What is C7? C7 Function C7 Test C7 Deficiency C7 Therapeutics
As a key component of the Membrane Attack Complex (MAC), C7 plays a critical role in the body's defense against pathogens. This article will provide an in-depth exploration of C7's structure, function, and significance in both health and disease.
What is Complement C7?
C7 is one of five precursor proteins of the MAC of complement. C7 is a mosaic protein composed of 821 amino acid residues, forming a single polypeptide chain with a molecular weight of 95-100 kDa. The protein's structure is characterized by several distinct domains.
-
MACPF domain: A single domain consisting of 240 amino acids.
-
Cysteine-rich modules: Eight modules, each containing approximately 34-75 amino acids.
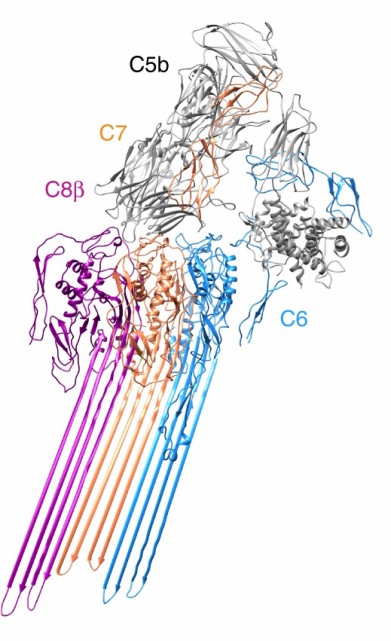 Fig.1 Structure of C7 (orange).1,3
Fig.1 Structure of C7 (orange).1,3
Structural features of the C7 protein:
-
Disulfide bonds: C7 contains 28 disulfide bonds that make up its tertiary structure.
-
Glycosylation: The protein is glycosylated at two sites.
-
Cysteine distribution: Most cysteine residues are found in small units of 35-77 amino acids.
C7 has 23-30% homology with complement components C8 and C9, especially in the amino-terminal two-thirds of the molecule.
Functional Role of C7 in the Complement System
C7 is one of the five precursor proteins of the MAC and plays a crucial role in the terminal complement pathway. Its primary functions include:
Table 1 Function of complement component 7.
|
Function
|
Description
|
|
Binding to C5b-6 Complex
|
C7 binds to the C5b-6 complex, forming the C5b-7 complex.
|
|
Hydrophilic-Amphiphilic Transition
|
C7 is responsible for the transition of the hydrophilic structure into an amphiphilic C5b-7 complex.
|
|
Membrane Anchoring
|
The C5b-7 complex serves as an anchor for the late complement components, C8 and C9.
|
The MAC is a crucial component of the complement system's lytic activity. C7's involvement in MAC assembly is as follows:
-
C7 binds to the C5b-6 complex, forming C5b-7.
-
The C5b-7 complex attaches to the target membrane.
-
C8 and multiple C9 molecules are recruited to form the complete MAC.
This process results in the formation of a pore in the target cell membrane, leading to osmotic lysis and cell death.
 Fig. 2 Complement C7 participates in the MAC assembly.2,3
Fig. 2 Complement C7 participates in the MAC assembly.2,3
C7 is integral to the activation of the complement system, serving as the final product of the complement cascade. Its importance is underscored by several key factors.
-
Rate-limiting factor: C7 acts as one of the major rate-limiting factors for MAC formation.
-
Amplification: Its involvement in the C5b-7 complex formation amplifies the complement response.
-
Specificity: C7 helps ensure that the MAC forms on target pathogen membranes.
C7 Functional Test
The C7 functional test measures the activity of complement component C7 in serum, specifically its ability to participate in the formation of the MAC. The most commonly used method for assessing C7 functionality involves mixing patient serum with C7-deficient serum and testing its ability to lyse target cells or liposomes.
