Liposome for Agricultural
Priorities for developing agriculture include lowering agricultural production costs, boosting food output, optimizing pesticide use, and minimizing environmental pollution. Advances in nanotechnology provide novel solutions to crop management, plant protection, and sustainable agricultural issues. Nanomaterials are employed to generate novel agrochemicals such as nanofertilizers and nanopesticides. Creative Biolabs, your partner in agricultural innovation. We can take your agricultural projects to new heights with our experience in liposomes and other nanoparticles.
Advantages of Liposomes in Agriculture
-
Environmentally friendly: Liposomes are biodegradable and do not cause long-term environment pollution.
-
Sustained release: Reduces pesticide runoff and usage, prolongs shelf life, and lowers agricultural production costs.
-
Responsive release: Allows for precise pesticide release by adjusting factors such as light, temperature, and pH, suitable for various scenarios.
-
Prevention of premature degradation: Protects active agricultural ingredients from premature degradation by environmental factors (light, oxygen, heat).
-
Improved dispersibility and adsorption: Smaller size and larger surface area enhance the coverage of active agricultural ingredients on plant leaves or surfaces of harmful organisms.
-
Enhanced foliar feeding efficiency: By penetrating leaf barriers, it enables the effective delivery of active agricultural ingredients to the whole plant.
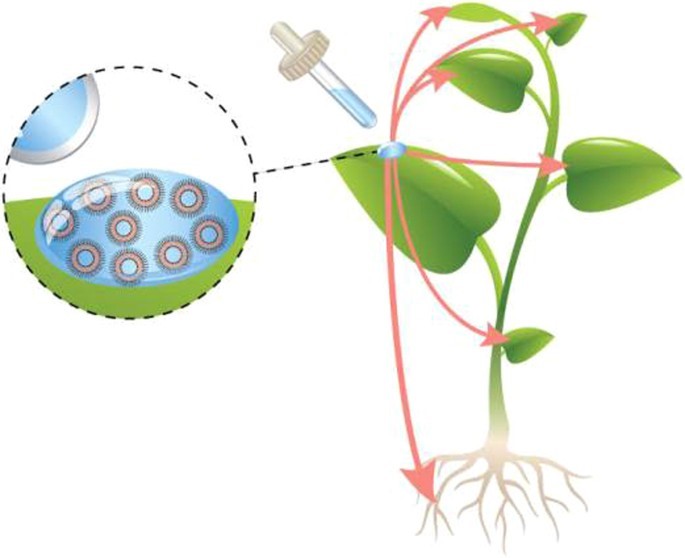 Fig.1 Liposomes penetrate the leaf barrier to deliver active agricultural ingredients to the whole plant.1
Fig.1 Liposomes penetrate the leaf barrier to deliver active agricultural ingredients to the whole plant.1
Application of Liposome in Agriculture
Liposome model membranes have been used to investigate the transport of active agricultural ingredients on cell membranes, as well as the functioning of proteins in terms of permeability, pH stability, and tolerance, to better understand their mechanisms of action.
RNAi technology is an effective method for pest and disease control in crops. It can be used on plants, nematodes, bacteria, fungi, viruses, and insects in agriculture. Liposomes can be utilized to deliver dsRNA while protecting it from degradation by environmental factors like enzymes and pH. Liposomes improve dsRNA stability and cellular uptake.
Antimicrobial peptides (AMPs) contain antiviral, antimicrobial and insecticidal capabilities that can be employed to resist diseases and pest attacks, ultimately improving agricultural productivity. To address obstacles in the agricultural application of AMPs, Creative Biolabs provides customized services for AMP liposomes and other nanoparticles. This involves improving the stability, bioactivity, targeting, release, and potential toxicity of AMPs in the environment.
Why Choose Us?
-
Efficient pesticide delivery
-
Customized variety of nanoparticles
-
Cost-effective solutions
-
Promoting green agricultural development
At Creative Biolabs, we are committed to addressing environmental challenges by providing sustainable solutions that minimize pollution and promote eco-friendly practices in agriculture. Specializing in customizing liposomes for agricultural purposes, we aim to meet a wide range of customer requirements, including efficient delivery of agricultural ingredients, mimicking organelle membranes, and more. We are excited to discuss how we can help you with your agricultural projects. Please contact us as soon as possible to schedule a consultation.
References
-
Karny, Avishai, et al. "Therapeutic nanoparticles penetrate leaves and deliver nutrients to agricultural crops." Scientific Reports 8.1 (2018): 1-10.
-
under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.

For Research Use Only. Not For Clinical Use

 Fig.1 Liposomes penetrate the leaf barrier to deliver active agricultural ingredients to the whole plant.1
Fig.1 Liposomes penetrate the leaf barrier to deliver active agricultural ingredients to the whole plant.1
 For Research Use Only. Not For Clinical Use
For Research Use Only. Not For Clinical Use