T and B Cell-based Binding Assay
To better understand vaccines or drugs' immune response to pathogens, it is necessary to investigate T and B cell epitopes to a specific antigenic peptide. With advanced technology and excellent in-house expertise, Creative Biolabs provides T and B cell-based binding assays for cancer epitope analysis.
T and B-cell Binding Epitope
T cell receptor (TCR) and B cell receptor (BCR) is responsible for pathogens recognition. The specific portions of antigens that bind to the receptor are named antigen determinants or epitopes. An antigen can have one or more epitopes. Typically, antibodies bind exposed solvent parts of the antigen with about five amino acids or sugars in size. TCRs recognize the cancer epitopes attached to major histocompatibility complex (MHC) molecules exhibited on the antigen-presenting cells (APCs), roughly 8 to 17 amino acid residues, including MHC I-presented epitopes and MHC II-presented epitopes.
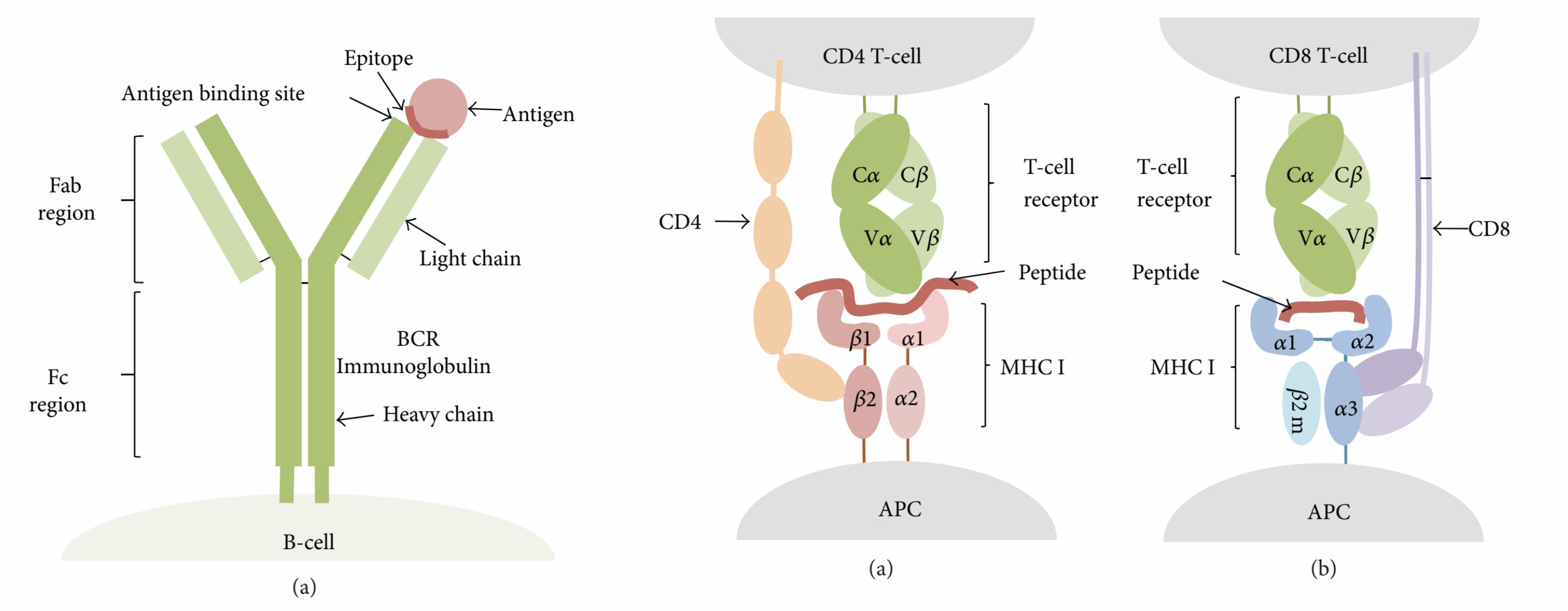 Fig.1 T and B cell-based epitope recognition.1
Fig.1 T and B cell-based epitope recognition.1
Binding Assay Service at Creative Biolabs
The binding assay has become an indispensable tool to analyze cancer epitopes and characterize binding affinity between immune complexes. Creative Biolabs offers this invaluable tool in identifying immunogenic peptides with strong and specific binding to T and B cell receptors.
Workflow

Key Features

Evaluate Binding Interactions
The binding activity is monitored qualitatively and quantitatively. In the quantitative binding assays, the binding strength of the receptor to the antigen peptide (ligand) can be measured.
 Fig.2 Illustration of the equilibrium between receptor-ligand complex formation rate and the dissociation rate.2
Fig.2 Illustration of the equilibrium between receptor-ligand complex formation rate and the dissociation rate.2
Binding Kinetics Data
-
Dissociation constan (KD). The equilibrium dissociation constant, KD, describes the binding affinity between a specific antibody and antigen. Commonly, Kd is calculated by a ratio of koff/kon.
-
On rate (kon). The association rate of the antibody. It describes the quickness of the antibody binding to its antigen.
-
Off rate (koff). The disassociation rate of an antibody. It describes the quickness of the antibody dissociated from its antigen.
-
Affinity constant. When the antibody-antigen complex forming reaches equilibrium, the affinity constant is 1/KD, which means the smaller the KD value, the stronger the antibody's affinity to its target.
-
Qualitative binding. Determine the antibody response levels to different epitopes and T cell expansion detected using multimer/tetramer assay.
Related Services
-
Binding interaction can be measured using various advanced techniques regarding your sample and requirements.
-
Combined binding assay with multiple 3D structure methods to determine epitope location and orientation.
With decades years of experience in antigen discovery and antibody development, Creative Biolabs has developed an immune-oncology platform to provide cancer epitopes analysis service for our clients. Our robust T cell assay platform for cancer research is of high efficiency and saves your research time and inputs. Please contact us for detailed services.
References
-
Sanchez-Trincado, J. L.; et al. Fundamentals and Methods for T- and B-Cell Epitope Prediction. Journal of immunology research. 2017: 2680160.
-
Bosma, Reggie.; et al. Ligand-Binding Kinetics on Histamine Receptors. 2017: 115-155.
For Research Use Only | Not For Clinical Use


 Fig.1 T and B cell-based epitope recognition.1
Fig.1 T and B cell-based epitope recognition.1


 Fig.2 Illustration of the equilibrium between receptor-ligand complex formation rate and the dissociation rate.2
Fig.2 Illustration of the equilibrium between receptor-ligand complex formation rate and the dissociation rate.2
 Download our brochure
Download our brochure