Creative Biolabs has developed ex vivo selection schemes using phage-displayed libraries. This can be used to discover peptide and protein ligands for macromolecules that are expressed in an organ- and tissue-specific manner. Our scientists commit to offer clients a reliable and robust ex vivo phage display service to meet each individual requirement.
The term of ex vivo phage display is a novel method using phage solutions to select the primary cell suspensions of organs and tissues or the cultured cells as targets. Compared with in vivo phage display, which phages are primarily exposed to the vascular endothelial cells, it is notable that ex vivo phage display is exposed to all cell types. Besides that, ex vivo phage display is higher throughput, which is able to screen a large amount of different phages by using material from one mouse. Moreover, ex vivo phage display also has lower background than in vivo phage display. In other words, ex vivo binding can be more discriminatory than in vivo homing. Therefore, the ex vivo phage display technology can be treated as a novel choice or combining with in vivo phage display technology to identify the most specific binding target.
The proprietary ex vivo phage display technology of Creative Biolabs is an improved biopanning technology for discovering peptide and protein ligands for organ- and tissue-specific macromolecules. Our scientists can generate high diversity phage display libraries with a great deal of candidate peptides and protein ligands. The peptides and ligands isolated by ex vivo phage display can distinguish between the different organs and tissues, and can be used as homing devices for therapeutic and imaging agents. Furthermore, they can be therapeutics themselves and provide tools for studying the underlying biology of processes such as lymphocyte homing, cancer metastasis, and the tropism of pathogenic microorganisms.
Creative Biolabs is a long-term expert in the field of phage display technology. With our most devoted scientists, fast delivery and efficient service are guaranteed. Meanwhile, as the chosen cooperation research partner of our global clients, Creative Biolabs is pleased to provide our professional skills to help customers achieve their research purpose and assist their project development.
Other optional phage display library screening services:
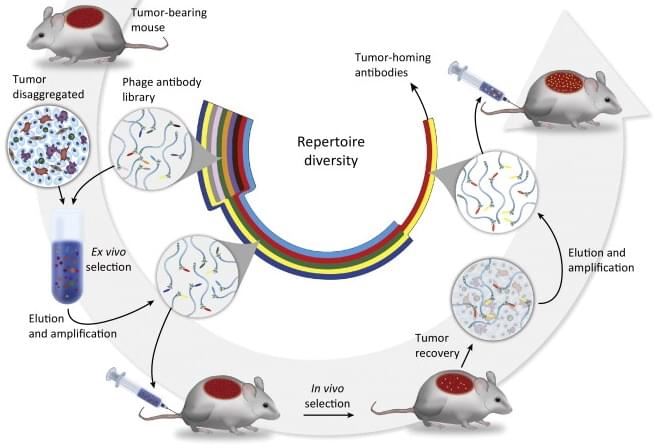 Fig.1 Various approaches in capturing high affinity peptide through phage display screening.1
Fig.1 Various approaches in capturing high affinity peptide through phage display screening.1
The research detailed in the article focuses on developing an oral vaccine strategy by targeting the mucosal transcytotic receptor GP-2, which is specifically expressed on M cells. Through ex vivo phage display library screening, the researchers identified a peptide ligand, Gb-1, with high affinity for GP-2. This peptide, when fused with an antigen (EGFP), significantly enhanced the antigen's uptake by M cells and stimulated a strong antigen-specific immune response in mice, including both mucosal IgA and systemic IgG responses. The importance of ex vivo phage display library screening in this study lies in its ability to identify ligands that can efficiently target antigens to M cells, promoting transcytosis and improving oral vaccine efficacy, particularly by inducing a Th2-type immune response.
Ex vivo phage display library screening is a technique used to identify peptide ligands or antibodies that bind specifically to target molecules, such as proteins, cells, or receptors, outside of a living organism. This process involves exposing a phage display library, which is a collection of bacteriophages displaying diverse peptides or antibody fragments on their surfaces, to the target. The phages that bind to the target are then isolated, amplified, and analyzed for further use in research or therapeutic applications.
Ex vivo phage display library screening is conducted outside a living organism, typically in a controlled laboratory environment, allowing for precise control over experimental conditions and target accessibility. In contrast, in vivo phage display involves screening within a living organism, which may better mimic physiological conditions but can be more complex and less controlled. Ex vivo screening is often used when the target is challenging to access in vivo or when higher specificity is required.
Ex vivo phage display library screening is widely used in identifying specific ligands or antibodies for drug discovery, vaccine development, and diagnostic purposes. It is particularly valuable in targeting cell surface receptors, enzymes, or other proteins involved in disease processes. Additionally, this technique can be employed to identify peptides that enhance drug delivery or target specific tissues or cells in therapeutic interventions.
Ex vivo phage display library screening has the ability to rapidly identify high-affinity binders for specific targets, such as receptors or enzymes involved in disease. It allows for the selection of ligands with high specificity, reducing off-target effects. Additionally, the screening process can be fine-tuned to identify ligands that function under specific conditions, such as those present in the human body, making it a powerful tool for developing targeted therapies.
A phage display library is constructed by inserting random peptide or antibody fragment sequences into the genome of bacteriophages, typically within a gene encoding a coat protein. This results in the display of a vast diversity of peptides or antibody fragments on the surface of the phages. The library is then used for screening against a target molecule in ex vivo conditions, allowing the identification of specific binders from millions or even billions of possible candidates.
The key steps in ex vivo phage display library screening include: (1) preparing the phage display library, (2) exposing the library to the target molecule, (3) isolating phages that bind to the target, (4) amplifying the bound phages, (5) performing multiple rounds of biopanning to enrich for high-affinity binders, and (6) analyzing the binding sequences of the selected phages. The identified peptides or antibodies can then be further characterized for their potential applications.
Ex vivo phage display library screening can be adapted to identify ligands for non-protein targets, such as carbohydrates, lipids, or small molecules. By modifying the screening conditions and the nature of the target presentation, researchers can use phage display libraries to discover peptides or antibody fragments that bind specifically to a wide range of molecules, broadening the potential applications of this technology.
The success of ex vivo phage display library screening is influenced by several factors, including the quality and diversity of the phage display library, the choice of target molecule, and the screening conditions. Ensuring that the target is presented in a way that mimics its natural state is crucial for selecting biologically relevant binders. Additionally, the number of screening rounds and the stringency of washing steps can impact the enrichment of high-affinity ligands. Proper optimization of these factors is key to achieving reliable and meaningful results.
Use the resources in our library to help you understand your options and make critical decisions for your study.
All listed services and products are For Research Use Only. Do Not use in any diagnostic or therapeutic applications.
| USA:
Europe: Germany: |
|
|
Call us at: USA: UK: Germany: |
|
|
Fax:
|
|
| Email: info@creative-biolabs.com |
