Overview Service Features Published Data FAQs Scientific Resources Related Services
Overview of Stem Cell Facilitated Drug Discovery
Various types of stem cells were used to facilitated drug discovery. Based on their own unique characteristics, these cells can be applied in the research setting for a plethora of uses. They can be potentially used as the disease models to treated or cure many life-threatening or chronic illnesses. Human embryonic stem cells (ESC) may store the genetic information which may be discovering how some diseases develop. Also, the human stem cells are being used to test new drugs. By using stem cells, not only the process of drug research and its subsequent path to becoming an approved drug can be accelerated, but also the potential side effects of the drug before it is tested on humans can be revealed. Cells taken from a patient, another approach, with a genetic disease can be reprogrammed as human induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) which is one of the most important developments in disease modeling. They are functionally equivalent to ESCs, and they can subsequently be differentiated into disease-relevant cell types to uncover molecular and cellular mechanisms and to screen for drug treatment options. Modeling the disorders with mild or complex phenotypes can be achieved by reprogramming process used to create the iPSCs, as known as variability. As a result, by performing targeted gene knock-outs, the tissue-specific cell lineage was generated, by overexpressing genes from defined genome location, the point mutations can be introduced. Consequently, the disease-relevant mutation can be discovered by the phenotypes identified in these cells.

According to the mechanisms which closely recapitulate the in vivo microenvironment, applying the stem cells for drug discovery can directly influence drug design and clinical strategies. At Creative Biolabs, various types of stem cells were used to facilitated drug discovery. Based on their own unique characteristics, these cells can be applied in the research setting for a plethora of uses. We provide two different stem cell facilitated drug discovery services. The stem cell-based disease modeling service which including the disease of Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, Zika Virus infection, Hepatic disorder, Spinal muscular atrophy, and the Long QT syndrome. Also, the iPSC facilitated drug discovery services of iPSC based drug screening, iPSC based toxicity and efficacy analysis, iPSC derived the animal model, iPSC based target identification and the discovery of the effects of the drug on individual persons.
Services at Creative Biolabs
Our service is designed to accelerate the process of drug discovery and development by leveraging the unique capabilities of stem cells. This innovative service provides researchers with a powerful platform to study disease mechanisms, identify drug targets, and evaluate the efficacy and safety of novel pharmaceutical compounds.
-
Our platform enables the creation of disease-specific cell types through differentiation protocols. Researchers can study disease mechanisms in vitro, facilitating the understanding of drug action and potential off-target effects.
-
We provide comprehensive profiling of drug candidates, including gene expression and molecular analysis, toxicology and safety assessment, pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics studies.
Our service is dedicated to advancing research in the biopharmaceutical industry, providing essential tools and insights necessary for the development of effective therapeutics. By harnessing the power of stem cells, we aim to revolutionize the drug discovery process and contribute to the future of personalized medicine.
Stem cell-based disease modeling services
-
Alzheimer's disease
-
Parkinson's disease
-
Zika Virus infection
-
Hepatic disorder
-
Spinal muscular atrophy
-
Long QT syndrome
iPSC facilitated drug discovery services
Our customized services according to the various situation of your projects, please feel free to contact us for professional consultation and welcome to get more information through the link below.
Service Features
-
Wide Range of Stem Cell Sources
-
Custom Stem Cell Line Development
-
Well-established Differentiation Protocols
-
Predictive Biomarkers Development
-
Advanced Bioinformatics tools
-
Collaborative Research Opportunities
-
Comprehensive Training Programs and Technical Support
Published Data
Below are the findings presented in the article related to stem cell facilitated drug discovery.
Yuta Koui et al. developed a culture system that generates quiescent hepatic stellate cells (qHSC cells) from human induced pluripotent stem cells (hiPSC), which can be transformed into activated HSC in culture. Using qHSC cells derived from an RFP reporter gene iPSC, they screened a repurposable chemical library and identified therapeutic candidates for the prevention of liver fibrosis.
Using this model, they demonstrated that A83-01 and ICG-001 inhibited HSC activation, and by screening drug relocation libraries, they identified compounds that inhibited HSC activation, among them the antimalarial drug artemisinin. They are currently conducting animal studies with another candidate compound identified by the drug screening system.
