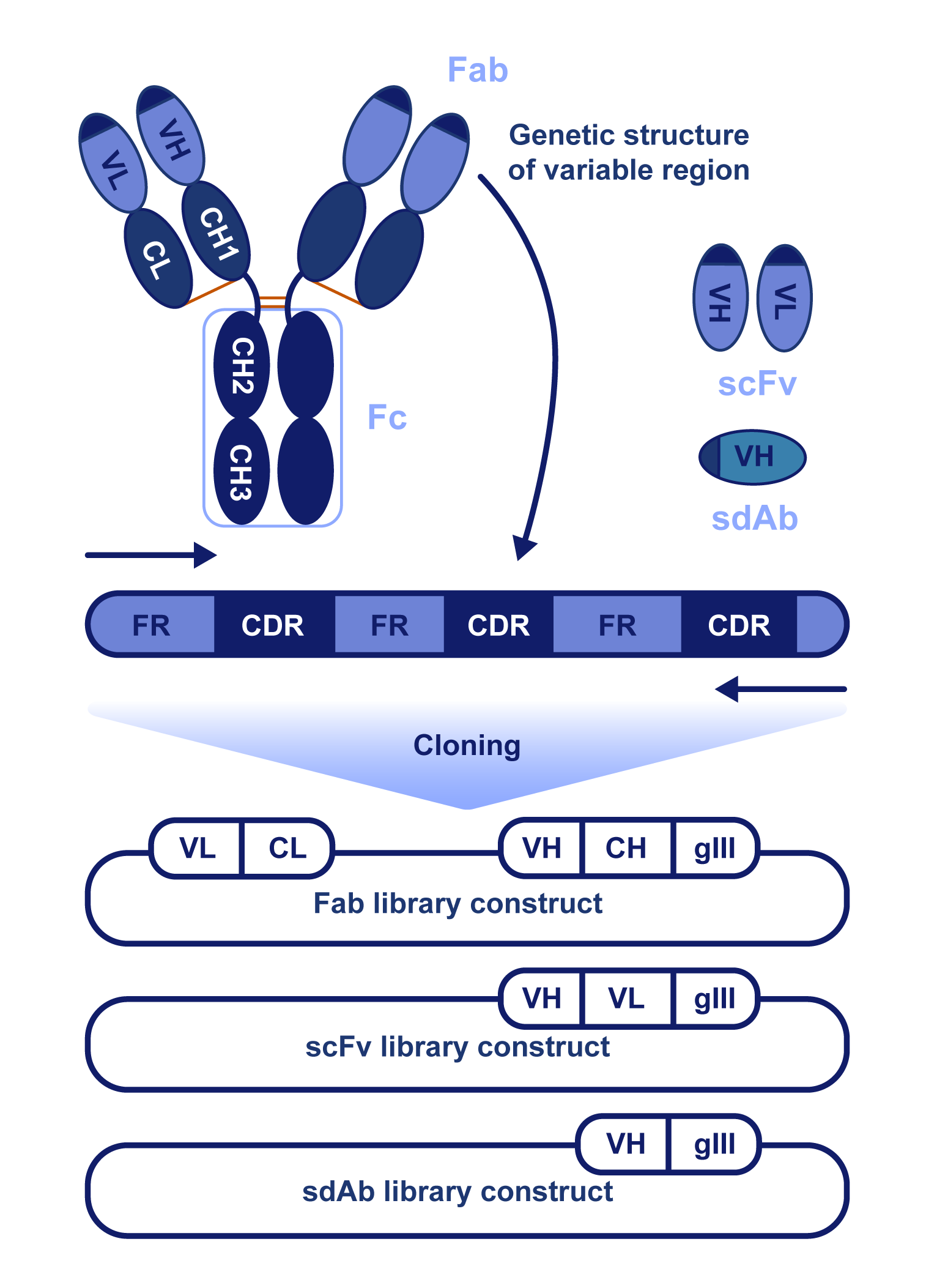
Phage Display Screening for Single Domain Antibody (SdAb)
Phage display screening is a well-established technique to identify antibody fragments and other binding molecules against any targets of interest. As each clone in phage display libraries represents a noncombinatorial functional domain of a naturally circulating antibody, phage display screening is a powerful method for sdAb discovery. Here, Creative Biolabs describes the phage display screening for sdAb generation.
