Nanoparticle based Delivery System Development Services
Liposomes are now critical components of two of six types of adjuvants present in licensed vaccines and are well-known as vaccine carriers. Liposomes and liposome-derived nanovesicles, such as archaeasomes and virosomes, have become important delivery systems in vaccine development. The field of liposomal vaccine adjuvants has long been dynamic and innovative, and as new commercial products appear in parallel with new vaccines, there is a growing interest in this area of research. Creative Biolabs gives a high priority to develop vaccines both in terms of its importance for public health and as a service to the biopharmaceutical industry. Our scientists are experts in the field of delivery system development. We are committed to offering our clients a series of liposomes development for vaccine delivery with the best quality and most competitive price.
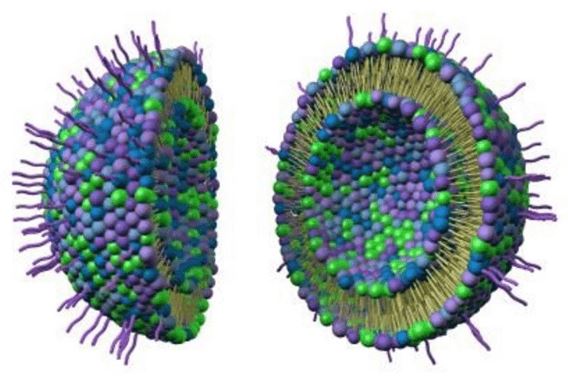
A key advantage of liposomes and liposome-derived nanovesicles is their versatility and plasticity. Liposomal compositions and formulations can be selected to achieve the desired characteristics, such as the lipid, size, size distribution, charge, entrapment, and location of antigens or adjuvants. Water soluble antigens such as nucleic acids, peptides, proteins, haptens, and carbohydrates are encapsulated within the aqueous interior of the liposomes while lipophilic compounds such as antigens, lipopeptides, adjuvants and linker molecules are inserted into the lipid bilayers, and antigens or adjuvants can be attached to the surface of the liposome by adsorption or by a stable chemical linkage. Coformulations containing different types of antigens or adjuvants can be combined with the parameters mentioned to tailor the individual application of the liposomal vaccine. Combinations containing different types of antigens or adjuvants can be combined with the mentioned parameters to tailor the individual application of the liposomal vaccine.
What Are Liposomes
A liposome is a spherical vesicle with lipid bilayer that encapsulates an aqueous volume. Liposomes are formed from biodegradable and non-toxic phospholipids. Liposomes can encapsulate antigens within the core for delivery and incorporate viral envelope glycoproteins to form virosomes. Liposomes that contain phospholipids as bulk lipids do have some adjuvant activity themselves because the antigenic microparticulate carriers generally have some immunostimulatory properties, which is because certain types of antigen-presenting cells have depot action and enhanced uptake. A thorough understanding of formulation parameters allows the design of effective liposomal vaccine delivery system.
The Role of Liposomes as Vaccine Adjuvants
Because the individual constituents of vaccine formulations sometimes may have inherent potential toxicities, and because they are often injected into apparently healthy individuals to prevent disease, safety considerations have paramount importance. The availability of recombinant proteins, synthetic peptides, or conjugated carbohydrates as antigens, and of purified immunostimulators or adjuvants for induction of innate immunity, offers the possibility of vaccine formulations that have a high degree of safety. However, in trying to emulate the composition and appearance of danger posed by foreign pathogens, simplified synthetic adjuvant formulations face the daunting challenge of having to stimulate complex natural defense mechanisms. Liposomes can create physical structures, or stimulate innate mechanisms, to overcome these problems and to promote a successful vaccine outcome. Due to their versatile nature, liposomes can be formulated in a range of sizes, charge and surface characteristics allowing them to not only deliver the antigen(s) to appropriate antigen-presenting cells in a controlled manner, but also for the liposomes to interact with and stimulate these cells to enhance immune responses.
Linads™ Lipid-based Nucleic Acid Delivery System
To provide effective delivery methods for DNA or RNA vaccines, Creative Biolabs has launched a lipid-based nucleic acid delivery system, Linads™, which has been validated by a large number of experimental cases. The Linads™ particles containing the nucleic acid vaccine rapidly enter the cell by endocytosis by interacting with the cell membrane of the target cell and are then encapsulated in endosomes. Over time, the acidity of the endosome continues to increase. Eventually, pH-mediated disruption causes Linads™ to rapidly degrade and release the nucleic acid payload. The nucleic acid molecules released in the cytoplasm interact with the transcriptional machinery and then initiate the synthesis of functional proteins.
For years, Creative Biolabs has consistently and effectively supported the vaccine development industry with a unique range of products and related services. Contact us, and you will get the best liposomes development services for your vaccine delivery with the most competitive price and the best quality.
All of our products can only be used for research purposes. These vaccine ingredients CANNOT be used directly on humans or animals.


