Creative Biolabs offers a full package of immunogenicity analysis services to support preclinical drug discovery for small molecule, biologic drugs, and immunotherapy development programs. Particularly, we are happy to help global customers analyze the potential immunogenicity of multiple immunomodulatory agents for cancer therapies, which including but not limited to antibodies targeting immune checkpoints, bispecific antibodies, and chimeric antigen receptor.
In the past few years, numerous immune checkpoint inhibitors, as well as immuno-oncology mAbs with different structures/composition and immunomodulatory activities, have revolutionized treatment regimens for several malignancies. Meanwhile, the increasing use of immunomodulatory agents arises the risk of unwanted immune responses on the safety and efficacy of treatment compared with non-immunomodulatory agents. For example, immunomodulatory agents may potentiate immune responses through direct immunomodulation or inhibit immune responses as in the case of proapoptotic/depleting antibodies that target immune cells. In addition, in some cases, unwanted immune responses may result in the induction of anti-drug antibodies (ADA), which can induce infusion-related reactions or alter the pharmacokinetics (PK) of an agent.
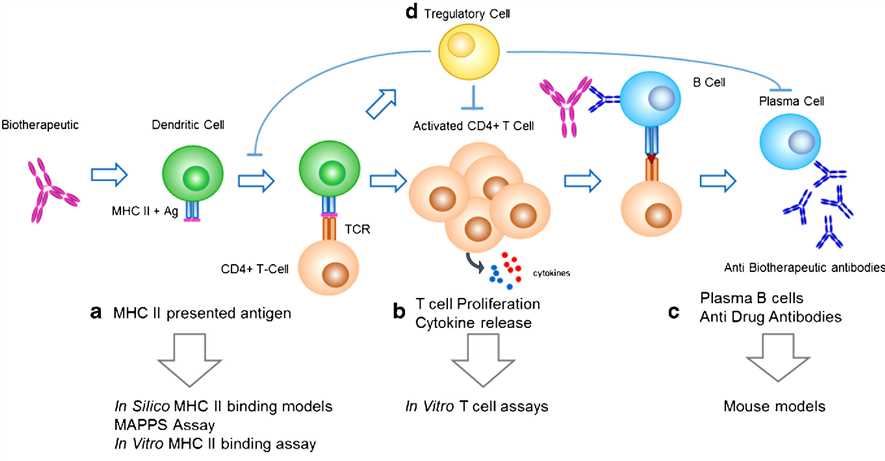 Fig.1 Key processes involved in the development of a humoral, MHC class II-mediated anti-biotherapeutic IgG response and corresponding predictive immunogenicity tools. (Gokemeijer, 2017)
Fig.1 Key processes involved in the development of a humoral, MHC class II-mediated anti-biotherapeutic IgG response and corresponding predictive immunogenicity tools. (Gokemeijer, 2017)
It has been reported that numerous factors such as product-related impurities, excipients, dosing regimen, type and stage of the disease, as well as prior and concomitant treatments, may affect the immunogenicity of a mAb. During preclinical development, both in silico algorithms and in vitro assays have been used to help select molecules with lower immunogenicity risk. Commonly, in silico algorithms are used to predict potential T cell epitopes. And in vitro binding assays are used to confirm the predicted sequences binding to MHC molecules. What’s more, the immunogenicity signals of a protein product can be assessed with dendritic cells (DC)-activation assay.
Working in the field of immunogenicity analysis for many years, Creative Biolabs has successfully established a top SIAT® immunogenicity platform to offer a full package of analysis services for global customers. Our experienced experts are able to provide high-quality immunogenicity evaluation services and reliable results analysis in a short period of time. Our comprehensive range of immunogenicity evaluation tests including:
For more details about our immunogenicity analysis services of tumors, please feel free to contact us or directly send us a quote.
Other optional immunogenicity analysis services for immune-related diseases:
Immunogenicity analysis in tumor treatments involves evaluating the immune system's response to anti-cancer biologics, including vaccines, antibodies, and cell therapies. This analysis helps determine if a therapeutic agent induces an immune response that could potentially enhance its anti-tumor effects or, conversely, lead to resistance or adverse immune-related events.
Immunogenicity can impact both the efficacy and safety of treatments. An ideal cancer treatment will induce a strong immune response against tumor cells without causing significant off-target effects. Understanding immunogenicity helps in predicting and managing potential side effects and tailoring therapies to achieve optimal patient outcomes.
Immunogenicity in tumor therapies is typically measured using assays that detect the presence of anti-drug antibodies (ADAs) and immune effector cells. These assays help ascertain whether the immune system is mounting a defense against the therapeutic agents, which can affect their effectiveness and the overall treatment strategy.
Tumors that are highly immunogenic often provoke a strong immune response, which can be leveraged to improve treatment outcomes through immunotherapy. However, if the immune response is directed against the therapy itself rather than the tumor, it may neutralize the treatment's effects and lead to therapeutic failure.
Immunogenicity can lead to drug resistance in tumor therapy, especially if the immune system develops neutralizing antibodies against a therapeutic agent. This can reduce the drug's efficacy over time, necessitating changes in treatment strategies, such as switching to different therapeutic agents or combining with other treatments to overcome resistance.
Strategies to minimize immunogenicity in cancer treatments include modifying therapeutic proteins to reduce their immunogenic potential, using immunosuppressive agents to temper the immune response, and selecting delivery routes that minimize immune activation. Advanced genetic engineering techniques are also employed to design therapies that are less likely to be recognized as foreign by the immune system.
Immunogenicity is a critical factor in the development of cancer vaccines. A successful vaccine must elicit a robust immune response specifically targeted against tumor antigens without inducing significant adverse reactions. Immunogenicity analysis helps optimize vaccine components, such as adjuvants and delivery systems, to enhance efficacy and safety.
Use the resources in our library to help you understand your options and make critical decisions for your study.
All listed services and products are For Research Use Only. Do Not use in any diagnostic or therapeutic applications.