Creative Biolabs offers clients a novel method for versatile DNA fragmentation and directed evolution: the NExT DNA shuffling. It is an efficient and robust approach to tailor-suit proteins with specified properties.
The demand for tailor-made proteins for chemical, pharmaceutical and food processing has been increasing in recent years. However, the rational approaches have been inefficient and required time-consuming cycles of design and testing. In these methods, the lack of controllability over the recombination and the range of fragment sizes generated is also obvious.
Mimicking natural evolution by DNA shuffling has been proved to be a fast and effective method for obtaining desired characteristics, even without knowledge of the protein structure or underlying principles. As a new DNA shuffling method, NExT DNA shuffling is based on the random incorporation of dUTP as a fragmentation-defining exchange nucleotide with the four standard dNTPs, without the need for further adjustment. NExT DNA shuffling is reproducible and easily performed with a predictable fragmentation outcome, compared with other traditional techniques.
In NExT study of chloramphenicol acetyl transferase I, the chloramphenicol tolerance level was increased from 25 ug/ml to 400 ug/ml, after the optimization. Key steps include the cloning, the uridine-exchange PCR, the enzymatic digest and chemical cleavage, the fragment purification, and the gene reassembly and amplification. Full-length gene was reassembled from the purified gene fragments, using an internal primer extension procedure with increasing annealing temperatures with a proofreading DNA polymerase. The fragments serve each other as primers and, thus, get longer with each cycle of the reaction, until full-length products are achieved. Products of the assembly reaction are amplified with a standard PCR with end primers, cloned, and sequenced. We can work on your protein engineering projects with NExT, screen the protein products for desired properties. If necessary, the screened proteins can have the structures determined for more detailed functional studies.
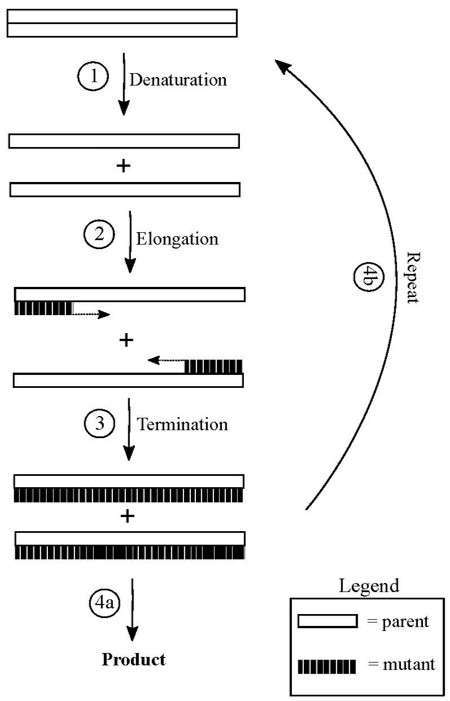 Fig.1 Process of DNA shuffling.1
Fig.1 Process of DNA shuffling.1
Reference
All listed services and products are For Research Use Only. Do Not use in any diagnostic or therapeutic applications.
| USA:
Europe: Germany: |
|
|
Call us at: USA: UK: Germany: |
|
|
Fax:
|
|
| Email: info@creative-biolabs.com |
