Creative Biolabs is a leading provider of phage display library construction services. In the process of antibody generation, biopanning is a critical step which directly affects the quality of the antibodies selected. Our scientists are able to employ a serial of selection methods to ensure the generation of high-quality antibodies. Cell-based screening is a method in particular for cell surface antigen selection. Creative Biolabs has developed an optimized procedure which facilitates the selection of antibody with high specificity and affinity.
In general, solid phase screening is the most common screening methods, which the antigens are attached to plates or other solid phases and then presented with the libraries. While, some obstacles may prevent the discovery of effective antibodies during this approach. For example, the antigens cannot maintain the native conformation since they are immobilized on the solid surface. Thus some antibodies selected from solid phase may not recognize the native antigen with high specificity and affinity. In addition, for some cell surface antigens that are hardly expressed as recombinant proteins, solid phase screening is likely to fail to isolate specific antibodies. In this case, cell-based screening can be a more reliable approach to be competent for such task.
The method of cell-based screening circumvents the disadvantages of solid phase selection by displaying the antigens in their native forms. The best application of this method is to select antibodies for cell surface receptors, such as G protein-coupled receptors (GPCR), ion channel-linked receptors and enzyme-linked receptors. In addition, it could be used to select antibodies for structure studies in co-crystallization. Furthermore, the cell-based selection could target the cell surface proteins that are overexpressed or modified by disease, which brings in the novel epitopes.
While using purified antigens could be very effective in selection, cell surface antigens are more complex therefore more challenging. Creative Biolabs has developed an advanced selection platform that ensures the high expression level of the targets. In addition, the incorporation of positive selection and depletion steps will further improve the affinity and the specificity of the selected binder.
Creative Biolabs has long-term devoted to developing and optimizing the effectiveness and the efficiency of phage display library screening. With years of experience, our scientists have developed several biopanning methods which apply to different types of targets to boost our global customers’ research and project goals. Among them, the cell-based library screening is highly promising for the development of therapeutic or imaging agents. We are pleased to use our extensive experience and advanced platform to offer the best service and the most qualified products to satisfy each demand from our customers.
Other optional phage display library screening services:
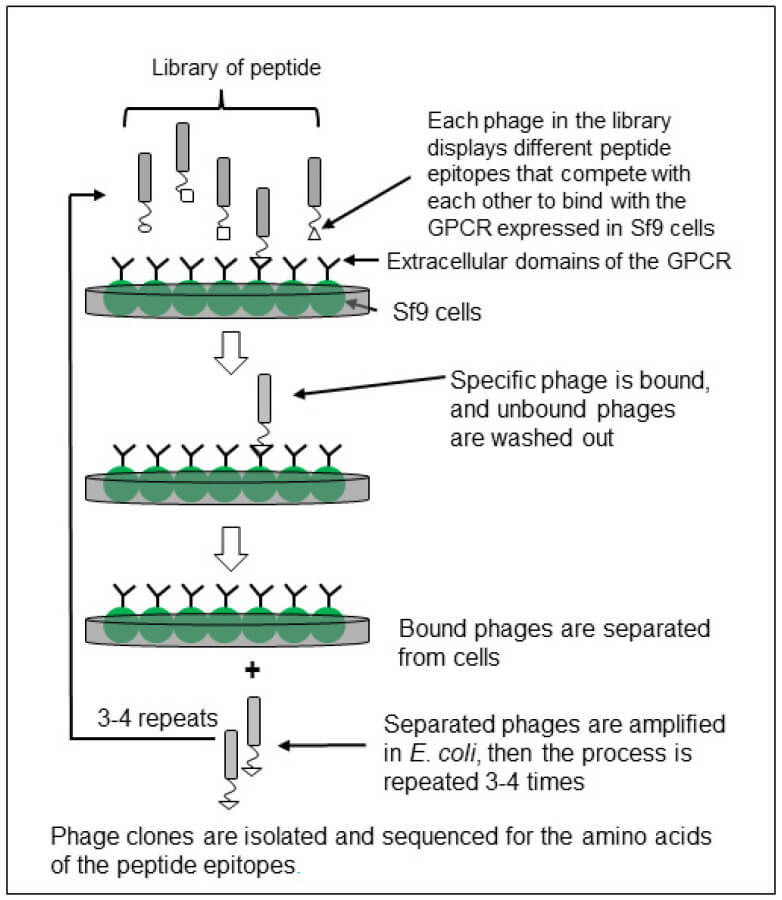 Fig.1 A schematic diagram of GPCR (G-Protein-Coupled Receptor) based screening using a phage display peptide library and biopanning using the insect Sf9 cell expression system.1
Fig.1 A schematic diagram of GPCR (G-Protein-Coupled Receptor) based screening using a phage display peptide library and biopanning using the insect Sf9 cell expression system.1
The article highlights the development of a novel screening method for insecticide discovery based on GPCRs (G-protein-coupled receptors) using phage-displayed peptides and an insect cell expression system. The significance of the research lies in its potential to identify bioactive peptides that disrupt critical insect physiological processes, offering new avenues for pest control. The study's results demonstrated that specific peptides could bind to and interfere with the GPCR-ligand function in the fire ant model, leading to reduced survival rates. This innovative method, called receptor interference (RECEPTORi), holds promise for more efficient insecticide discovery. The application of cell-based phage display library screening was crucial in rapidly isolating peptides that target GPCRs, proving to be cost-effective and time-efficient. This technique allows for a wide array of potential bioactive peptides to be screened, reducing the likelihood of insecticide resistance and enabling the design of targeted pest management strategies.
