Renal Cell Carcinoma Tissue Exosome Research and Application
Renal cell carcinoma (RCC) is the most common type of malignancy in the kidney. Because RCC is not detected early, most patients are already at an advanced stage when they are first diagnosed, and the tumor has already spread or metastasized. Therefore, it is necessary to find new effective biomarkers or molecular targets for early detection of RCC to prevent its malignant progression and improve the survival of RCC patients. Exosomes are nanoscale membranous vesicles that complete intercellular communication through efflux-fusion-endocytosis. They are widely present in the tissue microenvironment and can be transported into body fluids through circulation. Many studies have found that exosomes from various types of cells in RCC tissue play an important role in regulating tumor proliferation and metastasis, angiogenesis, and immune escape. However, most of these studies are based on exosomes derived from body fluids and RCC cell culture supernatants to propose potential liquid biopsy markers or therapeutic targets in exosomes. Since the exosomes derived from the supernatant of RCC cells do not have the authenticity and complexity in vivo and the body fluid exosomes are mixed with exosomes from other tissues or organs, these previous research results may not really indicate the communication mechanism of RCC exosomes in the microenvironment. Creative Biolabs has been committed to helping customers screen and verify promising active molecules in tumor exosomes and can isolate exosomes in RCC tissues for customers to promote the diagnosis and treatment of RCC in the clinic.
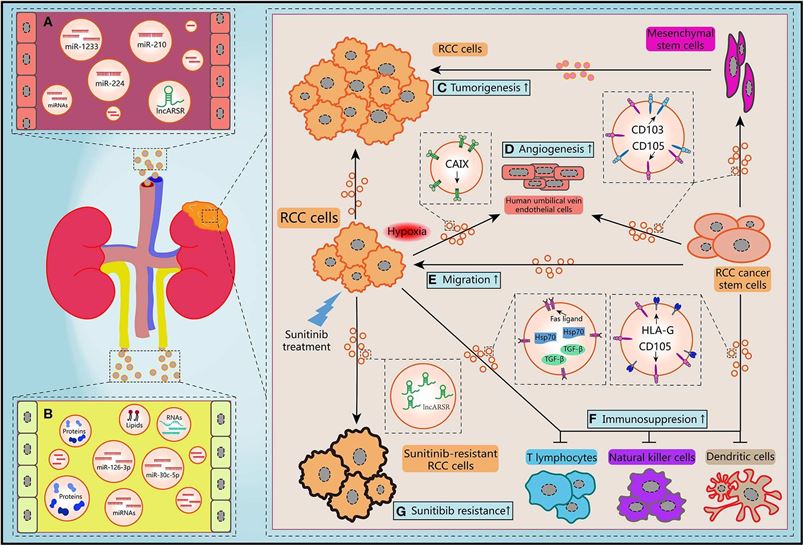 Fig.1 Schematic diagram of the biological features of EVs.1,2
Fig.1 Schematic diagram of the biological features of EVs.1,2
Renal Cell Carcinoma Tissue Exosome Research and Application
Researchers have extracted extracellular vesicles from the in vitro culture medium of RCC tissue excised during surgery. Then they found a high abundance of azurocidin through proteomic analysis of RCC extracellular vesicles. In order to further verify whether azurocidin in RCC extracellular vesicles can be used as a liquid biopsy marker of RCC, the team analyzed the protein expression profile in serum exosomes from RCC patients. The results showed that azurocidin was highly enriched in both RCC tissue extracellular vesicles and RCC patient serum-derived extracellular vesicles. Subsequent in vivo and in vitro studies found that azurocidin carried by RCC-derived extracellular vesicles could enter vascular endothelial cells and disrupt their membrane permeability, which may play an important role in the metastasis of RCC.
The above results shed light on the characteristics and research strategies of tissue exosomes and provide a strong experimental basis for the early diagnosis and treatment of RCC. Creative Biolabs has been paying attention to the latest progress of exosomes in the research of various diseases. After discovering the research results of tissue exosomes, we have continuously optimized the extraction process of tissue exosomes based on reports, and have developed a set of mature tissue exosome extraction method. Based on this report, we can provide customers with optimized RCC tissue exosome one-stop technical services, including renal cell carcinoma tissue exosome extraction service, exosome identification service, exosome profiling services, combined research service with body fluid exosomes, combined research services with single-cell transcriptomics and single-cell proteomics, functional research service for tissue exosomes, and possible therapeutic research service for tissue exosomes. If you want to study the exosome regulation mechanism of RCC in a more realistic tumor microenvironment, please contact us now.
References
-
Qin, Z.; et al. Extracellular vesicles in renal cell carcinoma: multifaceted roles and potential applications identified by experimental and computational methods. Frontiers in Oncology. 2020, 10:724.
-
under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only. Cannot be used by patients.
Related Services:

 Fig.1 Schematic diagram of the biological features of EVs.1,2
Fig.1 Schematic diagram of the biological features of EVs.1,2








