Liposome for Artificial Cells
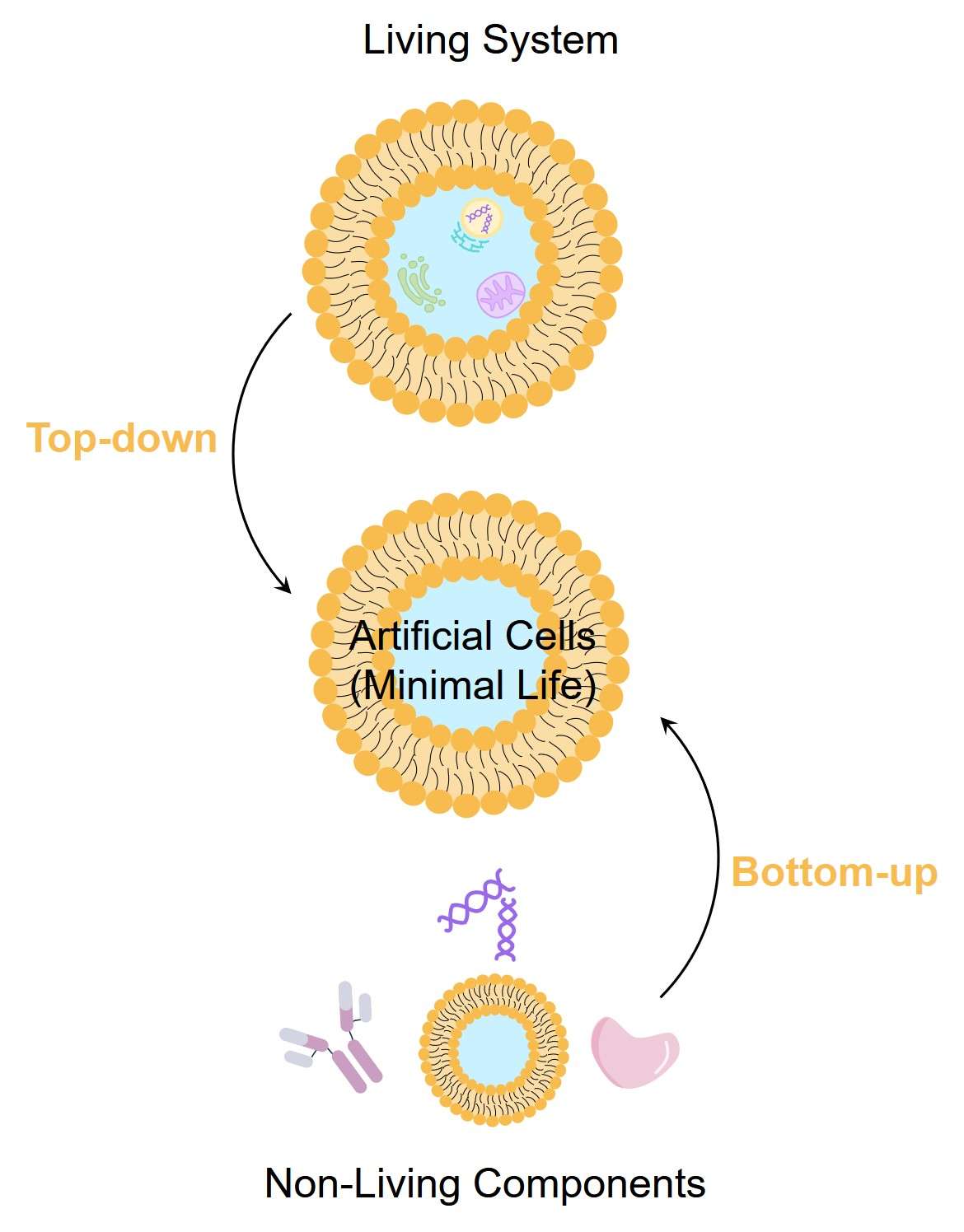
Cells are the smallest unit of life with independent replication ability. Artificial cells have similar structures and activities to natural cells (growth, division and replication, cell metabolism, cell communication, etc.) and can be used to research cell properties and imitate cell function. It can be constructed via two methods: top-down (removing unnecessary genes, and organelles from the cell until the smallest surviving unit is obtained) and bottom-up (assembling organic biomolecules or inorganic materials using chemical methods to construct micro-bubbles with specific simulated cellular functions). The bottom-up building process makes it easier, faster, and more cost-effective to produce artificial cells.
