Fluorescent Liposome Products
Product Details Technical Note Publish Data FAQs Resources
Product Details
Creative Biolabs offers various types of fluorescent liposomes labeled with lipophilic dyes for different applications. Our fluorescent liposome products include different sizes from 100 nm series to 500 nm to satisfy the need for particle size standards in the field of flow cytometry. The particle size present in the product sheet is for the mean diameter as measured by a standard DLS particle sizer.
Fluorescent liposomes are a new type of fluorescent markers by unilamellar liposomes encapsulated and surface-immobilized fluorophores to image flow profiles in microfabricated structures. The liposomes were produced with phospholipids and cholesterol by extrusion through a polycarbonate membrane. Carboxyfluorescein in the aqueous core and fluorescein labeled lipids in the bilayer endow them surface and volume fluorescence to maximize their fluorescence intensity. The composition of the liposome was chosen to give the liposome a net negative charge to minimize self-aggregation and interaction with the negatively charged channel glass surface. These liposomes were monodisperse, neutrally buoyant, and hydrophilic and exhibited no adsorption on glass surfaces.
Our fluorescent liposomes can be used to investigate pressure-driven flow and provide images with excellent signal-to-noise ratio. Fluorescent liposomes also can be custom-made for various applications to offer a broad range of surface and volume characteristics such as charge, size, and surface chemistry.

