Plant Expression System Evaluation Service for Vaccine Production
With expertise in vaccine development, Creative Biolabs is proficient in optimizing the expression system and is able to provide all kinds of services related. We are confident to help you step stably through your research.
Plant Expression System
Subunit vaccines consisting of antigenic epitopes or pathogen proteins are generally superior to traditional vaccines made by killing or attenuating. Mammalian, yeast, and insect cells are commonly used to produce such subunit vaccines because the recombinant proteins produced by these expression systems are similar in structure and activity to native proteins. However, the production of vaccines using these expression systems is not only costly but also cumbersome to the purification step. More importantly, the subunit vaccines produced are heat sensitive and require administration outside the gastrointestinal tract. These deficiencies limit the use of subunit vaccines in economically underdeveloped areas. The plant expression system has received great attention in recent years for its characteristics of low cost and compatibility with inexpensive, simple, well-defined industrial culture media, safety, and oral delivery. In addition, sexual reproduction between different transgenic plants allows multiple foreign genes to accumulate in a single plant, which is conducive to the production of multi-component vaccines. The cell surface-adhesion protein (spa A) from Streptococcu were the first vaccine candidate expressed by transgenic plants. It is worth noting that spa A contains more than 1500 amino acids with a molecular weight of up to 185 kDa, indicating that transgenic plants can accommodate large foreign genes and express them.
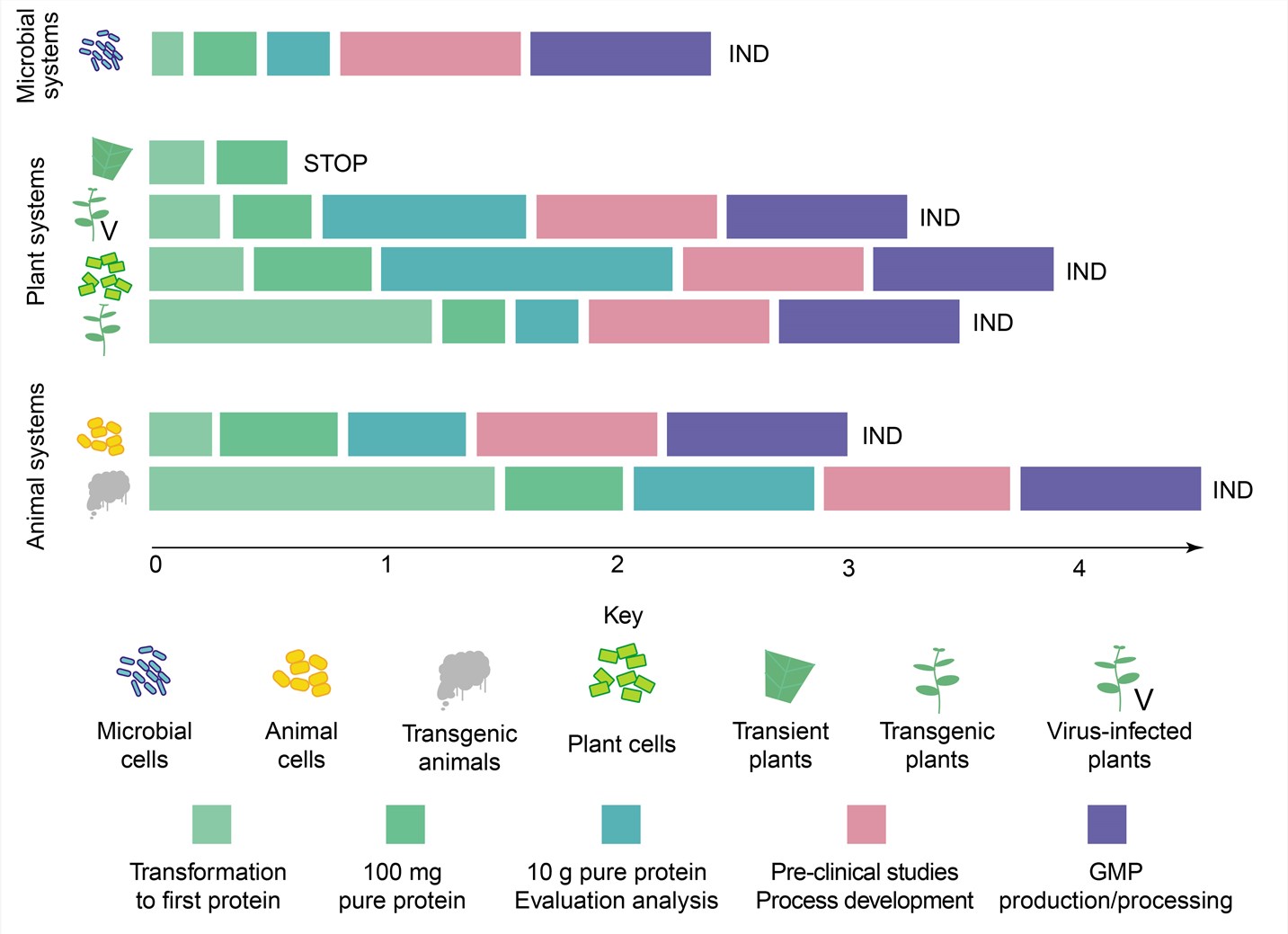
Fig.1 Comparison of different expression systems. (Twyman RM and Stoger E, 2003)
Stable or Transient Transformation Systems
Briefly, the plant expression system prepares a vaccine mainly by transferring a vector carrying an antigen gene into a plant cell and expressing the corresponding gene of interest in the plant in manners of stable transformation or transient transformation. The primary methods to achieve stable transformation are nuclear and plastid integration, in which the target transgene is inserted into the nuclear genome of host plant cells. The modified Agrobacterium and biolistic are able to realize permanent transformation. Nuclear transgene method is simple and is the main strategy for several years. Its advantages are that it is easy to expand the production of vaccine antigens through the transgenic seed bank and possible to express vaccines in fruits and other edible plant organs, thus oral administration of such vaccines avoiding the cumbersomeness of subsequent processing of traditional vaccines. However, products of stable nuclear integrated transgene expression are generally produced at lower yields.
