Exosome Cargo Loading Services
Overview Services Features FAQs
Exosomes can be effectively loaded with therapeutic medications, including synthetic oligonucleotides, small molecule chemicals, and viral vectors, as multiple investigations have demonstrated. To maximize exosome loading technology and raise production efficiency, Creative Biolabs offers exosome cargo loading services.
Overview
-
Exosomes are small extracellular vesicles that play a critical role in intercellular communication. They can be engineered to transport a variety of payloads, such as tiny compounds, RNAs, and proteins.
-
Exosome cargo loading services are designed to optimize the delivery of these agents for research applications. Our services encompass the entire spectrum of exosome cargo loading, from the isolation and purification of exosomes to the precise loading of desired cargo.
-
Our expertise extends to customizing exosomes for targeted delivery, enhancing the therapeutic potential of the cargo.
Cargo Loading Services in Creative Biolabs
Proteins - In addition to loading with small molecules, a key component of our exosome engineering services involves loading with large molecules such as proteins. It is possible to tailor and target the proteins onto the surfaces of exosomes, allowing for tissue targeting and surface display of proteins. Besides, proteins can also be loaded inside the exosomes for therapeutic delivery, leveraging both the natural properties of exosomes and the specificity of biological molecules.
Nucleic acids - Small interference RNA (siRNA), miRNA, short hairpin RNA (shRNA), and other nucleic acids can be incorporated into exosomes using different strategies. Numerous studies have employed exosomes from different sources as carriers of small RNAs to treat various diseases, especially brain diseases and tumors.
Several distinct approaches can be utilized at Creative Biolabs for cargo loading into exosomes:
Through the processes of electroporation, lipofection, sonication, and calcium chloride, exosomes can be directly loaded with exogenous nucleic acids or medications.
Loading the foreign payload into parental cells for release into exosomes.
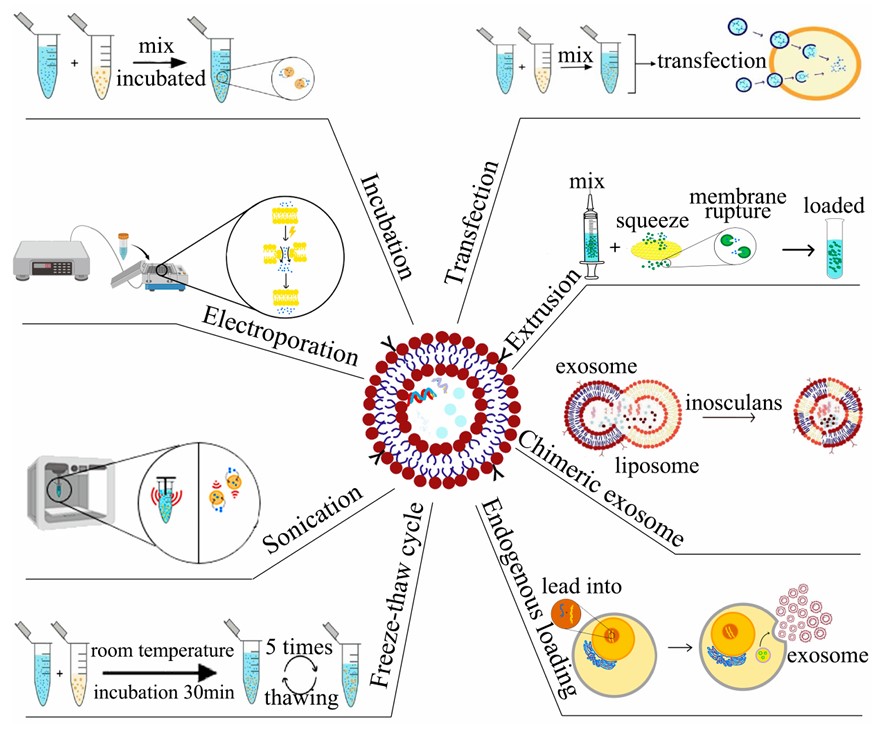 Fig. 1 Strategies for exosome drug loading.1
Fig. 1 Strategies for exosome drug loading.1
Features of Cargo Loading Services in Creative Biolabs
-
Customization: Ability to tailor cargo loading based on specific therapeutic needs.
-
Efficiency: High loading efficiency ensures maximum cargo delivery.
-
Stability: Maintaining cargo stability during the loading process to preserve efficacy.
-
Versatility: Accommodation of various cargoes including RNA, DNA, proteins, and small molecules.
-
Scalability: Capability to scale production for further applications.
Backed by our expert scientists and technology platform, Creative Biolabs can provide custom-specific cargo-loading services for proteins, nucleic acids, and small molecules of interest. Please contact us to discuss your project requirements.
FAQ
Q: How can exosomes be loaded with cargo for specific applications?
A: Exosomes can be loaded with cargo using various techniques such as electroporation, incubation with cargo-containing solutions, or engineering cells to produce exosomes with desired cargo. These methods allow for precise loading of therapeutic molecules or diagnostic agents into exosomes for targeted delivery.
Q: What kinds of cargo are possible to put into exosomes?
A: A wide range of cargo, including small molecules, nucleic acids (DNA, RNA), proteins, and even nanoparticles, can be loaded into exosomes. This versatility enables the delivery of therapeutics, such as drugs or gene therapies, and the development of exosome-based diagnostics and imaging agents.
Q: How does cargo loading affect exosome stability and functionality?
A: Cargo loading methods can influence the stability and functionality of exosomes. Careful optimization of loading techniques is crucial to maintain exosome integrity and ensure cargo stability during storage and delivery. Properly loaded exosomes retain their ability to interact with target cells and mediate therapeutic effects.
Q: What are the potential applications of exosome cargo loading in drug development?
A: Exosome cargo loading holds promise for various applications in drug development, including targeted drug delivery, immunotherapy, regenerative medicine, and biomarker discovery. By harnessing the natural properties of exosomes and customizing their cargo, researchers can advance the development of novel therapeutics and diagnostics with enhanced efficacy and specificity.
Reference
-
Zeng, Haifeng, et al. "Current Strategies for Exosome Cargo Loading and Targeting Delivery." Cells 12.10 (2023): 1416. Under Open Access license CC BY 4.0. The image was modified by revising the title.
For Research Use Only. Cannot be used by patients.
Related Services:

 Fig. 1 Strategies for exosome drug loading.1
Fig. 1 Strategies for exosome drug loading.1









