Drug-loaded Liposome Products
Product Details Publish Data FAQs Resources
Product Details
As a pioneer in the field of liposome development, Creative Biolabs has accumulated over a decade of experience, enabling us to offer a diverse range of drug-loaded liposomes to cater to your varied therapeutic needs. Our products are effective with consistent lot-lot characteristics, uniform particle size, and high encapsulation efficiency to address your challenges in delivering poorly soluble drugs, enhancing drug stability, and achieving sustained release.
Liposomes consist of phospholipids, essential components found in cellular membranes. This gives liposome membranes a phospholipid bilayer structure that closely resembles biological membranes, enabling them to mimic natural cell membranes and interact with mammalian cells, thereby facilitating efficient cellular uptake. Furthermore, liposomes possess attributes of biocompatibility, biodegradability, non-toxicity, and nonimmunogenicity, thereby endowing them with potent and versatile drug delivery capabilities. The encapsulation of drugs within liposomes not only enhances and prolongs their therapeutic effects but also safeguards them against enzymatic degradation, chemical and immunological inactivation, as well as rapid clearance from plasma. This encapsulation strategy minimizes the risk of exposure to healthy tissues, thereby mitigating adverse effects associated with free drugs.
If you require additional functionalities such as targeted delivery and prolonged circulation for drug-loaded liposomes, we offer a range of conjugating services for antibodies, proteins, peptides, and ligands. Furthermore, if you are interested in environmentally responsive liposomes, we can achieve controlled drug release in response to specific stimuli such as enzymes, light, pH, temperature, ultrasound, and more. Feel free to contact us without delay for a tailored program that aligns more closely with your research requirements.
| Cat |
Product name |
Lipid Composition |
Data sheet |
MSDS |
Inquiry |
| CLBD008LY |
Doxorubicin Liposome (PEGylated) |
HSPC, Cholesterol, DSPE-PEG(2000) |

|

|
Inquiry
|
| CLBD009LY |
Control Doxorubicin Liposome (PEGylated) |
HSPC, Cholesterol, DSPE-PEG(2000) |

|

|
Inquiry
|
| CLBD010LY |
Carboxylic Acid-Doxorubicin Liposome (PEGylated) |
HSPC, Cholesterol, DSPE-PEG(2000), DSPE-PEG(2000)-Carboxylic Acid |

|

|
Inquiry
|
| CLBD011LY |
Succinyl-Doxorubicin Liposome (PEGylated) |
HSPC, Cholesterol, DSPE-PEG(2000), DSPE-PEG(2000)-Succinyl |

|

|
Inquiry
|
| CLBD012LY |
Cyanur-Doxorubicin Liposome (PEGylated) |
HSPC, Cholesterol, DSPE-PEG(2000), DSPE-PEG(2000)-Cyanur |

|

|
Inquiry
|
| CLBD013LY |
Biotin-Doxorubicin Liposome (PEGylated) |
HSPC, Cholesterol, DSPE-PEG(2000), DSPE-PEG(2000)-Biotin |

|

|
Inquiry
|
| CLBD014LY |
Amine-Doxorubicin Liposome (PEGylated) |
HSPC, Cholesterol, DSPE-PEG(2000), DSPE-PEG(2000)-Amine |

|

|
Inquiry
|
| CLBD015LY |
DBCO-Doxorubicin Liposome (PEGylated) |
HSPC, Cholesterol, DSPE-PEG(2000), DSPE-PEG(2000)-DBCO |

|

|
Inquiry
|
| CLBD016LY |
Azide-Doxorubicin Liposome (PEGylated) |
HSPC, Cholesterol, DSPE-PEG(2000), DSPE-PEG(2000)-Azide |

|

|
Inquiry
|
| CLBD017LY |
Folate-Doxorubicin Liposome (PEGylated) |
HSPC, Cholesterol, DSPE-PEG(2000), DSPE-PEG(2000)-Folate |

|

|
Inquiry
|
| CLBD018LY |
PDP-Doxorubicin Liposome (PEGylated) |
HSPC, Cholesterol, DSPE-PEG(2000), DSPE-PEG(2000)-PDP |

|

|
Inquiry
|
| LDLY-1023-LD1 |
Gastrodin Liposome |
Soy PC, Cholesterol |

|

|
Inquiry
|
| LDLY-1023-LD2 |
Dexamethasone Palmitate Acid Liposome |
Cholesterol, DPPC |

|

|
Inquiry
|
| LDLY-1023-LD3 |
Dexamethasone Sodium Phosphate Liposome |
Soy PC, Cholesterol |