Liposomes: The Best Container for Artificial Cells
The creation of a "container" for its components is therefore a key stage in the bottom-up production of artificial cells. Phospholipids are characterized by their high permeability, lateral mobility, and limited biological toxicity. Liposomes prepared from phospholipids have a phospholipid bilayer structure similar to that of natural cells and may effectively encapsulate a wide range of biomolecules. Therefore, liposomes are the best choice as the compartment for an artificial cell to mimic the biological functions of natural cells.
Phospholipid Synthesis
Phospholipids are crucial components of cell membranes, and their synthesis is required for cell growth and division. A variety of enzymes regulate phospholipid synthesis via a cascade reaction. Enzymes expressed on the lipid membrane recreate the entire cascade of enzymatic processes in the Kennedy pathway, transforming precursors (e.g., 1-position of glycerol 3-phosphate) into multiple phospholipids such as PA, PE, PG, and PS.
Membrane Fusion
Membrane fusion (e.g., endocytosis, exocytosis) is a crucial mechanism in many biological processes that regulate intercellular molecule transport and communication. Liposomes can be utilized to investigate the mechanics of natural cell membrane fusion and to better understand membrane events like endocytosis and exocytosis.
Shape Deformation
The complex interactions between cytoskeletal proteins and cell membranes affect cell morphology. Creative Biolabs can help you understand the mechanisms affecting cell movement and shape deformation by encapsulating a wide range of cytoskeletal proteins.
Protein and gene expression
Protein expression from genes is critical for obtaining specific functions in artificial cells. Liposomes may effectively encapsulate the cell-free expression system for protein expression, resulting in controlled artificial cells.
Intracellular communication
Intercellular communication refers to cells' capacity to receive, analyze, and transmit diverse messages. Creative Biolabs can generate liposomes that mimic cellular communication. For example, embedding pore proteins on liposomes can initiate intracellular and extracellular information transmission in artificial cells.
Requirements for GUVs As the Container of Artificial cell
Giant unilamellar vesicles (GUVs) are ideal for constructing artificial cells due to their comparable size and appearance to eukaryotic cells (5-100 μm). To mimic the activity of natural cells with liposomes, the maturing of GUVs must focus on two aspects: membrane container and encapsulation of functional components.
Based on these two aspects, Creative Biolabs can provide the ideal artificial cell strategy in terms of size, phospholipid composition, and so on.
|
Requirements
|
Considerations
|
|
Size
|
5–100 μm range.
|
|
Phospholipid Composition
|
Synthetic/ Natural/ Functionalized lipids.
|
|
Controlled Permeability of Membrane
|
To provide deformability for growth and division.
|
|
Protein Reconstitution of Membrane
|
Membrane proteins allow the permeation of ions and large molecules.
|
|
Unilamellar Lipid Bilayer
|
Determine the probable shape changes and mechanical stability of liposomes.
|
|
Cleanliness
|
There is no residual oil or any other inclusions.
|
|
Mechanical Stability
|
Tuning the lipid composition, modifying bilayer asymmetry, adjusting cholesterol content, etc.
|
|
Buffer
|
Encapsulate physiological buffers without any kind of chemical that may interfere with biological processes.
|
|
Cross-compatibility
|
Encapsulation of many biological systems in a single liposome.
|
Our Features
-
Lipid-based artificial cell development services
-
Best-suited strategy
-
Reliable after-sales service
Artificial cells are crucial for investigating biological processes. As a well-known liposome manufacturer, Creative Biolabs is committed to supplying you with GUVs that meet your demands for a variety of cellular activities.

For Research Use Only. Not For Clinical Use


 For Research Use Only. Not For Clinical Use
For Research Use Only. Not For Clinical Use
