Monitoring of immune responses caused by biotherapeutic drug treatment is a regulatory requirement during preclinical development through to clinical trials. ADA is one of the most common causes of the efficacy loss of some drugs. Moreover, the appearance of ADA can trigger an allergic reaction. However, optimization and validation of assays for anti-drug antibodies (ADA) are challenging due to the excess of human antibodies in serum and the relatively low immune response. With the development of ADA assays, various methods have been used in actual applications. Among both of them, anti-idiotypic antibodies were widely applied as a positive control to measure the concentration of specific ADA conveniently and sensitively combined with quantitative methods such as sandwich ELISA.
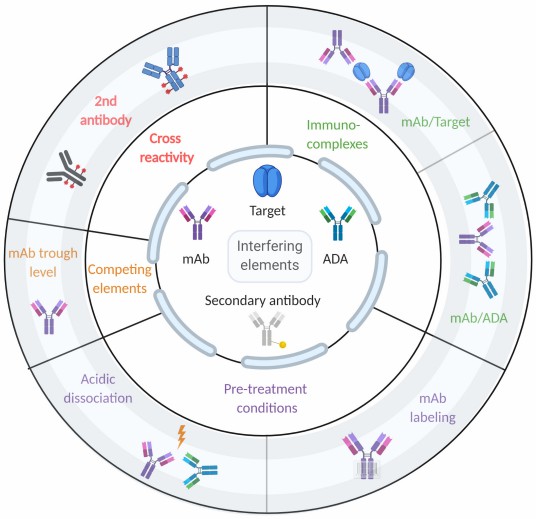 Fig.1 Factors influencing ADA detection in immunoassays.1,4
Fig.1 Factors influencing ADA detection in immunoassays.1,4
There are three commonly used methods in recent ADA assays: ELISA, cell-based assays, and label-free biosensors. As a mature method, ELISA is the simplest approach which also takes sensitivity into account. As a positive control, anti-idiotypic antibodies have strong specificity and high sensitivity, which provides a general approach to detect various target antibodies by ELISA. Therefore, the development of specific anti-idiotypic antibodies is necessary to expand the range of ELISA applications in ADA assay.
 Fig.2 ELISA for ADA detection.2,4
Fig.2 ELISA for ADA detection.2,4
Fortunately, recombinant monoclonal antibodies against biotherapeutics can be created using sophisticated antibody libraries and well-established phage display technology. Moreover, modified hybridomas technology also can be used to prepare anti-idiotypic antibodies.
 Fig.3 Binding profile analysis of four monoclonal anti-idiotypic antibodies to modified anti-CD3/CDR domains via ELISA and biolayer interferometry.3, 4
Fig.3 Binding profile analysis of four monoclonal anti-idiotypic antibodies to modified anti-CD3/CDR domains via ELISA and biolayer interferometry.3, 4
In developing strategies to analyze the impact of ADA on therapeutic exposure, a pharmacokinetic (PK) assay for the T-cell-engaging bispecific antibody was crafted, reflecting its mechanism of action. Utilizing monoclonal anti-idiotypic antibodies as surrogate ADAs, the assay assessed pre-clinical exposure impacts. Patient-derived ADA's neutralizing potential was evaluated through advanced characterization, including binding assessments to cibisatamab's antibody domains and their effects on targeting capabilities. By comparing these patient ADA interactions with monoclonal anti-ID antibody controls, insights into ADA-driven influences on drug activity were gained, facilitating a comprehensive understanding of ADA's role in therapeutic efficacy.
Creative Biolabs provides Anti-Idiotypic Antibody Discovery Service for ADA Assay tailored to various drug types. For biosimilars, we focus on the drug's variable region, either developing new solutions or utilizing original ADA products. For monoclonal, bispecific, and antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs), as well as nanobodies or scFvs, we specialize in creating polyclonal antibodies targeting the respective regions or full structures of these drugs.
References
All listed services and products are For Research Use Only. Do Not use in any diagnostic or therapeutic applications.
| USA:
Europe: Germany: |
|
|
Call us at: USA: UK: Germany: |
|
|
Fax:
|
|
| Email: info@creative-biolabs.com |
