What is C5? C5 Function C5 Test C5 Deficiency C5 Therapeutics
The complement system relies on the precise orchestration of over 30 proteins to defend against pathogens and maintain homeostasis. At the heart of this system lies complement component C5, a glycoprotein whose cleavage into bioactive fragments C5a and C5b drives both protective immunity and pathological inflammation. As a central node in the complement cascade, C5 has emerged as a high-value therapeutic target, offering opportunities to modulate immune responses in diseases ranging from rare hematologic disorders to neurodegenerative conditions.
What is Complement C5?
C5 is the fifth component of the complement system. It is a 190 kDa glycoprotein central to the complement system, encoded by the C5 gene located on chromosome 9 in humans. Structurally, it comprises α- and β-chains linked by a disulfide bond, with a domain organization resembling complement component C3 but distinct functional features. Its activation occurs via C5 convertases, which cleave C5 into:
-
Complement component C5a: A 74-amino acid anaphylatoxin that binds G protein-coupled receptors (C5aR1 and C5aR2), inducing chemotaxis, cytokine release, and vascular permeability.
-
Complement component C5b: The initiator of the membrane attack complex (MAC), a pore-forming structure (C5b-9) that lyses pathogens but can also damage host cells.
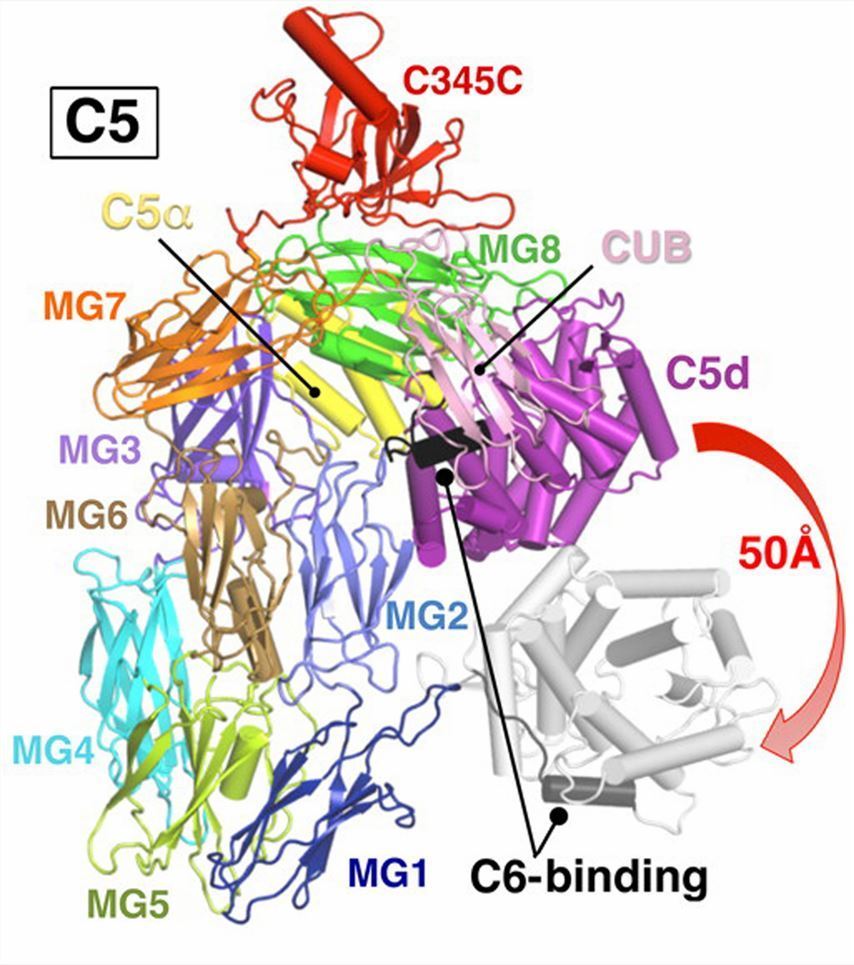 Fig.1 Structure of C5.1,3
Fig.1 Structure of C5.1,3
Structural features of the C5 protein:
-
Domain flexibility: The C345C domain, critical for interactions with convertases and regulators, is flexibly attached to the core structure, enabling conformational shifts during activation.