Cell-based phage display library screening is a technique that utilizes bacteriophages to display a wide array of peptides or proteins on their surfaces. These phage-displayed peptides are screened against target proteins or receptors expressed in living cells. This allows researchers to identify peptides or ligands that bind specifically to the target receptors, aiding in drug discovery, antibody development, or, as in some cases, identifying bioactive peptides for pest control.
In a cell-based system, specific target proteins, often G-protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) or other membrane proteins, are expressed in the cells. A library of phages, each displaying a unique peptide, is exposed to the cells. The phages that bind to the target proteins are isolated, amplified, and further screened to identify strong binders. This iterative process is known as biopanning, which helps isolate the most specific and effective peptides.
Cell-based phage display offers several advantages, including the ability to screen for peptide interactions in a more biologically relevant environment, where membrane proteins are properly folded and functional. It allows the identification of peptides that specifically bind to the natural conformation of targets in living cells. Additionally, it is a cost-effective, rapid, and scalable method that can screen large peptide libraries for potential drug or therapeutic leads.
Cell-based phage display is commonly used to screen membrane proteins like GPCRs, ion channels, or other receptors. These proteins are essential for signaling pathways and serve as common drug targets. Additionally, phage display can be used to identify ligands or inhibitors for enzymes, antibodies, or protein-protein interactions in both medical and agricultural research, such as in the discovery of novel insecticides.
In drug discovery, phage display libraries are screened against target receptors or proteins expressed in cells to identify peptides that bind with high specificity. These peptides can serve as leads for the development of small molecules or biologics, such as antibodies, that modulate the activity of these targets. This method allows researchers to identify potential therapeutic candidates quickly and cost-effectively.
GPCRs are among the most important drug targets due to their role in many physiological processes. Cell-based phage display screening for GPCRs allows the identification of peptides that bind to specific GPCRs, which can modulate receptor functions. These peptides may act as agonists, antagonists, or modulators and can lead to new therapies for a wide range of diseases, from cancer to cardiovascular conditions.
Biopanning is a key process in phage display that involves iterative rounds of screening, where phages binding to target proteins are separated, amplified, and subjected to additional rounds of screening. This process allows for the enrichment of high-affinity binders over multiple rounds. Each round refines the pool of peptides, ensuring that only the best candidates with the strongest binding properties are identified.
Peptides identified through phage display can have numerous applications, including the development of therapeutic drugs, diagnostic tools, and vaccines. In agriculture, they can be used for pest control, as seen in the discovery of bioactive peptides that interfere with insect physiological processes. Additionally, these peptides can serve as molecular tools to study receptor functions or as leads in cancer therapy by targeting specific receptors on tumor cells.
Phage display uses bacteriophages to present peptides or proteins. Unlike chemical screening, which relies on large collections of small molecules, phage display enables the presentation of a vast diversity of peptides or proteins in a more natural context. It is also more flexible, cost-effective, and can be tailored to specific protein targets, making it highly advantageous for biologic discovery.
Use the resources in our library to help you understand your options and make critical decisions for your study.
All listed services and products are For Research Use Only. Do Not use in any diagnostic or therapeutic applications.
| USA:
Europe: Germany: |
|
|
Call us at: USA: UK: Germany: |
|
|
Fax:
|
|
| Email: info@creative-biolabs.com |
