Neurodegenerative Disease related Vaccine Design Services
Common neurodegenerative diseases (Parkinson's disease, Alzheimer's dementia, and ALS) are among the leading causes of death in the world. Numerous research institutions are trying to use vaccine technology to eliminate these diseases. Creative Biolabs has provided services in vaccine development against neurodegenerative diseases for many clients with individual requirements. We can assist your researches in development of neurodegenerative disease vaccine at each stage.
Neurodegenerative Disease
Neurodegeneration is a process of gradual loss of neuronal structure or function, including neuronal death. Neurodegenerative diseases include pathological processes in which conformational changes occur in specific proteins without altering their biochemical composition (misfolded proteins) and are transmitted to normal cell proteins by similar mechanism, thereby spreading the disease’s pathological alterations.

The neurodegenerative diseases that Creative Biolabs focuses on are:
- Parkinson's Disease (PD)
- Alzheimer's Disease (AD)
- Huntington's Disease (HD)
- Lewy Body Disease (LBD)
- Multiple System Atrophy (MSA)
- Prion Disease
- Primary Progressive Aphasia (PPA)
These diseases are incurable, leading to progressive degeneration and death of neuron cells. Alzheimer's disease (AD) affects about 20 million people worldwide and 6 million for Parkinson's disease (PD). Neither of these diseases has been effectively treated, posing a significant financial and social burden for health care. As research progresses, many similarities have been found between different neurodegenerative diseases on a sub-cellular level, including atypical protein assemblies and induced cell death, which can occur in various levels of neuronal circuitry ranging from molecular to systemic. The discovery of these similarities offers hope for therapeutic advances and can improve many diseases simultaneously.
Vaccinal Strategies Against Neurodegenerative Diseases
Most of the vaccine research and development in this area have focused on the two most common neurodegenerative diseases, Alzheimer's disease (AD) and Parkinson's disease (PD), which are characterized by progressive dementia and motor system disorders, respectively.
Alzheimer's Disease (AD)
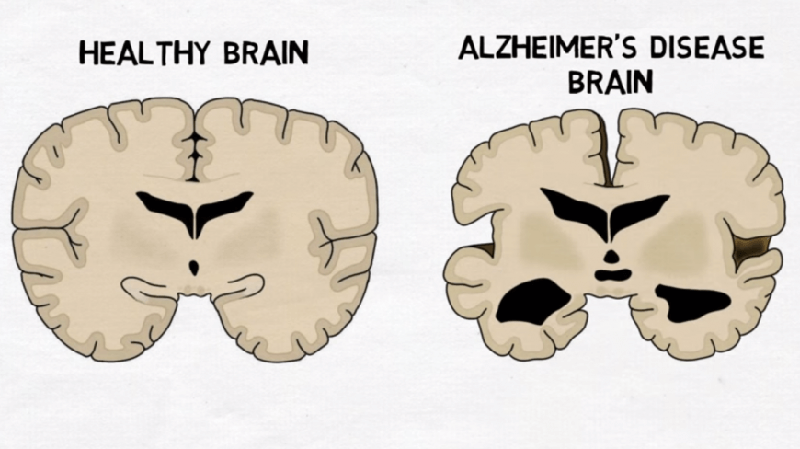
Since Solomon presented that the outcomes of the action of specific monoclonal antibodies could dissolve the aggregates of pathological -amyloidpeptide (A) in vitro, which is the cause of the alterations observed in AD, as well as impede the formation of new aggregates, the possibility of using antibodies that recognize and neutralize abnormal proteins specifically for certain neurodegenerative diseases has been considered. These studies were performed in transgenic (Tg) mice which expressing human Abeta. Promising results were obtained in these experiments, including reducing brain Abeta levels and improving cognitive deficits in mice. However, the results in human trials seemed to be positive initially, but the first-generation vaccine caused significant adverse effect, forcing the trial to be suspended in phase II. It is hypothesized that the vaccine adjuvant used in this clinical trial and the related activation of Abeta T cell epitopes may be the major mediators of most serious side effect. Therefore, the safety and efficacy of Abeta peptides lacking T-cell epitopes as vaccines are currently being evaluated. Moreover, in addition to Abeta, tau protein, a component of neurofibrillary tangles, is also considered to be involved in the pathogenesis of AD and being studied as a potential vaccine target. [1]
Parkinson's Disease
Vaccines against PD-associated protein antigens are more limited than AD. In theory, the major protein involved in the pathological loss of dopaminergic neurons in PD is alpha-synuclein (α-syn). Targeted passive immunotherapy strategies and α-syn peptides or recombinant protein vaccines against PD have been evaluated. Tg mice expressing the α-syn gene or rat models expressing the α-syn gene delivered by the adeno-associated virus 9 (AAV-9) vector have been demonstrated to improve some of the pathological and cognitive deficit characteristics of these models. These findings suggest that immune-based interventions may have a protective effect against PD and AD.
Degenerative neurological diseases can be serious or even life-threatening. Treatments may help to improve symptoms, relieve pain, but most of them do not have cure. Recently several neurodegenerative diseases have been targeted as well by immune-based prophylactic and immunotherapeutic strategies. Many studies confirm the feasibility of this strategy for several neurodegenerative diseases, which offer the exciting prospect that the immune system or derivative components can be used against misfolded or aggregated proteins that accumulate in many neurodegenerative diseases. It is hoped that effective immunotherapy for neurodegenerative diseases will be available in the near future.
With years of experience, Creative Biolabs has provided custom services in vaccine development against neurodegenerative diseases for many clients with individual requirements. We have been dedicating ourselves to helping every customer to facilitate their projects in a highly productive and cost-effective way. You can count on us through your entire project!
Reference
- Kudrna JJ; et al. Gene-based vaccines and immunotherapeutic strategies against neurodegenerative diseases: Potential utility and limitations. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2015,11(8): 1921-6.
All of our products can only be used for research purposes. These vaccine ingredients CANNOT be used directly on humans or animals.


