Subunit Vaccine Design Services
Creative Biolabs has long-term devoted to the development of vaccine technology. We offer multiple vaccine design services such as subunit vaccine design. Instead of the entire microbe, a subunit vaccine presents antigens that best stimulate the immune response to the immune system. One method of production involves isolating the specific protein from the virus and administering on its own. Subunit vaccines contain only the necessary antigens, not all other molecules that make up the microbes, so the likelihood of adverse reactions to the vaccine is very low.
Advantages:
- Applicable to people with weakened immune systems
- Long-lived immunity
- Relatively safe since only parts of the virus are used for these vaccines
Disadvantages:
- Low immunogenicity, needed to be used with good adjuvant
- Multiple doses needed for long-term immunity
It is a tricky and time-consuming process to determine the best antigen to stimulate the immune system. However, once scientists are able to solve the puzzle, they can prepare subunit vaccines in the following two ways:
- Scientists cultivate microbes in the laboratory, then break them apart with chemicals and collect important antigens.
- Scientists use recombinant DNA technology to make antigen molecules from microbes. Vaccines produced in this method are called "recombinant subunit vaccines".
Recombinant Subunit Vaccine
Recombinant subunit vaccines use attenuated virus or bacterium to introduce microbial DNA to cells of the body. “Vector” refers to the virus or bacterium used as the carrier. The protein components that induce immune response are synthesis peptides or antigens expressed in eukaryotic or prokaryotic expression system (e.g., E. coli, yeast) using recombinant protein expression technologies. Most of the vaccines currently being developed are based on this purified recombinant protein or antigen subunit. Five recombinant subunit vaccines are currently available in the United States including Hepatitis B (HBV), human papillomavirus (HPV), and influenza (one brand) vaccines.
A recombinant subunit vaccine has been made for the hepatitis B virus. It is a non-infectious subunit viral vaccine derived from Hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) produced in yeast system. Scientists inserted a portion of the hepatitis B virus gene that code for HBsAg into common baker’s yeast. The antigen for hepatitis B is produced from cultures of this recombinant yeast strain, which is collected and purified for use of the Hepatitis B vaccine.
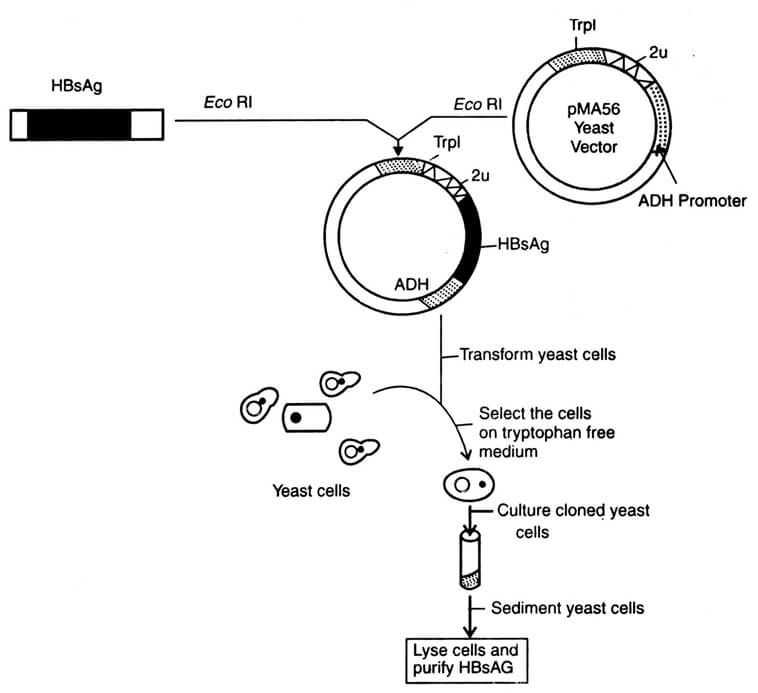
Fig. 2 Expression of HBsAg gene in yeast
Expression systems for vaccine production include prokaryotic expression system such as E. coli, and eukaryotic system such as yeast, mammalian or insect cells. These factors should be considered before choosing the right vaccine antigen expression system: expression levels, selection markers and the presence of post-translational modifications. Due to the high level of expression and ease of handling, bacterial expression system is the most widely used system. For the antigens which need post-translational modification, yeast, mammalian or insect cells system should be considered.
With years of experience, Creative Biolabs are capable to provide services for vaccine design according to customers' need. Our experts are pleased to help you with our advanced platforms and extensive experiences.
All of our products can only be used for research purposes. These vaccine ingredients CANNOT be used directly on humans or animals.