|

|
Inquiry
|
| LDLY-1023-LD4 |
Ornithine Aspartate Liposome |
Cholesterol, DPPG |

|

|
Inquiry
|
Publish Data
Impact of PEGylated Liposomal Doxorubicin and Carboplatin Combination on Glioblastoma
Author: Ghaferi, Mohsen, et al.
This study explored the therapeutic effects of liposomes encapsulating doxorubicin (DOX) and carboplatin (CB) on glioblastoma. Using reverse-phase evaporation, researchers created co-delivery of DOX and CD liposomes (PEGylated and non-PEGylated). These liposomes were utilized in the glioblastoma rat model, which was established by rat glioma C6 cells. The study assessed the rats' survival time, weight changes, serum levels of blood urea nitrogen (BUN), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), alanine aminotransferase (ALT), and creatinine. Results indicated that PEGylated liposomes led to lower increase in serum levels of BUN, AST, ALT, and creatinine than non-PEGylated liposomes. This could be attributed to PEG improving the stability of liposomes in the circulation, resulting in prolonged drug release. This study demonstrates that PEGylated liposomes have stronger therapeutic effects on glioblastoma than non-PEGylated liposomes. Moreover, PEGylated liposomes serve as an effective drug delivery platform for co-delivery.
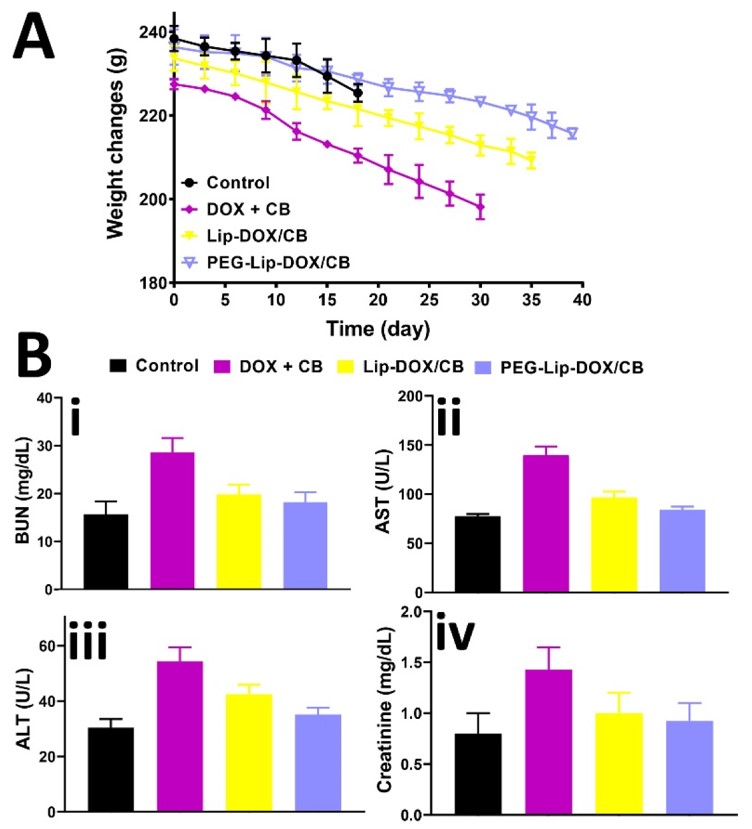 Fig.1 Weight changes and serum concentrations of ALT, AST, BUN and creatinine in rats with glioblastoma.1,2
Fig.1 Weight changes and serum concentrations of ALT, AST, BUN and creatinine in rats with glioblastoma.1,2
FAQs
How are drug-loaded liposomes prepared?
Drug-loaded liposomes are typically prepared using methods such as thin-film hydration, reverse-phase evaporation, and the use of multi-inlet vortex mixers (MIVM). These methods ensure proper encapsulation and stability of the drug within the liposome, optimizing size and encapsulation efficiency.
What factors influence the encapsulation efficiency of drugs in liposomes?
Encapsulation efficiency depends on several factors, including the liposome preparation method, the physicochemical properties of the drug, the lipid composition, and the lipid-to-drug ratio. Conditions such as pH and temperature during preparation also play crucial roles.
What are the common applications of drug-loaded liposomes in research?
Drug-loaded liposomes are widely used in cancer research, antimicrobial studies, and gene therapy. They serve as a model for studying drug delivery mechanisms, improving drug formulations, and evaluating new therapeutic agents in preclinical and clinical settings.
How do drug-loaded liposomes enhance drug stability and release?
The lipid bilayer of liposomes protects the encapsulated drug from degradation, thereby enhancing its stability. Controlled release of the drug can be achieved by modifying the liposome's lipid composition, size, and surface characteristics, allowing for sustained therapeutic effects.
What are the challenges associated with drug-loaded liposome research?
Key challenges include ensuring uniform drug loading, achieving consistent liposome size and stability, scaling up production, and maintaining reproducibility. Overcoming these challenges requires precise control over preparation techniques and thorough characterization of liposome properties.
Resources
References
-
Ghaferi, Mohsen, et al. "Impact of PEGylated liposomal doxorubicin and carboplatin combination on glioblastoma." Pharmaceutics 14.10 (2022): 2183.
-
under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.

For Research Use Only. Not For Clinical Use

 Fig.1 Weight changes and serum concentrations of ALT, AST, BUN and creatinine in rats with glioblastoma.1,2
Fig.1 Weight changes and serum concentrations of ALT, AST, BUN and creatinine in rats with glioblastoma.1,2



 For Research Use Only. Not For Clinical Use
For Research Use Only. Not For Clinical Use