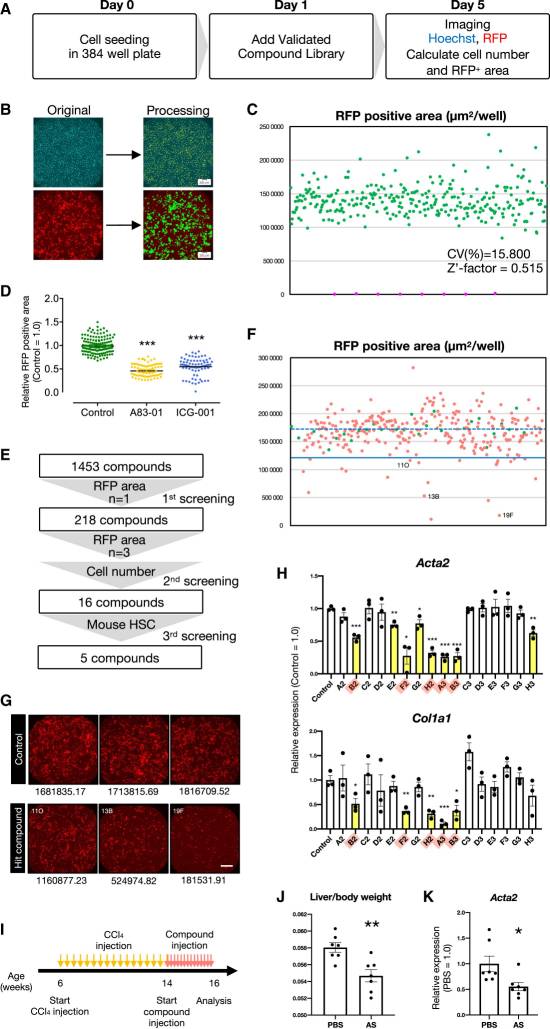 Fig. 1 Screening of therapeutic agents for liver fibrosis.4
Fig. 1 Screening of therapeutic agents for liver fibrosis.4
FAQs
-
Q: Can your services assist in identifying new drug targets using stem cells?
A: Yes, our stem cell models can be used to identify novel drug targets, particularly in disease-specific contexts. By mimicking human disease conditions in vitro, we can identify cellular pathways and molecular interactions that may serve as therapeutic targets. This approach is highly valuable for diseases where traditional models have failed to capture the underlying pathology.
-
Q: What types of assays do you offer with your stem cell-facilitated drug discovery services?
A: We offer a broad range of assays, including cytotoxicity assays, functional assays, phenotypic screening, high-content imaging, and gene expression analysis. We can also conduct organoid-based assays for more complex tissue modeling. Each assay is tailored to your specific research needs, enabling comprehensive evaluation of drug effects on stem cell-derived tissues.
-
Q: Can you customize the stem cell models to specific disease conditions?
A: Absolutely. We offer disease-specific stem cell models by utilizing patient-derived iPSCs or genetically modified stem cells that carry disease-relevant mutations. This allows us to replicate the pathophysiology of a particular condition in vitro, enabling more accurate testing of drugs targeting specific diseases, from neurodegenerative disorders to cardiovascular diseases, and even rare genetic conditions.
-
Q: How does stem cell technology enhance the drug discovery process in your services?
A: Stem cell technology revolutionizes drug discovery by providing a more biologically relevant model system. Our stem cell-based assays allow for testing drugs on human-like cells, offering insights into toxicity, efficacy, and potential side effects in a human context. This improves the translatability of preclinical findings and reduces the likelihood of failure in later clinical stages, offering a more predictive and efficient approach to drug discovery.
-
Q: How long does it typically take to complete a drug discovery project using your stem cell services?
A: The timeline for a drug discovery project can vary depending on the complexity of the assay, the type of stem cells used, and the specific goals of the project. Typically, early-stage testing, such as cytotoxicity or functional assays, can be completed within a few weeks. More complex studies involving organoid models or disease-specific iPSC lines may take several months. We work closely with clients to establish realistic timelines and provide regular progress updates throughout the project.
Scientific Resources
References
-
Suh, W. (2016). A new era of disease modeling and drug discovery using induced pluripotent stem cells. Archives Of Pharmacal Research, 40(1), 1-12. doi: 10.1007/s12272-016-0871-0.
-
Johnson, J., & Hockemeyer, D. (2015). Human stem cell-based disease modeling: prospects and challenges. Current Opinion In Cell Biology, 37, 84-90. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2015.10.007.
-
Borooah, S., Phillips, M., Bilican, B., Wright, A., Wilmut, I., & Chandran, S. et al. (2013). Using human induced pluripotent stem cells to treat retinal disease. Progress In Retinal And Eye Research, 37, 163-181. doi: 10.1016/j.preteyeres.2013.09.002.
-
Koui, Yuta, et al. "Development of human iPSC-derived quiescent hepatic stellate cell-like cells for drug discovery and in vitro disease modeling." Stem Cell Reports 16.12 (2021): 3050-3063.
For Research Use Only. Not For Clinical Use.

 Fig. 1 Screening of therapeutic agents for liver fibrosis.4
Fig. 1 Screening of therapeutic agents for liver fibrosis.4