Tumor Diagnosis-Applied Exosomes
Overview Services Features FAQs
Tumor-derived exosomes (TDEs) consist of various molecular components such as lipids, tumor-associated proteins, and nucleic acids that mediate tumor formation and invasion. With many years of research experience in the field of exosome tumor diagnostic applications, Creative Biolabs specializes in providing unique insights and customized research services related to exosomes in tumor diagnosis.
Rationale
TDEs, which are continuously released extracellularly through exocytosis during tumorigenesis and progression, have the corresponding antigens and abundant molecular information inherited from their donor sources to closely participate in pathological processes such as tumor progression, formation of metastatic ecological niches, and immune evasion. Abnormal cells and diseased organs can produce higher levels of exosomes than the normal physiological state and have increased heterogeneity with tumor evolution, suggesting that TDEs are potential markers with promising applications in the fields of tumor diagnosis, prognosis, and therapeutic evaluation.
Liquid biopsies compensate for the shortcomings of traditional solid biopsies and show significant advantages in terms of precision, dynamics, and individualization of medical diagnosis. TDEs as diagnostic markers combined with liquid biopsies are promising platforms for non-invasive tumor diagnosis and prognostic assessment.
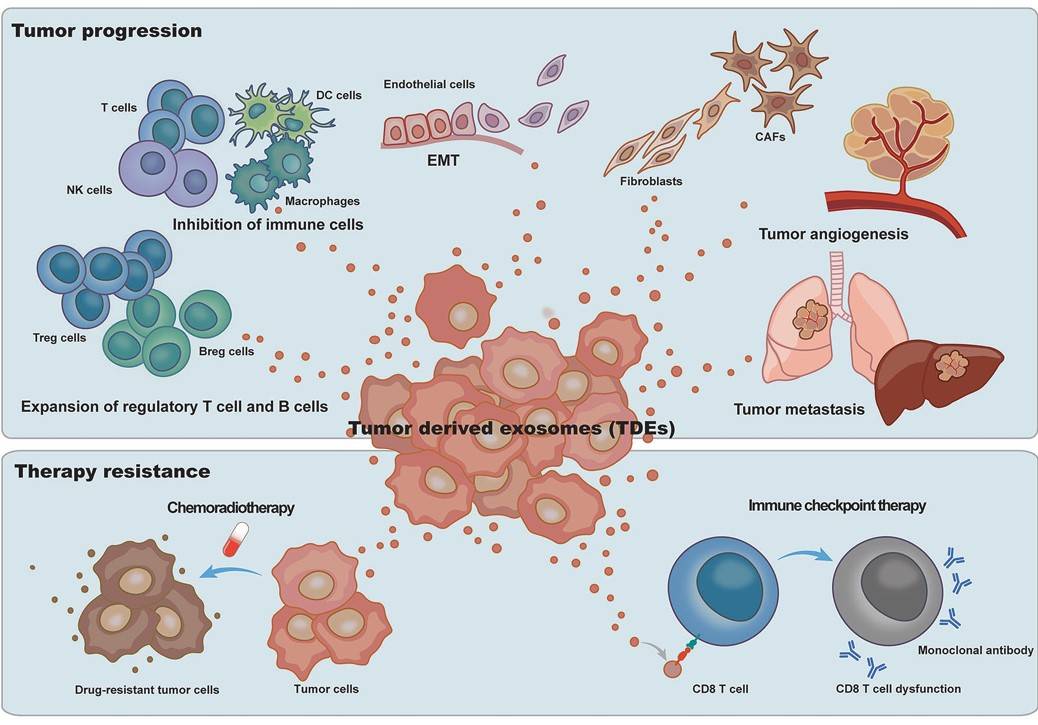 Fig.1 TDEs play critical roles in tumor progression and impede tumor therapy.1, 3
Fig.1 TDEs play critical roles in tumor progression and impede tumor therapy.1, 3
Exosomes in Tumor Diagnosis at Creative Biolabs
The histological analysis and sequencing of exosomes isolated from different biological fluid samples to analyze their components provide a diagnostic basis for the assessment of tumorigenesis and pathological processes and the development of new tumor markers. Applications of exosomes involved in tumor diagnosis include:
TDE Features in Tumor Diagnosis
In different stages of tumor growth and metastasis, there are often detectable differences in TDEs' contents such as protein expression profiles and miRNAs, which involve their participation in various tumor stages such as tumor invasion and migration, epithelial-mesenchymal transition, angiogenesis, microenvironment reconstruction, and other processes of tumor development and regulation of tumor-related immunity in an autocrine or paracrine way.
-
On the one hand, TDEs surface proteins and lipids are involved in antigenic rapture, inducing an immune response and mediating tumor metastasis to target areas. For example, glycoproteins and integrins of TDEs are associated with their target specificity and mediate tumor migration, which can be used as prognostic markers of tumor metastasis and predict organ-specific metastasis.
-
On the other hand, TDEs can also deliver luminal cytokines including pro-inflammatory cytokines, pro-angiogenic factors, and tumor growth factors for the rebuilding of the tumor microenvironment. Meanwhile, TDEs deliver miRNAs that regulate the expression of tumor-related genes, which are the basis for diagnosing tumor pathological staging, while TDEs proteins are also closely related to chemotherapy resistance of tumors.
In summary, powerful evidence suggests that TDEs and their contents carry tumor-related information and can be used as significant biomarkers for tumor diagnosis.
