Exosome-Based Vaccine against Virus Infection
The long-standing global trend of epidemic transmission of COVID-19 has created an urgent requirement for the vaccines against diseases caused by viral infections. Exosome-based vaccines is possible for the prevention of diseases caused by multiple viral infections, whether non-infectious diseases such as HIV and HBV, or malignant infectious diseases such as SARS and COVID-19. As a distinguished exosome vaccine research company, Creative Biolabs is able to provide services for the customized exosome-based vaccines studies against virus infections.
Diseases Caused by Virus Infections
The process of invasion of disease-causing viruses into the body through the skin, respiratory tract and mucous membranes, and their parasitic multiplication and dissemination can lead to diseases caused by a variety of viral infections, including HIV, HBV, SARS and COVID-19. On the one hand, viruses invade the organism and compete for nutrients and genetic material of the host, which adversely affects the normal metabolism of the host cells, thus causing cell death and dysfunction. On the other hand, viruses, as foreign invaders, stimulate the immune and inflammatory responses in the organism, and the accompanying immune attack and inflammatory damage are the main mechanisms of disease development. Also, because of the similarity of some viral components to those of the host, immune tolerance is overcome and autoimmune and inflammatory factor storms occur under the effect of molecular mimicry. To interfere with and prevent host damage caused by viral infections, studies on exosome platforms that can be engineered to provide new insights for vaccine development and disease intervention.
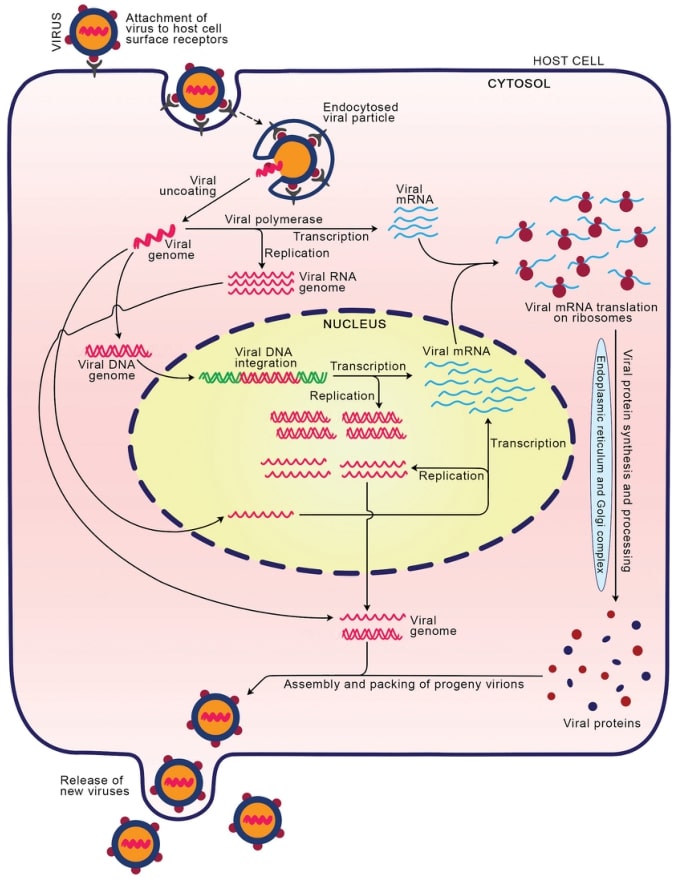 Fig.1 Virus proliferation in the host. (Tompa, 2021)
Fig.1 Virus proliferation in the host. (Tompa, 2021)
Exosome-based Vaccines for Non-infectious diseases
Researchers have focused on non-malignant infectious diseases caused by viral infections, primarily HIV and HBV. HIV causes damage and disruption of the immune system by attacking CD4+ T lymphocytes and NK cells, causing patients to develop immune failure and defects. One study developed dendritic cell-derived exosomes expressing the specific HIV envelope glycoprotein, which successfully induced independent specific CD8+ T cell immunity. Meanwhile, the efficacy of further improved exosomes based on the HIV structural protein was enhanced in terms of induction. In addition, vaccine strategies targeting multiple functionally relevant HIV antigens such as HIV maturation and infection have been applied in the development of exosome-based vaccines. For example, loading proteins involved in cell survival and vesicle transport into exosomes induces antigen presentation and CTL immune responses in target cell DCs. HBV is capable of promoting the progression of chronic liver diseases such as hepatocellular carcinoma. The use of exosomes as vaccine adjuvants to design vaccines based on recombinant HBV antigens is promising, and immune responses to Th1 and secretion of IFN-у have been observed in vaccine-treated mouse models.