-
Activation-induced changes: Cleavage by C5 convertases (e.g., CVF, Bb) at Arg74-Leu75 in the α-chain triggers a conformational rearrangement, exposing transient binding sites for C6 and initiating MAC assembly. Unlike C3, C5 lacks a thiol ester bond, relying instead on non-covalent interactions for membrane targeting.
Functional Role of C5 in the Complement System
Complement component C5 plays a pivotal role in the complement system, bridging innate immune defenses and inflammatory responses. Its cleavage into C5a and C5b drives two critical pathways: inflammatory signaling and MAC formation.
Table 1 Key functional roles of C5 fragments.
|
Fragment
|
Primary Functions
|
Mechanistic Impact
|
|
C5a
|
Chemotaxis, leukocyte activation, cytokine release, vascular permeability
|
Binds C5aR1/C5aR2 on immune cells (e.g., neutrophils, macrophages), amplifying inflammation.
|
|
C5b
|
MAC assembly
|
Forms lytic pores on pathogens or host cells, mediating direct cytolysis.
|
 Fig. 2 The generation of C5a and C5b.2, 3
Fig. 2 The generation of C5a and C5b.2, 3
This dual functionality positions C5 at a critical juncture: while C5a amplifies inflammation, MAC formation provides direct microbial killing. Regulatory proteins like CD59 and vitronectin prevent uncontrolled MAC activity on host cells.
The C5 functional test is a specialized assay used to assess the activity of complement component C5 in serum samples. This test is crucial for diagnosing C5 deficiency and investigating complement system abnormalities.
Hemolytic assays are one of the primary complement C5 function tests that may be performed. By combining patient serum with a C5-deficient serum, component C5 activity is assessed. The serum mixture's lytic activity is evaluated against SRBC or sensitized, tagged liposomes. If lysis happens, the C5 must originate from the patient's serum.
With years of experience in complement tests, Creative Biolabs supports complement C5 functional tests to help advance your programs. Notably, we can tailor complement test assays based on multi-disciplinary scientists and comprehensive platforms.
Hemolytic assays
 Fig.3 Workflow of C5 functional test with hemolytic assays.
Fig.3 Workflow of C5 functional test with hemolytic assays.
C5 ELISA
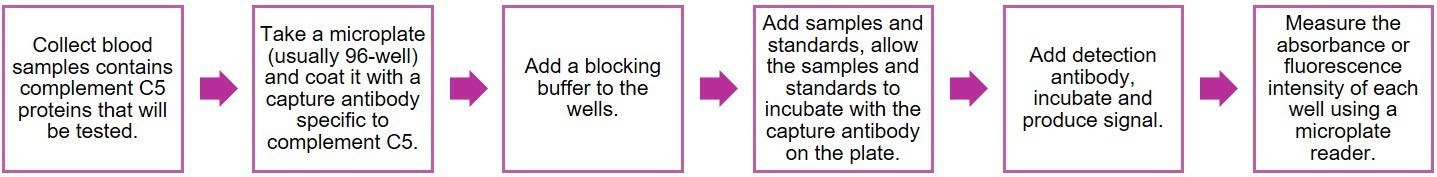 Fig.4 Workflow of C5 functional test with ELISA.
Fig.4 Workflow of C5 functional test with ELISA.
C5 in Health and Disease
C5 dysregulation can lead to various pathological conditions due to its crucial role in the complement system. The main implications include:
-
Increased susceptibility to infections.
