Ii-Key/HER-2/NEU Hybrid Cancer Vaccine Development Service
The treatment of cancer is a worldwide problem. Breast cancer is the most common tumor in women. Even if there are many treatments such as surgery, radiotherapy, and chemotherapy, the high recurrence rate of the disease makes the patient suffer a lot. Significant advances in basic research on cancer have made it possible to prevent the recurrence of such cancers. Creative Biolabs closely tracks the latest advances in world research and leverages its unique technological advantages to quickly turn it into an available product and service. We have industry-leading experience and technology in the development of cancer vaccines. Ii-Key/HER-2/neu hybrid is a promising cancer vaccine strategy. We have mature technology and perfect service in this aspect and will do our best to provide you with the best service in this regard.
Background
The discovery of tumor-associated antigens (TAAs) is the result of the development of cancer vaccines. Vaccines targeting TAAs are a cancer treatment regimen with high specificity and minimal toxicity, and the vaccines based on this are mainly peptide vaccines. The Her-2/neu protein belongs to the epidermal growth factor receptor family. The amplification and overexpression of this protein gene are found in many epithelial tumors, and Her-2/neu is also a marker of high recurrence rate in breast cancer. In addition to overexpression in breast cancer, overexpression of Her-2/neu is present in the ovary, lung, pancreas, prostate, biliary, and gastric cancer. Some of the peptides of Her-2/neu have the ability to stimulate cytotoxic T lymphocytes to recognize and kill cancer cells expressing Her-2/neu. E75 and GP2 are safe and effective in the treatment of patients with Her-2/neu+ breast cancers, and E75 can prevent the recurrence of breast cancer, but the immunity provided by this peptide vaccine is not long-lasting, for which a strategy for hybridizing Her-2/neu to the helper peptide is created to increase the persistence of the efficacy of the vaccine.
MHC Class II associated Ii protein could block the processing of endogenous peptides by cells and prevents their binding to MHC molecules leading to the failure of presentation of antigens. Inhibition of Ii protein in rat tumor and tumor cell lines can increase the efficiency of tumor antigen presentation, and antigen-specific tumor cell killing ability is also improved. The li-Key peptide of li protein is the most important sequence for the function of this protein, and its binding to the allosteric site that located outside the epitope-binding groove ensures the maintenance of the conformation of the epitope-binding groove, which is very important for MHC class II molecules exchanging epitopes. Studies have shown that li-Key can increase the efficiency of hen egg white lysozyme-specific T cell hybridoma stimulated by HEL peptide by 50-fold.
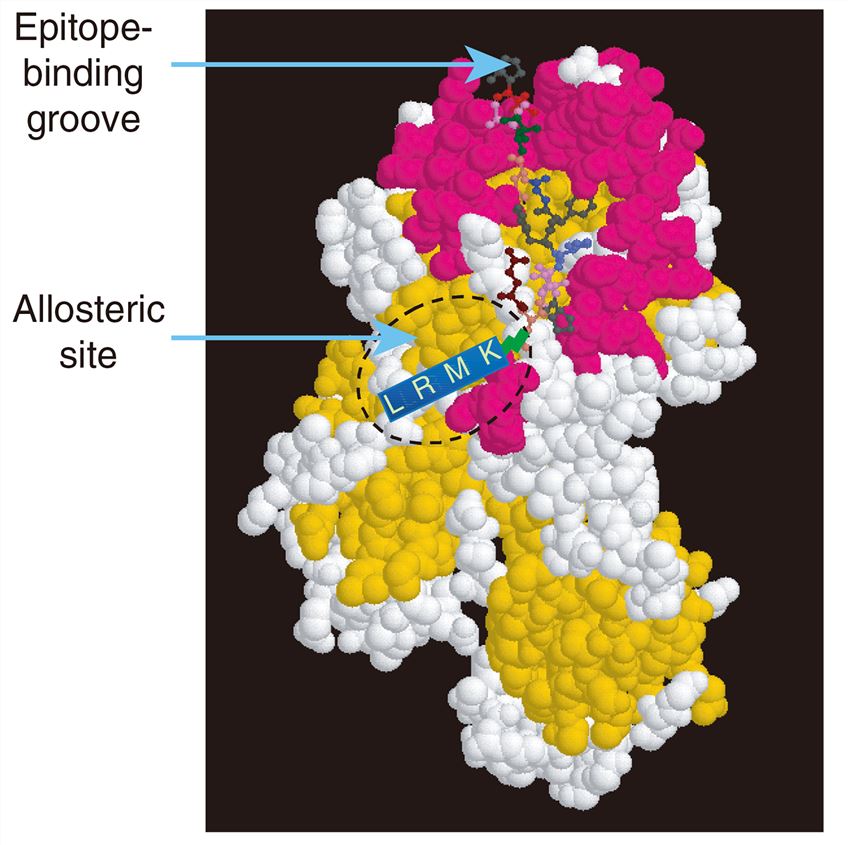
Fig.1 Diagram of the relationship of the epitope binding groove and allosteric site on MHC class II molecules. (Kallinteris NL and Lu X, 2006)
Ii-Key/HER-2/neu Hybrid Cancer Vaccine
Tumor-associated antigens may cause tolerance problems because of low levels of expression in normal cells, and the discovery of the function of li-Key may increase the activation of Th1 CD4+ cells and reduce tumor antigen tolerance. Some in vivo and in vitro experiments have shown that li-Key can significantly increase the activity of CD4+ T cells after hybridization with some epitope peptides. In most cases, peptide vaccines do not provide sufficient therapeutic effects, and li-Key can promote the binding of epitopes to MHC class II molecules because epitope peptides are difficult to replace the pre-bound peptide on the MHC class II without the presence of li-Key. Therefore, hybridization of the li-Key and MHC class II epitope peptide can significantly increase the effectiveness of the epitope peptide. Peptide vaccines originally targeted MHC class I epitopes to stimulate CTL activity, but recent studies have shown that activation of CD4+ Th cells stimulated by MHC class II epitopes is also important for the effectiveness of immune responses. Antigen-specific Th cells are required for CD8+ CTL activation and are capable of inducing and maintaining CD8+ T cell and B cell responses and maintaining immune memory.
Hybrid AE37, which is produced by linking the active fragment tetrapeptide LRMK of li-Key to the N-terminus of the HER2/neu (AE36) peptide, induces stronger Th cells in PBMCs of HER2/neu-positive tumor patients than treated with AE36 alone and the resulting stronger epitope-specific CTL responses. Clinical trials of AE37 in HER2/neu-positive breast cancer patients have shown good safety and tolerability. Therefore, the use of li-Key technology to hybridize with the tumor antigen HER2/neu to prepare cancer vaccine is a promising way to prevent tumor recurrence.
Creative Biolabs has a passion for human health and has been focusing on vaccine research for decades. We have provided countless quality products and services to vaccine researchers around the world, which has enabled the company to continue to improve itself while earning a high reputation in the industry. Please do not hesitate to contact us if you are interested in our vaccine development service.
Reference
- Kallinteris NL, Lu X. (2006). “Ii-Key/MHC class II epitope hybrids: a strategy that enhances MHC class II epitope loading to create more potent peptide vaccines”. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 6(12):1311-21
All of our products can only be used for research purposes. These vaccine ingredients CANNOT be used directly on humans or animals.