For Research Use Only. Not For Clinical Use
Technical Note
-
The primary concern with fluorescent clodronate liposomes or mannosylated fluorescent liposomes involves the potential generation of inaccurate or uninterpretable data. This is due to the disruption of the fluorescent lipid during clodronate liposomes-induced macrophage apoptosis causing it to disperse among subsequent phagocytosing macrophages. High background fluorescence may also result from lingering fluorescent lipids in undisposed extracellular "garbage". The time of apoptosis onset with clodronate liposome treatment can vary widely, hence for the most accurate results, tracking should be established within each experimental model. For tracking purposes, Creative Biolabs may make DiA/DiD/DiI/DiR-labelled clodronate liposomes available upon request which can provide clear and valid biodistribution data.
-
Due to margination post-liposome phagocytosis, circulating monocytes may "disappear" or show reduced counts within the first 2 hours. Such cells usually return to the circulation within a few hours.
-
For in vivo injections, liposomes should be homogeneously suspended. To maintain homogeneity, slowly invert the vial prior to usage and avoid vigorous shaking to prevent foaming.
-
If unacquainted with large-volume injections, have extra animals on hand for practice to minimize injection-related adverse events.
-
For intravenous dosing, adopt standard precautions for larger volumes, including warming the product to room temperature, ensuring air bubble removal, and injecting at a steady rate. If unusual animal reactions are observed, the infusion rate should be reduced.
-
Animals may exhibit gasping or seizures post-infusion, however, most tend to recover without permanent injury.
-
Liposomes should be stored at 4°C and freezing should be avoided.
Publish Data
Improved vessel painting with carbocyanine dye-liposome solution for visualisation of vasculature
Author: Konno, Alu, Naoya Matsumoto, and Shigetoshi Okazaki.
This study used fluorescent liposomes for vascular visualization studies. The researchers employed DiIC18 and DiIC12 liposomes to perfuse mice's left ventricles. Figure A shows that the DilC12 liposome stated veins that were nearly invisible with DilC18 staining. Figure B illustrates how vascular endothelial cells may be identified in the DiIC12 liposome-perfused brain. Some cells' nuclei were evident even in the absence of nuclear labeling. This work shows that fluorescent liposomes (DiIC12 liposomes) are a simple, practical, and cost-effective approach for vascular visibility, expanding the options for visualization investigations.
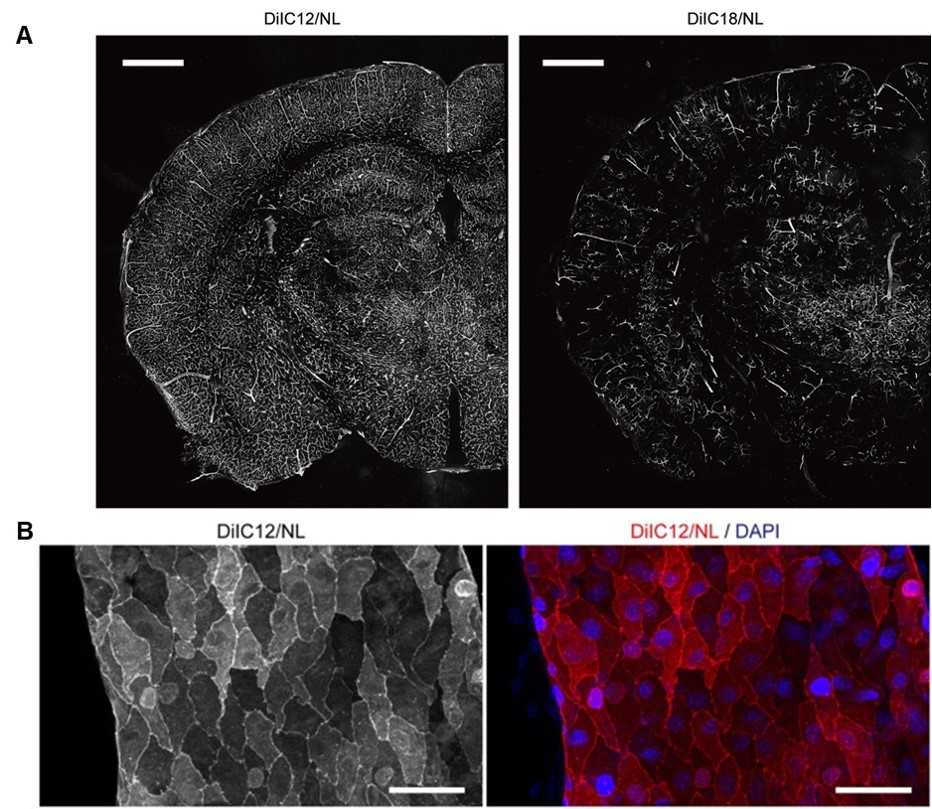 Fig.1 Vessel painting with DiIC18 liposome and DiIC12 liposome.1,2
Fig.1 Vessel painting with DiIC18 liposome and DiIC12 liposome.1,2
FAQs
How are fluorescent liposomes used in drug delivery research?
In drug delivery research, fluorescent liposomes are utilized to investigate the distribution, targeting, and release of therapeutic agents within biological systems. Their fluorescent properties enable real-time tracking and imaging of the liposomes, providing insights into the efficacy and mechanism of drug delivery systems.
What are the advantages of using fluorescent liposomes in research?
Fluorescent liposomes offer several advantages in research, including the ability to simulate biological membranes, encapsulate a variety of compounds, and provide real-time visualization of interactions and processes at the cellular level. Their versatility and biocompatibility make them valuable tools in drug delivery studies, diagnostics, and cellular imaging.
How can I choose the appropriate fluorescent liposome for my research?
When selecting fluorescent liposomes for your research, consider the following factors: the specific application (e.g., in vitro or in vivo studies), the excitation and emission wavelengths of the fluorescent dye, the size and charge of the liposomes, and the compatibility of the liposome composition with your biological system. It's important to select a product that matches your experimental requirements and provides optimal visibility under your imaging conditions.
Can I customize fluorescent liposomes to match my specific research needs?
Creative Biolabs offers custom services for fluorescent liposomes, allowing you to tailor the liposome size, lipid composition, and fluorescent dye to your specific research requirements. Contact us to discuss your needs and explore the available customization options for your project.
Resources
References
-
Konno, Alu, Naoya Matsumoto, and Shigetoshi Okazaki. "Improved vessel painting with carbocyanine dye-liposome solution for visualisation of vasculature." Scientific reports 7.1 (2017): 10089.
-
under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, the image is a composite of figure 4 and figure 5.

For Research Use Only. Not For Clinical Use

 For Research Use Only. Not For Clinical Use
For Research Use Only. Not For Clinical Use
 Fig.1 Vessel painting with DiIC18 liposome and DiIC12 liposome.1,2
Fig.1 Vessel painting with DiIC18 liposome and DiIC12 liposome.1,2




