Title: Exosome-like nanovesicles derived from Phellinus linteus inhibit Mical2 expression through cross-kingdom regulation and inhibit ultraviolet-induced skin aging.
Research Methods:
-
Facial imaging systems are used to assess the anti-aging effects of Phellinus linteus extract on the facial and forearm skin of volunteers.
-
Exosomes derived from Phellinus linteus are isolated using differential centrifugation techniques, and their morphology and particle size are determined to confirm that the extracted material is indeed exosomes.
-
Cell proliferation assays using CCK8 are conducted to study the effects of exosomes derived from Phellinus linteus on skin cells subjected to ultraviolet (UV) radiation.
-
The anti-aging effects of exosomes derived from Phellinus linteus are evaluated by measuring levels of MMP1, COL1A2, ROS, MDA, SOD enzyme activity, and SA-β-Gal in skin cells.
-
miRNA sequencing analysis is performed on exosomes derived from Phellinus linteus to identify key miR-CM1.
-
miR-CM1 is transfected into cells to evaluate its role in anti-UV-induced cell aging. Further, qPCR and Western blot are used to detect the expression of Mical2 and its interaction with miR-CM1.
-
An in vivo mouse model of UV-induced skin aging is established. Engineered exosomes loaded with miR-CM1 and exosomes derived from Phellinus linteus are used to treat this mouse model to assess the anti-aging effects of miR-CM1 from Phellinus linteus in vivo.
Research Results:
a. Phellinus linteus extract demonstrates significant anti-aging effects on the facial and forearm skin of volunteers, reducing skin blemishes, UV spots, wrinkles, and more.
b. Exosomes derived from Phellinus linteus exhibit the ability to inhibit UV-induced skin cell aging, including reduced MMP1 expression, increased COL1A2 expression, and decreased ROS levels.
c. miR-CM1 is identified as one of the miRNAs present in exosomes derived from Phellinus linteus. It inhibits Mical2 expression through cross-kingdom regulation, leading to reduced levels of cellular aging markers.
d. In the in vivo mouse model, engineered exosomes containing miR-CM1 and exosomes derived from Phellinus linteus both demonstrate anti-aging effects, including reduced skin thickness and increased collagen content.
Conclusion: Exosomes derived from Phellinus linteus carry miR-CM1, which plays an anti-aging role by inhibiting the expression of Mical2, reducing ROS levels, and lowering the levels of cellular aging markers. This research provides a potential anti-aging treatment approach and forms an important scientific basis for the development of anti-aging products and therapies.
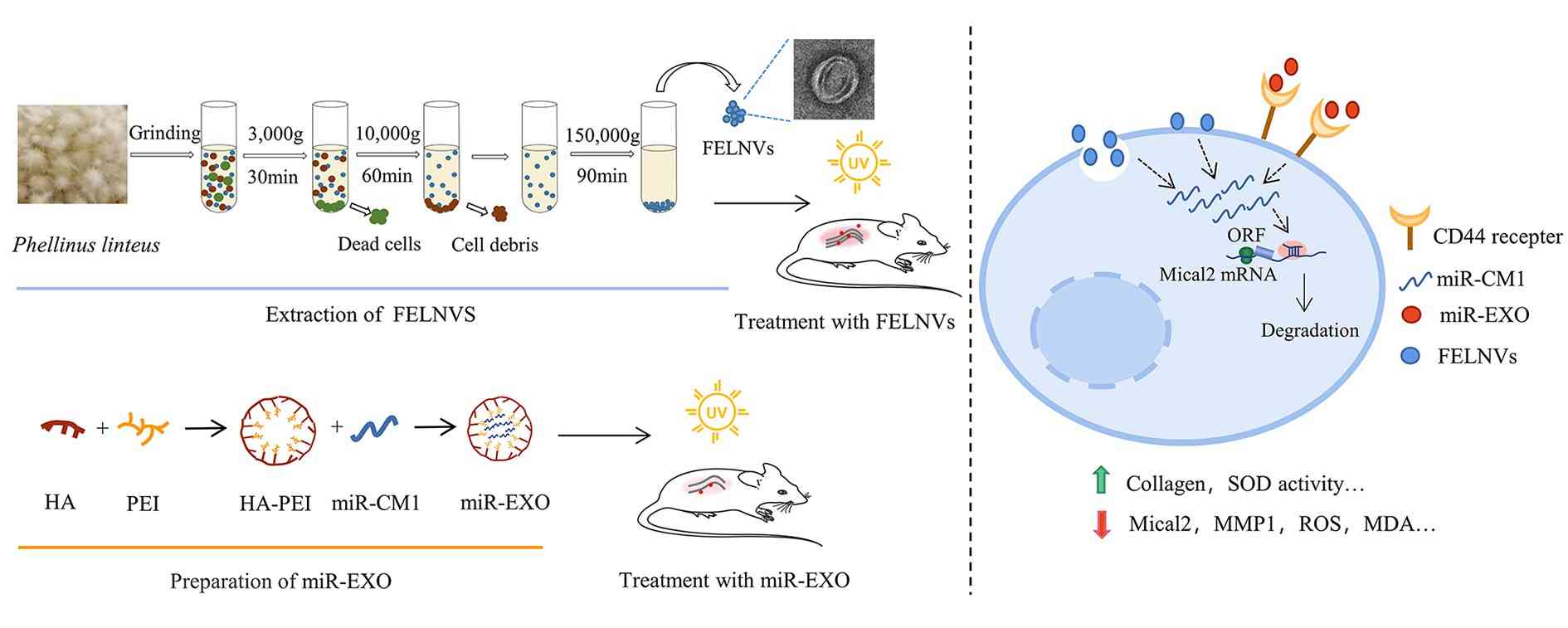 Fig.1 Exosomes derived from Phellinus linteus inhibit Mical2 expression through cross-kingdom regulation and inhibit ultraviolet-induced skin aging.1,2
Fig.1 Exosomes derived from Phellinus linteus inhibit Mical2 expression through cross-kingdom regulation and inhibit ultraviolet-induced skin aging.1,2
Plant-Derived Exosome Isolation
Plant-Derived Exosome Identification
High-Throughput Screening Analysis (Proteins, RNA, Lipids and Metabolites)
Large-Scale Production of Plant-Derived Exosomes

 Fig.1 Exosomes derived from Phellinus linteus inhibit Mical2 expression through cross-kingdom regulation and inhibit ultraviolet-induced skin aging.1,2
Fig.1 Exosomes derived from Phellinus linteus inhibit Mical2 expression through cross-kingdom regulation and inhibit ultraviolet-induced skin aging.1,2









