Lung Disease Diagnosis-Applied Exosomes
Overview Services Features FAQs
Exosomes take advantage of their intercellular messaging to modulate the function of receptor cells, suggesting the onset and progression of lung diseases, as diagnostic markers for a variety of lung diseases. With years of experience in exosome research and projects, Creative Biolabs is capable of providing clients with exosome research services related to lung disease diagnostic applications.
Overview of Exosome Applications for Disease Diagnosis
Delivering disease-related information, exosomes are considered to be an important biomarker in liquid biopsies with the advantages of being non-invasive, easily accessible, and convenient to detect. In addition, biomolecules carrying disease characteristics are easily degraded by various enzymes during the circulation of body fluids and thus exhibit a certain degree of instability, which can be protected to a certain extent by the encapsulation of exosomes, thus prolonging their existence. It has been shown that pathological tissues secrete more exosomes than normal tissues, and disease-related markers are also enriched in their corresponding exosomes. Therefore, the detection and analysis of exosomes and their encapsulated cargoes are valuable as important biomarkers in disease diagnosis.
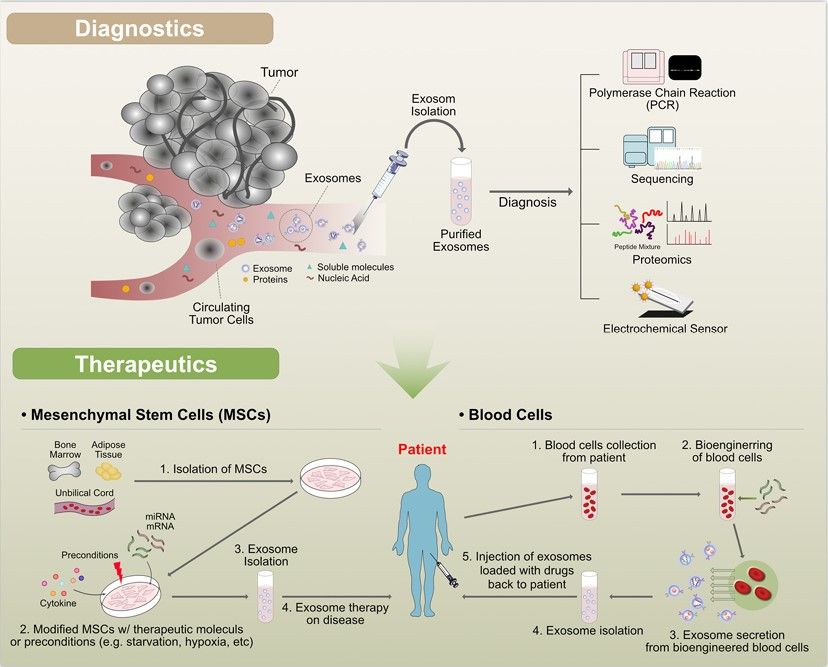 Fig. 1 Diagnostic and therapeutic applications of exosomes.1
Fig. 1 Diagnostic and therapeutic applications of exosomes.1
Investigation of Exosomes For Diagnostic Applications in Lung Diseases
Comprehensive exosome profiling, including proteomic analysis and exosome RNA sequencing, can provide a wealth of information for liquid biopsy studies of exosomes in lung diseases.
-
Bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) is an important source of samples used in the diagnosis of lung disease and contains exosomes (BALF-EXO) that can influence lung tissue conditions. In asthma, BALF-EXO mediates the transfer of antigens to the adaptive immune system and stimulates mast cells, eosinophils, and alveolar macrophages, which results in airway remodeling, reversible airway hyperresponsiveness, and airway obstruction. Acute lung injury in BALF-EXO has a high loading of proteins associated with apoptosis, cell necrosis, and autophagy.
-
Wnt5a is upregulated within BALF-EXO after the onset of lung fibrosis, and lung fibroblasts are a major source of Wnt5a-containing BALF-EXO. Studies on primary lung fibroblasts revealed that either primary lung fibroblast-derived exosomes or pulmonary fibrosis-derived BALF-EXO could induce the proliferation of primary lung fibroblasts via intrinsic Wnt5a.
-
miR-21 promotes type 1 collagen and type 3 collagen synthesis through inhibition of platelet-responsive protein type 1 expression, which in turn promotes the development of pulmonary fibrosis. Upregulated levels of exosomal miR-21 have been found in the lung tissue of patients with idiopathic fibrosis. The miR-21-containing serum-derived exosomes are involved in and promote the development of pulmonary fibrosis, which may serve as an indicator of prognosis.
-
In addition to components such as nucleic acids and proteins in exosomes, the associated inflammatory factors carried in exosomes can also be used as a basis for determining the onset of lung disease. The elevated levels of various inflammatory factors including TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-10 contained in exosomes suggest the occurrence of inflammatory response in acute lung injury.