Introduction of Phage Display
Phage display refers to the processes that foreign proteins expressed on the surface of filamentous phage through fusion with phage coat protein. The main theoretical basis for phage display libraries is the combination of antibody genotype (sequence) with the phenotype (specificity and affinity). Bypassing the animal immunization procedure, the novel therapeutic antibodies can be obtained in a short period. Combined with a series of antibody libraries, phage display allows the rapid selection of antigen-specific antibodies, especially for the poorly immunogenic targets. As the first well-established high throughput screening methodology for human therapeutic antibody discovery, phage display technology presents great potential for therapeutic and diagnostic applications.
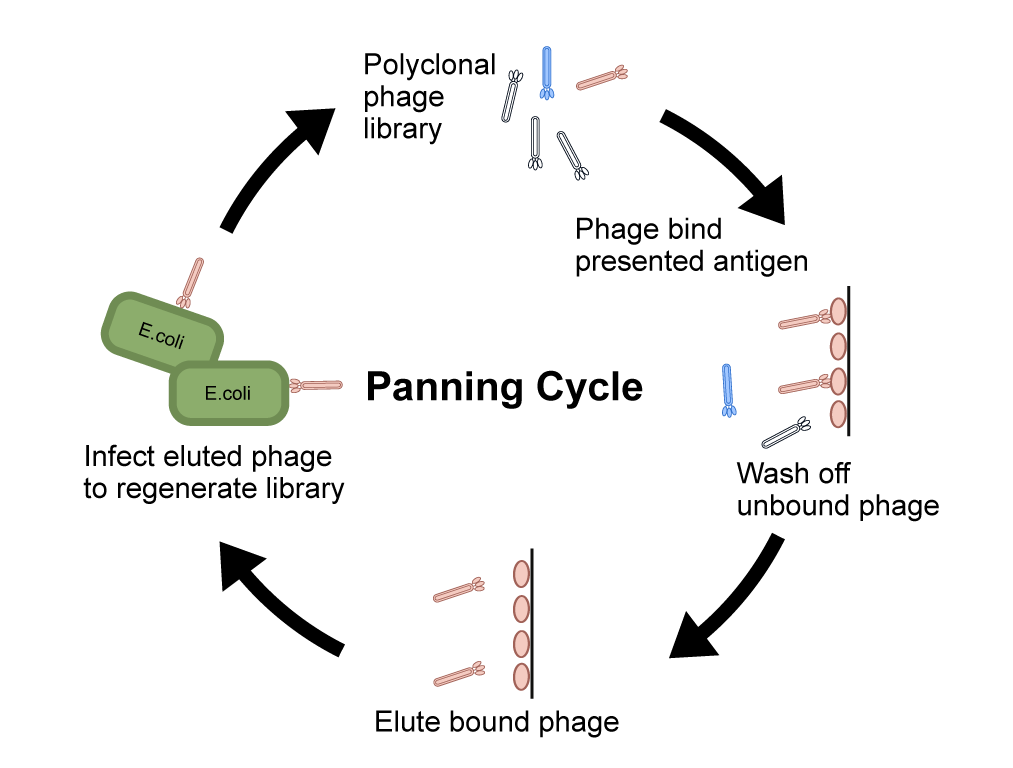
Phage Display Screening Procedures
Depending on the available functional format of the antigen, the phage display can be performed under different conditions. Solid-phase screening is the most straightforward screening method that coats antigens directly on a solid surface. An alternative method is liquid-phase screening in which biotinylated antigens bind to the phage in solution. Compared with solid-phase screening, the antigen concentration can be controlled and the possible conformational changes can be avoided. Then the complexes of phage bound to the antigen can be captured. Next, the antigen-bound phage is eluted off via pH change or protease digestion and reinfected into E. coli. After 3-4 rounds of screening, the target-specific clones can be obtained. Compared with immune libraries, selections with naïve or synthetic sdAb libraries are performed similarly but need 1 or 2 more selection rounds as these libraries are not target-specific.
Advantages of Phage Display Screening
-
The in vitro sdAb identification process allows for selection methodologies not possible with in vivo sdAb generation.
-
The sdAb generation can be biased towards desired regions of the target via the control of screening conditions.
-
Available for antigen presented on the surface of whole cells or tissue.
-
Organ targeting of phage libraries can be used to identify potential therapeutic sdAbs and determine the accessibility of a given target.
We are offering highly customized CRO services to assist your Single Domain Antibody (sdAb) related projects. Please Contact Us for more details.