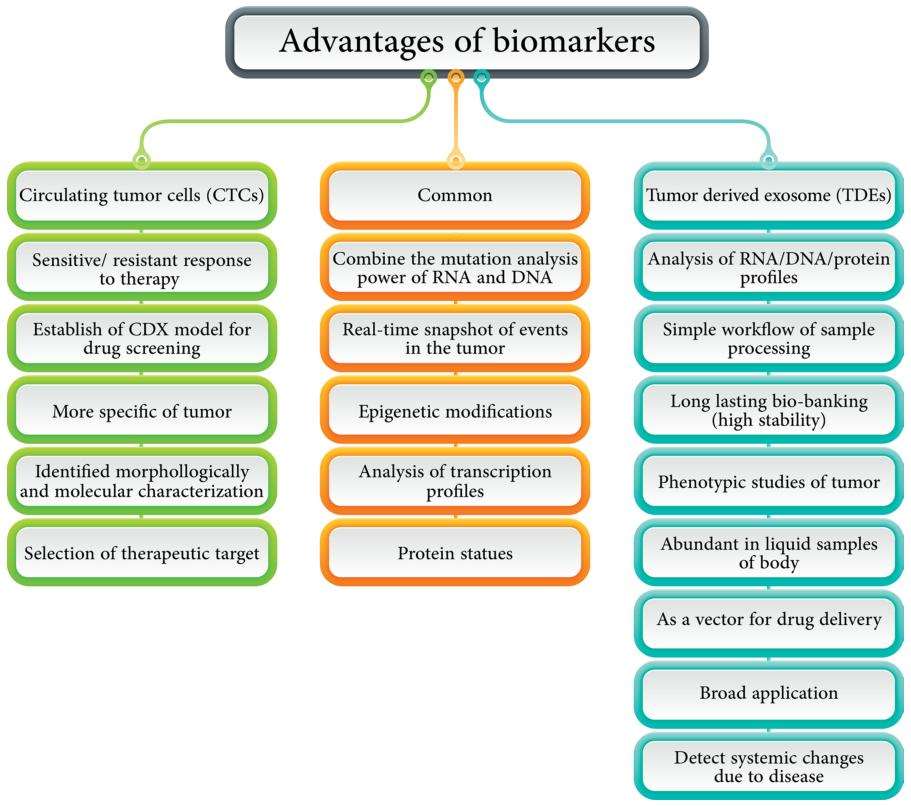 Fig.2 Comparison of the merits of CTCs (green boxes) and TDEs (blue boxes) together.2, 3
Fig.2 Comparison of the merits of CTCs (green boxes) and TDEs (blue boxes) together.2, 3
Tumor-derived exosomes mirror the rich biological information related to tumorigenesis and the development of their tumor source, serving as liquid biopsy biomarkers in tumor diagnosis. At Creative Biolabs, our expert team is long committed to studying the application and biological value of exosomes in tumor diagnosis, involving exosomes as biomarkers in the early diagnosis, prognosis, and therapeutic response of a wide range of tumors. Please feel free to contact us.
FAQs
Q: How are exosomes related to tumor diagnosis?
A: Exosomes derived from tumor cells often carry specific biomarkers that reflect the presence and characteristics of the tumor. By analyzing these biomarkers, researchers can detect tumors earlier, monitor disease progression, and evaluate responses to treatment.
Q: What benefits might exosomes offer in the context of tumor diagnosis?
A: Exosomes provide a non-invasive or minimally invasive approach to tumor diagnosis. They can be obtained from bodily fluids such as blood, urine, or saliva, making the diagnostic process less invasive compared to traditional biopsy methods. Additionally, exosomes can offer insights into the molecular composition of the tumor, aiding in personalized treatment plans.
Q: How are exosomes collected for diagnostic purposes?
A: Exosomes are typically collected from blood, urine, or other bodily fluids through a process called centrifugation. This process separates the exosomes from other cellular components, allowing for further analysis in the laboratory.
Q: What techniques are used to analyze exosomes in tumor diagnosis?
A: Several techniques are employed to analyze exosomes, including NTA, electron microscopy, flow cytometry, and various molecular assays such as PCR and RNA sequencing. These methods help identify and quantify the biomarkers carried by exosomes.
Q: What future developments are expected in exosome-based tumor diagnosis?
A: Future developments may include enhanced methods for exosome isolation and analysis, improved understanding of exosome biology, and the integration of exosome-based diagnostics into routine practice. Research and technological developments are probably going to improve these diagnostic instruments' accessibility and accuracy.
Q: Can exosome-based diagnostics be used for all types of tumors?
A: Diagnostics based on exosomes exhibit potential for various cancer types, such as pancreatic, lung, breast, and prostate cancers. However, depending on the particular biomarkers implicated and the type of tumor, the efficacy and accuracy may differ. The goal of ongoing research is to broaden the range of cancer types for which exosome-based diagnostics can be used.
References
-
Li, Ye, et al. "Targeted inhibition of tumor-derived exosomes as a novel therapeutic option for cancer." Experimental & molecular medicine 54.9 (2022): 1379-1389.
-
Vafaei, Somayeh, et al. "Potential theranostics of circulating tumor cells and tumor-derived exosomes application in colorectal cancer." Cancer cell international 20 (2020): 1-15.
-
Under Open Access license CC BY 4.0. The image was modified by revising the title.
For Research Use Only. Cannot be used by patients.
Related Services:

 Fig.1 TDEs play critical roles in tumor progression and impede tumor therapy.1, 3
Fig.1 TDEs play critical roles in tumor progression and impede tumor therapy.1, 3
 Fig.2 Comparison of the merits of CTCs (green boxes) and TDEs (blue boxes) together.2, 3
Fig.2 Comparison of the merits of CTCs (green boxes) and TDEs (blue boxes) together.2, 3