-
Autoimmune and inflammatory conditions
-
Complement-mediated diseases
-
Neurological disorders
-
Other implications
Table 2 The potential relationship between C5 and diseases.
|
Diseases
|
Potential Relationships
|
|
Neisseria Infections
|
-
C5 deficiency significantly increases the risk of recurrent and severe infections, particularly with Neisseria species.
|
|
Other Pathogens
|
|
|
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE)
|
-
C5 dysregulation has been linked to SLE, where complement consumption can lead to tissue damage.
|
|
Rheumatoid Arthritis
|
-
Defects in the C5 gene have been associated with susceptibility to rheumatoid arthritis.
|
|
Liver Fibrosis
|
-
C5 gene defects have also been linked to increased susceptibility to liver fibrosis.
|
|
Paroxysmal Nocturnal Hemoglobinuria (PNH)
|
-
Excessive C5 activation leads to complement-mediated destruction of red blood cells.
|
|
Atypical Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome (aHUS)
|
-
Dysregulation of the complement system, including C5, contributes to this rare but severe condition.
|
|
Guillain-Barré Syndrome (GBS)
|
-
C5a and C5aR1 signaling are involved in the pathogenesis of GBS and its variants.
|
|
Chronic Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyradiculoneuropathy (CIDP)
|
-
C5 dysregulation contributes to the inflammatory processes in CIDP.
|
|
Peripheral Neuropathies
|
-
Inappropriate activation of C5 is implicated in various peripheral neuropathic diseases.
|
|
Leiner's Disease
|
-
C5 deficiency is thought to be a cause of this rare condition characterized by severe dermatitis.
|
|
Complement Consumption
|
-
In conditions with autoantibodies, such as SLE, complement engagement can lead to consumption of C5 and other components, resulting in acquired deficiencies and tissue damage.
|
Component C5 Based Therapy
C5 appears to be an attractive therapeutic target to control because of the release of the potent proinflammatory peptide C5a and to the assembly of the terminal complex responsible for tissue damage and inflammation to fight infection, clear immunocomplexes and maintain self-tolerance.
Various types of antibodies and compounds such as peptides or non-peptides have actively been developed, and these substances act as inhibitors of complement components C5 and C5a and antagonists of the C5a receptor, which selectively allows inhibition of the C5b and C5a-mediated responses while leaving the rest of complement unaffected. These C5 and C5a receptor antagonists may be efficacious at treating various inflammatory diseases involving complements.
Table 3 C5 in drug development.
|
Therapeutic Approaches
|
Mechanism of Action
|
|
Eculizumab
|
First approved C5 inhibitor
|
|
Ravulizumab
|
Long-acting C5 inhibitor
|
|
Zilucoplan
|
Subcutaneous C5 inhibitor
|
|
C5a receptor antagonists
|
Block C5a-C5aR1 signalingAntibody-drug couplings
|
|
Small-molecule C5 inhibitors
|
Oral agents targeting C5 convertases
|
|
Gene-editing therapies
|
C5 knockout
|
At Creative Biolabs, we leverage decades of experience to advance C5-focused therapies through:
If you want more information, please feel free to contact us.
References
-
Aleshin, Alexander E., et al. "Crystal structure of C5b-6 suggests structural basis for priming assembly of the membrane attack complex." Journal of Biological Chemistry 287.23 (2012): 19642-19652. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M112.361121
-
Horiuchi, Takahiko, and Hiroshi Tsukamoto. "Complement-targeted therapy: development of C5-and C5a-targeted inhibition." Inflammation and regeneration 36.1 (2016): 1-5. https://doi.org/10.1186/s41232-016-0013-6
-
under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.
Related Sections:

 Fig.1 Structure of C5.1,3
Fig.1 Structure of C5.1,3
 Fig. 2 The generation of C5a and C5b.2, 3
Fig. 2 The generation of C5a and C5b.2, 3
 Fig.3 Workflow of C5 functional test with hemolytic assays.
Fig.3 Workflow of C5 functional test with hemolytic assays.
 Fig.4 Workflow of C5 functional test with ELISA.
Fig.4 Workflow of C5 functional test with ELISA.