Exosome Cargo Pre-loading Service
Overview Services Features FAQs
Exosome-based delivery platform offers significant advantages, making it an excellent choice due to its specificity, stability, extended circulating half-life, and biocompatibility with minimal toxicity to the target tissue. At present, Creative Biolabs has successfully realized the loading of cargo into exosomes by using the pre-loading strategy.
Introduction of Pre-loading Strategy
Loading cargo into exosomes requires bypassing the barrier of the outer membrane. Exosomes can be pre-loaded in situ by adding exogenous drugs to parental cells. Co-expressed proteins in parental cells can also be guided into exosomes through designed protein-protein interactions. In the pre-loading technique, the exosomes are loaded with cargos indirectly, that is to say, the parental cells are incubated with cargos at room temperature, and the selected proteins or drugs can be loaded in advance. When the cells release exosomes, these vesicles will be loaded with cargo. This strategy is particularly conducive to the loading and delivery of oligonucleotides.
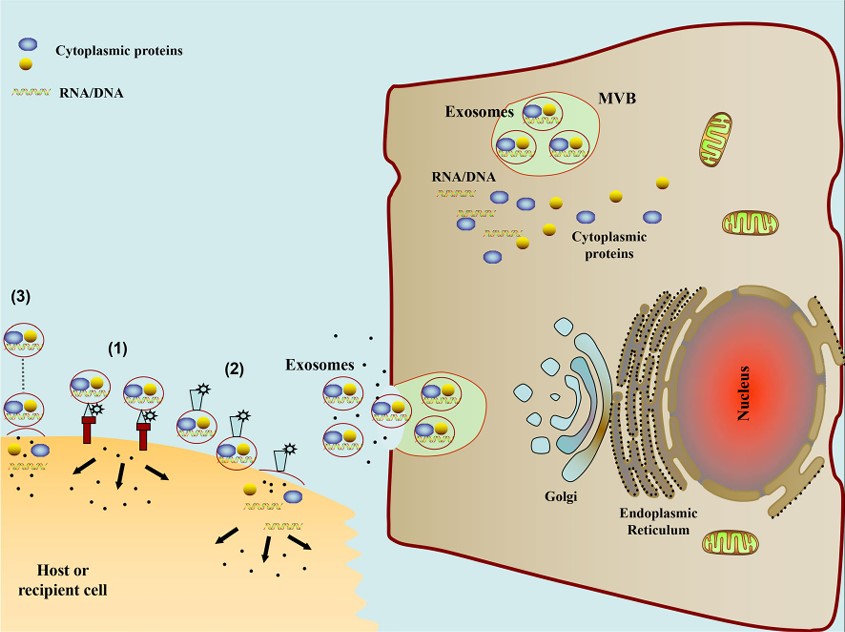 Fig. 1 Schematic diagram of the exosome-mediated intercellular communication pathway.1
Fig. 1 Schematic diagram of the exosome-mediated intercellular communication pathway.1
Cargo Pre-loading Service at Creative Biolabs
The majority of exosome modification has been carried out on parental cells, which are subsequently cultivated to produce the modified exosomes, thanks to the availability of numerous cellular engineering techniques. Possible pre-loading strategies include:
-
Introducing therapeutically active chemicals into parental cells through transfection or infection, followed by their release through exosomes;
-
Directly loading parental cells with drugs and then releasing them in exosomes, mainly used in small molecule chemical drugs with low cytotoxicity.
When transfecting cells, protein sequences, and various RNA types are frequently employed, which eventually modifies the released exosomes' phenotype. Lipid techniques (e.g., Lipofectamine) may be necessary for genetic engineering tactics to load cargo or achieve the required gene expression. People can modify the therapeutic payload that exosomes carry by altering the way they are synthesized.
 Fig.2 Design strategies for the modifications of exosomal surface.2
Fig.2 Design strategies for the modifications of exosomal surface.2
Technical Advantages
-
The output of exosomes is controllable. This pre-loading strategy is suitable for the types of projects that require downstream animal experiments;
-
We can provide the services of cell culture and stable cell line construction, providing the prerequisite for mass production of exosomes loaded with cargo;
-
No damage to exosome structure.
Exosomes can function as information messengers between cells by delivering encapsulated proteins and genetic information to target cells. Creative Biolabs has successfully established the pre-loading strategy to efficiently load exogenous cargos into exosomes. Please contact us with your demands.
FAQs
Q: What is exosome cargo pre-loading, and how does it differ from traditional cargo loading methods?
A: Exosome cargo pre-loading involves loading therapeutic cargo into exosomes during their biogenesis within donor cells, before their secretion. This approach offers advantages in cargo stability and loading efficiency compared to post-secretion loading methods, ensuring uniform cargo distribution within exosomes.
Q: How does exosome cargo pre-loading enhance therapeutic efficacy?
A: Exosome cargo pre-loading ensures efficient encapsulation of therapeutic cargo within exosomes, enhancing cargo stability and protecting it from degradation. This promotes sustained release and targeted delivery of therapeutics to recipient cells, ultimately improving therapeutic efficacy and reducing off-target effects.
Q: What are the advantages of using exosome cargo pre-loading over other loading techniques?
A: Exosome cargo pre-loading offers several advantages over post-secretion loading techniques, including improved cargo stability, uniform cargo distribution within exosomes, and enhanced loading efficiency. Moreover, pre-loaded exosomes exhibit enhanced bioavailability and therapeutic efficacy, making them ideal candidates for drug delivery applications.
Q: How can researchers evaluate the efficacy of exosome cargo pre-loading in their studies?
A: Researchers can evaluate the efficacy of exosome cargo pre-loading by assessing cargo loading efficiency, release kinetics, and therapeutic effects in relevant cell culture models or animal studies. Additionally, monitoring changes in cellular pathways or biomarkers associated with therapeutic responses provides insights into exosome-mediated effects in target cells.
References
-
Zhang, Yuan, et al. "Exosomes: biogenesis, biologic function and clinical potential." Cell & bioscience 9 (2019): 1-18. Under Open Access license CC BY 4.0. The image was modified by revising the title.
-
Xu, Mengqiao, et al. "Recent advancements in the loading and modification of therapeutic exosomes." Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology 8 (2020): 586130. Under Open Access license CC BY 4.0. The image was modified by extracting and using only a part of the original image.
For Research Use Only. Cannot be used by patients.
Related Services:

 Fig. 1 Schematic diagram of the exosome-mediated intercellular communication pathway.1
Fig. 1 Schematic diagram of the exosome-mediated intercellular communication pathway.1
 Fig.2 Design strategies for the modifications of exosomal surface.2
Fig.2 Design strategies for the modifications of exosomal surface.2