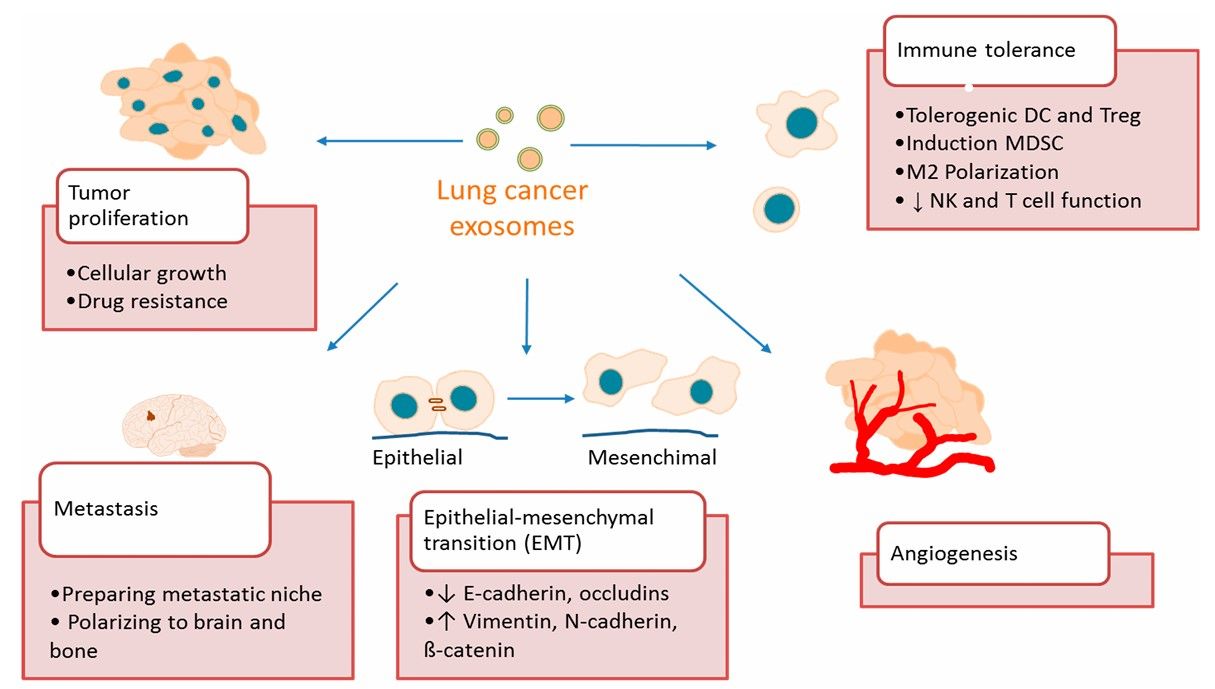 Fig. 2 Role of exosomes in lung cancer.2
Fig. 2 Role of exosomes in lung cancer.2
Features
-
Advanced Diagnostic Capabilities:
-
Makes use of exosome-based biomarkers to identify lung illnesses accurately and early.
-
Provides enhanced sensitivity and specificity compared to traditional diagnostic methods.
-
Non-Invasive Procedure:
-
Involves the collection of biological fluids (such as blood or sputum) for exosome isolation, minimizing discomfort and risk to patients.
-
High-Resolution Molecular Analysis:
-
Employs cutting-edge technologies such as NTA and mass spectrometry to characterize exosome content.
-
Allows for detailed profiling of exosomal proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids relevant to lung diseases.
-
Research and Clinical Integration:
-
Closes the gap that exists between clinical application and research findings.
-
Promotes further studies and validations in various lung disease contexts, including COPD, lung cancer, and pulmonary fibrosis.
As a novel biomarker for lung disease diagnosis, exosomes have the advantages of being easily accessible, widely available, highly stable in various body fluids, and intracellular cargoes that reflect well the physiological and pathological status of their parental cells. Creative Biolabs provides an innovative platform for exosome isolation and profiling to expand the prospects of exosome application in lung disease diagnosis. Please contact us to learn more.
FAQs
Q: How are exosomes isolated from biological samples?
A: Exosomes are typically isolated using methods such as ultracentrifugation, size exclusion chromatography, or precipitation-based techniques. These methods help separate exosomes from other components in biological fluids like blood or sputum.
Q: What technologies are used to analyze exosomes?
A: Exosome analysis can be facilitated by advanced technologies such as next-generation sequencing, mass spectrometry, and NTA. These technologies help profile exosome content in detail, identifying potential biomarkers for lung diseases.
Q: Can exosome-based diagnostics replace traditional methods?
A: While exosome-based diagnostics offer promising advantages, such as non-invasive sampling and enhanced biomarker detection, they are currently complementary to traditional diagnostic methods. They may not entirely replace conventional methods but can significantly improve diagnostic accuracy and provide additional insights.
Q: What possible drawbacks might exosomes have for lung disease diagnosis?
A: Challenges include standardizing exosome isolation and analysis methods, ensuring reproducibility and reliability of results, and addressing potential variability in exosomal biomarkers. Furthermore, to verify clinical utility, additional validation in larger patient cohorts is required.
Q: Is exosome-based lung disease diagnosis currently available in clinical practice?
A: As of now, exosome-based diagnostics are primarily used in research settings and are in various stages of clinical development. Some diagnostic tests and platforms may be available in specialized centers, but widespread clinical adoption is still under development.
References
-
Gurunathan, Sangiliyandi, et al. "Review of the isolation, characterization, biological function, and multifarious therapeutic approaches of exosomes." Cells 8.4 (2019): 307. Under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
-
Sandúa, Amaia, Estibaliz Alegre, and Álvaro González. "Exosomes in lung cancer: Actors and heralds of tumor development." Cancers 13.17 (2021): 4330. Under Open Access license CC BY 4.0. The image was modified by revising the title.
For Research Use Only. Cannot be used by patients.
Related Services:

 Fig. 1 Diagnostic and therapeutic applications of exosomes.1
Fig. 1 Diagnostic and therapeutic applications of exosomes.1
 Fig. 2 Role of exosomes in lung cancer.2
Fig. 2 Role of exosomes in lung cancer.2