C7 measurements are most informative when used in conjunction with C5b-9 assays and functional assays. This integrated approach allows for a more detailed assessment of the overall state of the complement system and helps to identify specific pathway defects or patterns of activation.
As a leading service provider in complement testing, Creative Biolabs offers expert analysis of C5b-9 complex levels.
 Fig.3 Workflow of C5b-9 complex functional test.
Fig.3 Workflow of C5b-9 complex functional test.
C7 in Health and Disease
C7 plays a crucial role in the innate immune system, especially as part of the MAC. Its functions and effects on health and disease are diverse and important. Mutations in the C7 gene can lead to C7 deficiency, a disorder associated with:
-
Increased susceptibility to recurrent neisserial infections.
-
Immune responses to other pathogens may be altered.
Although less common, C7 deficiency has been associated with autoimmune diseases and cancers.
Table 2 The potential relationship between C7 and diseases.
|
Diseases
|
Potential Relationships
|
|
Autoimmune diseases
|
-
Some patients with C5-9 deficiency suffer from SLE-like illnesses, rheumatoid arthritis, noma and scleroderma.
|
|
Cancer
|
-
C7 expression is increased in hepatocellular carcinoma stem cells and enhances the stemness of hepatocellular carcinoma stem cells through upregulation of Nanog, Oct4, Sox2 and C-myc.
-
C7 has been shown to be a potential tumor suppressor in some cancers.
-
C7 may serve as a prognostic biomarker for specific cancer types.
|
Component C7 Based Therapy
C7 plays a crucial role in the formation of the MAC, making it an important target for therapeutic intervention. Current and potential C7-based therapies include:
Table 3 C7 in drug development.
|
Therapeutic Approaches
|
Mechanism of Action
|
|
Monoclonal Antibodies
|
-
Block C7 activity
-
Prevent MAC formation
-
Modulate complement-mediated inflammation
|
|
Small Molecule Inhibitors
|
-
Interfere with the ability of C7 to bind to the C5b-6 complex
-
Block the insertion of C7 into the target cell membrane
|
|
Gene Therapy
|
-
Upregulation in the absence of C7
-
Downregulation of C7 in the presence of deleterious complement overactivation
|
|
Targeted Drug Delivery
|
-
Nanoparticle-based drug delivery systems
-
Antibody-drug couplings
|
The multifaceted nature of C7 provides multiple avenues for future research and potential therapeutic applications.
-
Complement-mediated diseases: Understanding the role of C7 may help to find new ways to treat complement dysregulation diseases.
-
Cancer therapy: Given its potential tumor suppressor properties, C7 could be explored as a target for cancer therapy.
-
Diagnostic tool: C7 levels can serve as a biomarker for certain conditions.
-
Immunomodulation: Manipulation of C7 function may provide novel ways to modulate the immune response.
The role of C7 in MAC formation and its interactions with other complement proteins highlights its importance in immune defense and potential involvement in a variety of pathological conditions. As research continues to unravel the complexity of C7 function, it is expected to open new avenues for diagnostic and therapeutic interventions in complement-related and other diseases.
Creative Biolabs offers a full range of complement component C7-related services and products, including:
If you want more information, please feel free to contact us.
References
-
Menny, Anaïs, et al. "CryoEM reveals how the complement membrane attack complex ruptures lipid bilayers." Nature communications 9.1 (2018): 5316. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-07653-5
-
Couves, Emma C., et al. "Structural basis for membrane attack complex inhibition by CD59." Nature Communications 14.1 (2023): 890. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-023-36441-z
-
under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.
Related Sections:

 Fig.1 Structure of C7 (orange).1,3
Fig.1 Structure of C7 (orange).1,3
 Fig. 2 Complement C7 participates in the MAC assembly.2,3
Fig. 2 Complement C7 participates in the MAC assembly.2,3
 Fig.3 Workflow of C5b-9 complex functional test.
Fig.3 Workflow of C5b-9 complex functional test.