Corn-derived Exosome Research and Application
Corn-derived exosomes have demonstrated excellent medical activity and clinical translational potential. Additionally, the low cost of acquisition and suitability for large-scale production make corn-derived exosomes easier to study. Creative Biolabs can provide customized research solutions for corn-derived exosome production and research.
Isolation of Corn-derived Exosomes
-
Washing fresh sweet corn with distilled water
-
Make corn homogenate with distilled water in a breaker.
-
Filter corn juice and then centrifuge at differential speeds to exclude coarse corn particles
-
Ultracentrifugation of corn supernatant in sucrose solution to obtain corn exosomes.
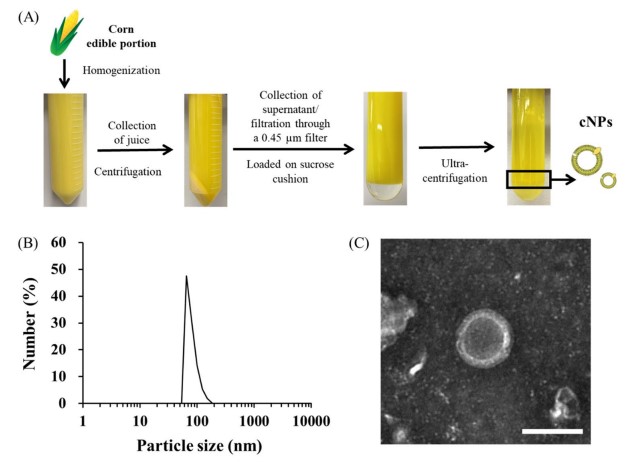 Fig. 1 Isolation and characterization of corn-derived exosomes.1
Fig. 1 Isolation and characterization of corn-derived exosomes.1
Research on Corn-derived Exosomes
|
Research
|
Conclusion
|
|
Characterization of corn-derived exosomes.
|
Corn-derived exosomes were about 80 nm in size, negatively charged and showed cup-shaped structural features, and these characterizations were reproducible. LC-MS/MS analyses revealed that corn-derived exosomes contain phosphatidylcholine, phosphatidylglycerol, and sphingomyelin, phospholipid fractions that are typical of plant exosomes.
|
|
Cellular uptake of corn-derived exosomes.
|
Tracer experiments with fluorescent fuel-labeled corn exosomes revealed that mice colon adenocarcinoma cells, fibroblasts, and macrophages were able to uptake corn exosomes. In addition, comparisons by treatment with endocytosis inhibitors indicated that the uptake of corn-derived exosomes by colon adenocarcinoma cells involved the cholesterol-dependent pathway.
|
|
Effect of corn-derived exosomes on cancer cells.
|
Corn-derived exosomes inhibited cell proliferation in mice colon cancer cells, human breast cancer cell lines, and human pancreatic cancer cell lines. Corn exosome-treated mice colon cancer cells were induced to undergo cell cycle arrest in the G2 phase and were inhibited from proliferation in a time-dependent manner.
|
|
Corn-derived exosomes acted against tumors by activating immunity.
|
ELISA assay revealed that corn-derived exosomes were able to significantly stimulate macrophages to release the pro-inflammatory factor TNF-α, which resulted in colon cancer cell death, suggesting that corn-derived exosomes are capable of anti-tumor activity through the activation of immune cells. In vivo experiments in animals confirmed the suppression of colon cancer tumor size in corn-derived exosomes-treated homozygous mice.
|
|
PEG modification on corn-derived exosomes adjusted their tissue distribution.
|
PEG modification of corn-derived exosomes by sonication significantly enhanced the retention effect of corn exosomes in the circulation. After intravenous administration, the PEG-modified corn exosomes were more effectively enriched in the target tissues to further enhance their anticancer activity.
|
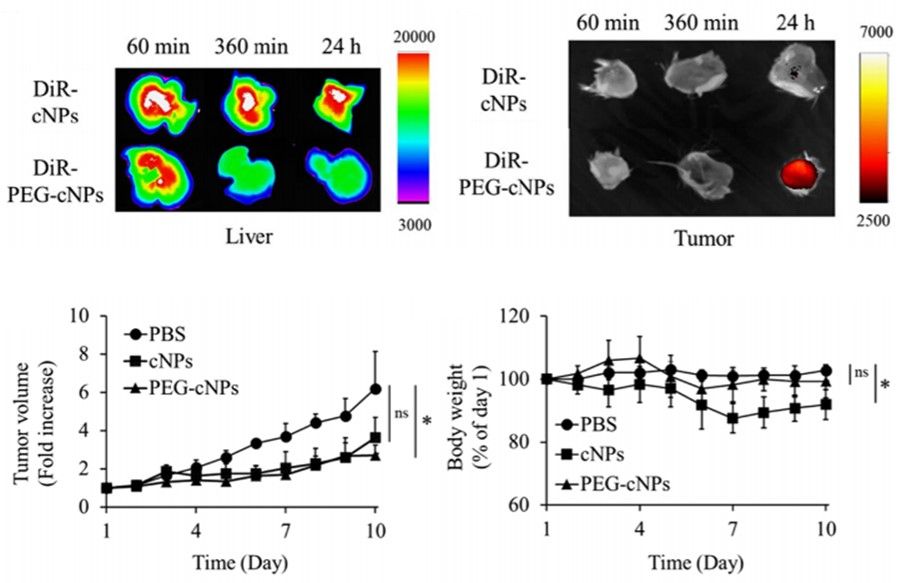 Fig. 2 Tissue distribution and delivered antitumor activity of corn-derived exosomes.2
Fig. 2 Tissue distribution and delivered antitumor activity of corn-derived exosomes.2
Corn-derived exosomes can exert anti-tumor activity by inducing macrophages to release TNF-α, and can be surface modified to enhance their anti-tumor activity after enrichment into target tissues. Meanwhile, the raw material of corn, as the most widely available cereal grain, is easily accessible and less cost-effective than other materials. Creative Biolabs has been focusing on providing reliable exosome research services for many years, and can support clients' corn-derived exosome-related production and research. Please contact us to advance your corn-derived exosome-related projects.
References
-
Sasaki, Daisuke, et al. "Development of nanoparticles derived from corn as mass producible bionanoparticles with anticancer activity." Scientific reports 11.1 (2021): 22818.
-
Sasaki, Daisuke, Kosuke Kusamori, and Makiya Nishikawa. "Delivery of Corn-Derived Nanoparticles with Anticancer Activity to Tumor Tissues by Modification with Polyethylene Glycol for Cancer Therapy." Pharmaceutical Research 40.4 (2023): 917-926.
For Research Use Only. Cannot be used by patients.
Related Services:

 Fig. 1 Isolation and characterization of corn-derived exosomes.1
Fig. 1 Isolation and characterization of corn-derived exosomes.1
 Fig. 2 Tissue distribution and delivered antitumor activity of corn-derived exosomes.2
Fig. 2 Tissue distribution and delivered antitumor activity of corn-derived exosomes.2









