With the commitment of being your best immunologic analysis partner, Creative Biolabs has established the utmost efficient integrated solutions to innovate and accelerate your drug development for various types of diseases. Equipped with a team of professional scientists, we are capable of providing our clients with a variety of customized services on 2D cell culture. We can accommodate the specific properties of your product and provide flexible integrated solutions.
Two-dimensional (2D) cell culture has been considered as an attractive tool for studying the formation, function, and pathology of tissues or organs in human diseases. In general, the primary cell will be collected from animal models or patients to observe the differentiation, metabolism, and apoptosis of cells outside the body. Pilot studies suggest that cell cultures play an important role in understanding the cell function, mechanism of various diseases, as well as drug-disease interaction. In this condition, a wide variety of cell cultures have been generated and widely used in early drug development. For example, suitable cell culture methods have been used for cancer therapy, allowing to reveal tumor pathogenesis and to optimize many cancer treatment strategies. In recent years, 2D culture has become one of the most common types of cell culture in drug research. Cells are attached to the coated surface of a culture flask or a flat Petri dish and are cultured as a monolayer. The results have demonstrated that it is a simple, cost-effective way for cell culture. And the results have shown that cells are typically easier to analyze by a number of functional tests in 2D cell culture system, such as in vitro immunogenicity tests.
 Fig.1 SIAT® 2D Cell Culture Services.
Fig.1 SIAT® 2D Cell Culture Services.
In vitro cell cultures are critical to revealing the cell biology of tissues or organs, including cell growth, cell metabolism, and cell death. In 2D cell culture, cells bind to the flat surface and 2D monolayers will provide nutrients or growth factors for cells. This cell culture has proven its simplicity or efficacy for cell growth and proliferation in vitro and has been frequently used in preclinical studies. As a result, Creative Biolabs offers a wide collection of SIAT® 2D cell culture services to relieve our customers from the cumbersome process of cell cultures. Up to now, we provide many ready-to-use 2D cell cultures that derived from different kinds of primary cells or cell lines. More recent studies conducted by our labs have illustrated that SIAT® 2D cell culture is an ideal tool for many therapeutic applications, such as drug discovery, protein immunologic analysis, as well as human system research. For instance, a highly immunogenic human renal carcinoma cell line has been cultured by our 2D cell culture, and the cell line characterization has been performed by a number of genomics, proteomics, and immunologic analysis assays.

With extensive expertise and experience in the field of 2D cell culture, Creative Biolabs has established protocols for 2D model development tailored to your specifications. If you are interested in our services, please contact us for more details. Let us know what you need and we will accommodate you. We look forward to working with you in the future.
Other optional in vitro human system models:
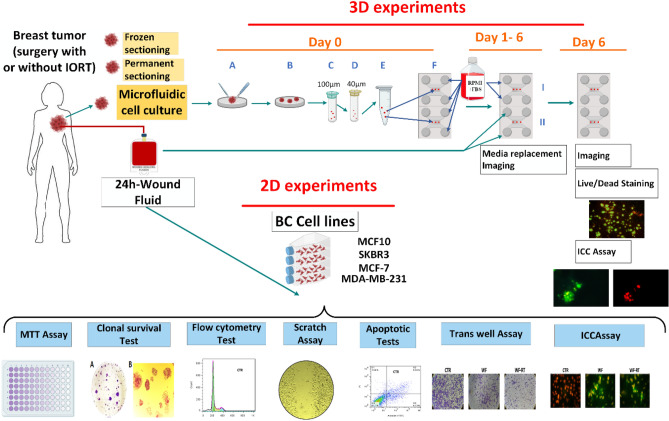 Fig. 3 The graphical abstract of the study. (Shabnam Jeibouei, 2022)
Fig. 3 The graphical abstract of the study. (Shabnam Jeibouei, 2022)
The study investigated the effects of intraoperative radiotherapy (IORT)-induced wound fluid on breast cancer progression using 2D cell cultures and microfluidic systems. In 2D cultures, it was found that wound fluids affected cell viability differently across various breast cancer cell lines, with some showing increased viability and others not, depending on the cell type and exposure duration. Specifically, the 2D cell culture experiments revealed that different breast cancer cell lines responded variably to the treatment with wound fluids, demonstrating that this traditional in vitro model can effectively be used to study immediate cellular responses to treatment environments, such as changes in cell viability, apoptosis, and cell cycle progression.
2D cell culture involves growing cells in a flat, two-dimensional environment, typically in plastic dishes or flasks coated with a substrate to support cell attachment. This method allows cells to spread out on a single plane, facilitating easy observation and manipulation, making it a foundational technique for studying cellular behaviors and responses under controlled conditions.
2D cell culture provides a simple and cost-effective method to study cell biology, physiology, and biochemistry. It allows researchers to control the environment, test pharmaceuticals, understand disease mechanisms, and study cellular responses to various stimuli, providing foundational insights that are essential in fields like cancer research and drug development.
The advantages of 2D cell culture include simplicity, cost-effectiveness, and the ease of setting up and maintaining cultures. It facilitates high-throughput screening, rapid growth and analysis of cells, straightforward imaging, and consistent results that are ideal for preliminary studies before more complex in vivo experiments.
In 2D cultures, cells often exhibit altered shapes, growth patterns, and metabolic activities compared to their behavior in three-dimensional in vivo environments. For example, the lack of complex cell-cell and cell-extracellular matrix interactions can affect gene expression, signaling pathways, and cellular responses to treatments.
This system is widely used in cancer research for drug screening, studying the mechanisms of cancer progression, and testing genetic manipulations. It allows researchers to rapidly assess the efficacy of chemotherapeutic agents against different cancer cell lines, although it may not fully mimic the tumor's microenvironment.
In drug discovery, 2D cell cultures are used for initial screening of compounds to assess cytotoxicity and pharmacological properties. This approach can quickly identify promising drug candidates before more costly and time-consuming in vivo studies and clinical trials are conducted.
2D cell culture plays a crucial role in genomics and proteomics by providing a controlled environment for studying the effects of genetic modifications and protein expressions under specific conditions. This allows for detailed analysis of gene and protein functions, interactions, and pathways involved in cellular processes.
Use the resources in our library to help you understand your options and make critical decisions for your study.
All listed services and products are For Research Use Only. Do Not use in any diagnostic or therapeutic applications.