Transient transformation system introduces the desired gene into the host cell and produce the antigen of interest transiently without integrating heterologous gene into the genome of the recipient plant cells. No need to regenerate the whole plant makes the production of antigen by transient expression much more efficient. Compared to the stable transformation, transient expression system is time-efficient and can produce target protein at a high yield, as well as uniformity and consistency of product accumulation, scalability, and environment friendly. In addition, The Chloroplast Genetic Engineering System is the most promising method in transient transformation. Commonly used methods to express recombinant subunit vaccines in transient transformation system are genetically modified plant virus and particle bombardment.
In general, there are three widely used plant expression systems, including plant cell culture, culture of organized plant tissue and the whole plants.
Strategies to Improve Expression Level
- Robust promotor
- Elimination of instable sequence in mRNA
- Codon optimization
- Protein targeting
- Chloroplast expression
- Integration of nuclear genome with chloroplast sequence
Plant Cell Culture
Undifferentiated plant cells can be cultured in liquids, and the cultivation of plant cells is hardly influenced by seasonal changes, resulting in continuous supply of products. Chlamydomonas is one of the mostly used species in plant cell culture which has the advantages of being able to realize nucleus, chloroplast, and mitochondrial transformation, rapid gene expression, scale-up production, a number of promoters available and the ability to produce secreted glycosylated proteins. Tobacco lines are usually nucleus transformed by Agrobacterium to express vaccines through cell culture. The traits of the transgenic lines are ease to amplify the scale, high and constant expression level and closed culture conditions to meet requirements of good laboratory and manufacturing practices.
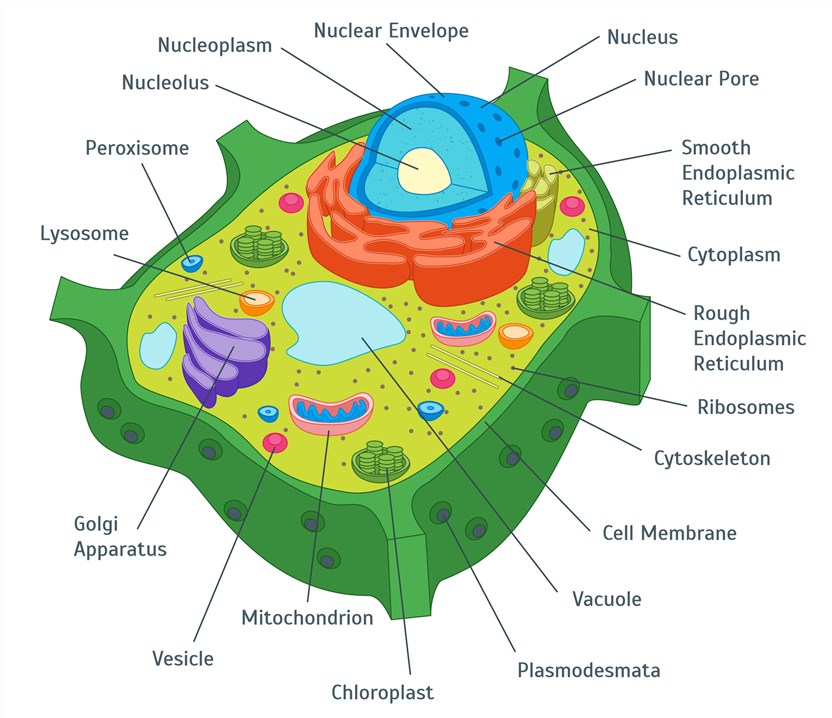
Fig.2 Plant cell.
Culture of Organized Plant Tissue
Common plant tissues used to express antigens are shoot culture and hairy root culture. Hairy roots grow fast, do not require additional auxin and light supply, and the genetically engineered tissue are able to express secreted protein of interest. A comparison made by Sharp and Doran (2001) among N. tobaccum cell culture, shoot culture and hairy root culture shows that hairy root grows slower than that of shoot culture and cell culture, but produces more products than shoot culture.
Whole Plants
Vaccines are expressed by plant either from transient or stable transformation. Whole plant expression requires for sunlight, water, nutrients, and other inexpensive inputs. The key step in expressing vaccines using whole plants is to select an appropriate line before production.
Our Services of Plant Expression System
- Design and construction of expressing vector
- Optimization of medium formulation
- Glycoengineering for the product
- Enhancement for the antigen immunogenicity
Our Platforms
- Multiple plant species for vaccine expressing
- Numerous and mature viral expression vectors
- Well-established transient or stable transformation systems
- Different production systems for particular demands
Creative Biolabs has an expertise in vaccine development for years and has served hundreds of clients solving all kinds of problems they met. With a variety of mature and comprehensive platforms and technologies in vaccine expression systems, especially in plant expression system, we can meet the various requirements of our customers at highly affordable price.
Reference
- Twyman RM. (2003). “Molecular farming in plants: host systems and expression technology” Trends Biotechnol. 21(12): 570-8.
All of our products can only be used for research purposes. These vaccine ingredients CANNOT be used directly on humans or animals.