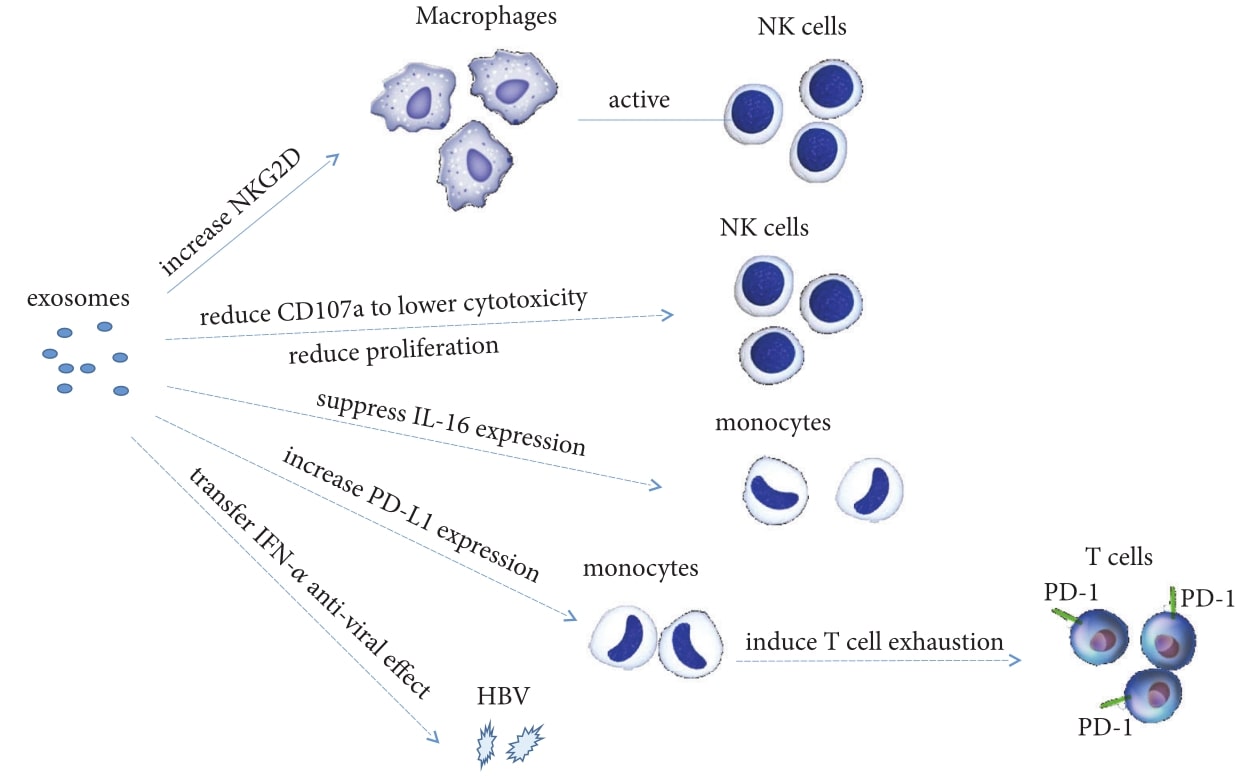 Fig.2 Exosomes modulate immune response during HBV infection. (Li, 2019)
Fig.2 Exosomes modulate immune response during HBV infection. (Li, 2019)
Exosome-based Vaccines for Infectious Diseases
The occurrence of malignant infectious diseases caused by viral infections often poses a huge economic loss and health threat to humans. Processes based on prevention of viral invasion or interference with viral proliferation are viable vaccine development strategies. For example, exosome-based vaccines that chimerize the Spike protein of coronaviruses and their subunits as attenuated antigens function as specific stimulators of IFN-γ secretion. Exosomal vaccines delivering IFITM3, an immune protein that interferes with viral invasion and detoxification, are able to stimulate the host to produce higher levels of antibodies compared to adenovirus vector vaccines, achieving prevention and resistance against infectious viruses.
 Fig.3 Exosome-based vaccine presenting coronavirus Spike protein antigen. (Mishra & Banerjea, 2021)
Fig.3 Exosome-based vaccine presenting coronavirus Spike protein antigen. (Mishra & Banerjea, 2021)
The ability of exosomes to modulate immune and inflammatory responses offers the potential for their use as cell-free strategies for vaccine development in a wide range of viral infectious diseases. There is a need to continuously investigate vaccine strategies with engineered exosomes loaded with disease-specific antigens or co-adjuvants to show higher disease disrupting efficacy. With a proven platform for cell-free vaccine development, storage and administration, Creative Biolabs can provide clients with research services for exosome vaccines against viral infections. Please feel free to contact us.
References
-
Tompa, D.R.; et al. Trends and strategies to combat viral infections: A review on FDA approved antiviral drugs. Int J Biol Macromol. 2021, 172: 524-541.
-
Li, S.; et al. Exosomes modulate the viral replication and host immune responses in HBV Infection. Biomed Res Int. 2019, 2019: 2103943.
-
Mishra, R.; Banerjea, A.C. SARS-CoV-2 Spike targets USP33-IRF9 axis via exosomal miR-148a to activate human microglia. Front Immunol. 2021, 12: 656700.
For Research Use Only. Cannot be used by patients.
Related Services:

 Fig.1 Virus proliferation in the host. (Tompa, 2021)
Fig.1 Virus proliferation in the host. (Tompa, 2021)
 Fig.2 Exosomes modulate immune response during HBV infection. (Li, 2019)
Fig.2 Exosomes modulate immune response during HBV infection. (Li, 2019)
 Fig.3 Exosome-based vaccine presenting coronavirus Spike protein antigen. (Mishra & Banerjea, 2021)
Fig.3 Exosome-based vaccine presenting coronavirus Spike protein antigen. (Mishra & Banerjea, 2021)








