Extracellular Vesicle related Research Services
Overview Services Features FAQs
Sensitive preparation and analysis techniques for EVs facilitate the resolution of barriers to their application potential and translation. Creative Biolabs is actively developing new access to research platforms for providing comprehensive EV production and profiling services.
EVs Classification and Functions
EVs have different subgroups depending on their diameter and mode of occurrence, ranging from 30, 40 nm to 8, 9 μm in diameter, mainly including:
-
Exosomes: Exosomes are the most intensively studied subtype of EVs. They are formed by the inward concavity of endosomes and released by the fusion of multivesicular bodies into cell membranes, with a diameter of 50-100 nm. Exosomes not only deliver mRNA and miRNA, oncogenetic receptors, and viral particles horizontally, but also have antigen presentation, immune activation, and immunosuppressive activities.
-
Migrasomes: In the process of directional cell migration, the cell tails produce contractile filaments. At the end of the contractile filaments or the crossover site, monolayer membrane vesicle structures of 0.5~3.0 μm in diameter called microsomes are produced. When the cells migrate away, the migratory bodies remain in place until they rupture or are engulfed by later cells, releasing the contents of the donor cells.
-
Microvesicles: Microvesicles are produced by platelets, red blood cells, or epithelial cells and exert a procoagulant effect. Cell membranes with a diameter of 100–1000 nm budding outward produce microvesicles. The generation of microvesicles can be induced by the activation of cell surface receptors, apoptosis, or increased intracellular calcium ion concentration.
-
Apoptotic body: Apoptotic vesicles are 1-5 μm in diameter and are generated by blistering during apoptosis. Apoptotic vesicles can deliver DNA and oncogenes horizontally and present T-cell antigenic determinants when taken up by phagocytes, which act as immunosuppressive agents.
-
Ectosome: Activated neutrophils undergo morphological changes, extend pseudopodia, and break off to form small vesicles. Moreover, the activated neutrophils form small vesicular projections of 70-300 nm on the surface, which are finally released into the extracellular space as vesicular structures, both of which are defined as ectosomes.
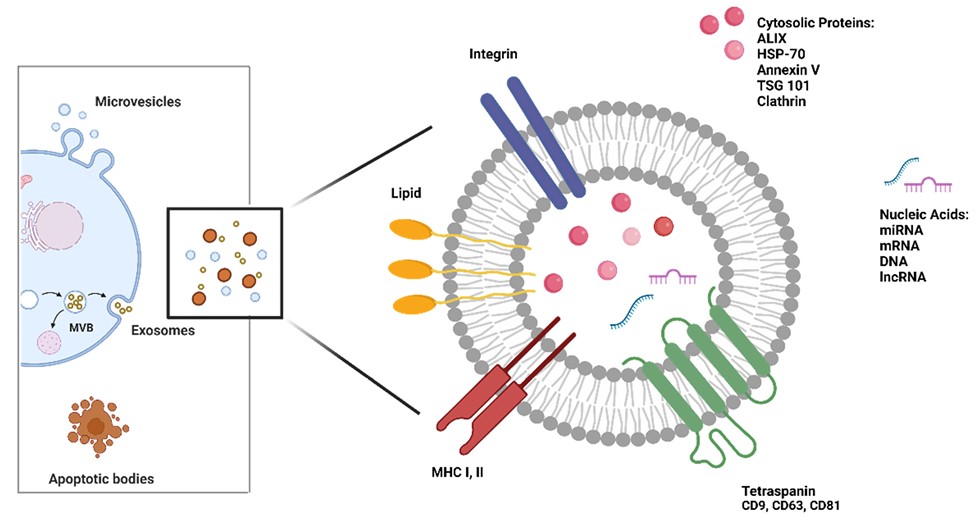 Fig. 1 Biogenesis and structure of EVs.1
Fig. 1 Biogenesis and structure of EVs.1
Comprehensive EVs Services at Creative Biolabs
The development and improvement of EV technology platforms will have a profound impact on basic and translational research of EVs. One-stop EV development, preparation, and profiling services are provided by Creative Biolabs, and they include, but are not limited to:
Features
-
Isolation Techniques: Utilize validated methods for isolating EVs from various samples.
-
EV Characterization: Comprehensive analysis to determine EV size distribution, morphology, and cargo composition.
-
Functional Studies: Assess EV functionality in vitro and in vivo, including cellular uptake assays and bioactivity assays.
-
Customizable Solutions: Tailor services to meet specific research needs, from sample collection to data interpretation.
-
Quality Assurance: Rigorous quality control procedures ensure reproducibility and reliability of EV-related data.
-
Bioinformatics Support: Analysis of omics data related to EVs, facilitating insights into biomarker discovery and disease mechanisms.
-
Collaborative Partnerships: Foster collaborations with academic, preclinical, and industrial partners to advance EV research and applications.
EVs are thought to be a means for secretory cells to dispose of harmful or unwanted intracellular components, and also mediate communication with other cells. Creative Biolabs offers services related to EV isolation and profiling with its comprehensive EV platform. Please contact us to create a custom quote.
FAQs
Q: What are the advantages of studying EVs for biomarker discovery?
A: EVs contain biomolecules reflective of their cell of origin, making them promising candidates for non-invasive biomarker discovery in various diseases.
Q: Can you perform functional assays to assess EV bioactivity?
A: Yes, we conduct functional studies including cell uptake assays and assays to evaluate the biological activity of EV cargo.
Q: What steps do you take to guarantee the accuracy of data of EVs?
A: We adhere to strict quality control standards throughout the EV isolation, characterization, and analysis processes to ensure reliable and reproducible results.
Reference
-
Mastrolia, Ilenia, et al. "Chasing the Role of miRNAs in RCC: From Free-Circulating to Extracellular-Vesicle-Derived Biomarkers." Biology 12.6 (2023): 877. Under Open Access license CC BY 4.0. The image was modified by revising the title.
For Research Use Only. Cannot be used by patients.
Related Services:

 Fig. 1 Biogenesis and structure of EVs.1
Fig. 1 Biogenesis and structure of EVs.1









