Therapeutic Exosomes for Asthma
Asthma is a heterogeneous disease with respiratory symptoms such as cough, chest tightness, wheezing, and shortness of breath as the main clinical manifestations. Recent studies have shown that exosomes secreted from autologous cells can directly stimulate target cells or aggravate or attenuate inflammatory responses in recipient cells by transferring proteins, lipids, nucleic acids, and metabolites to target cells. Exosomes have important biological functions in regulating airway immune responses. Creative Biolabs has always been a leading exosome service provider, dedicated to providing customers with high-quality services and excellent technology.
The Relationship between Exosomes and Asthma
Asthma is a chronic inflammatory response in the respiratory tract, leading to various pathological changes such as bronchoconstriction, airway remodeling, and mucus hypersecretion. Asthma is prevalent worldwide, with approximately 310 million bronchial asthma sufferers. Atmospheric particulate matter, pollen, dust mites, and animal dander are all allergens of asthma. With the continuous deterioration of air quality and environmental conditions, the incidence of asthma is increasing year by year. Asthma has a great impact on the daily life and work of patients. If effective and reliable measures are not taken in time for treatment, it may cause many diseases, such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, heart failure, etc., and even life-threatening in serious cases. Current scientific advances have shown that all types of inflammatory cells, including neutrophils, dendritic cells, lymphocytes, and eosinophils, release exosomes. In addition, structural lung cells such as airway epithelial cells and airway smooth muscle cells also secrete exosomes. These different cell-derived exosomes play an important role in the pathogenesis of asthma.
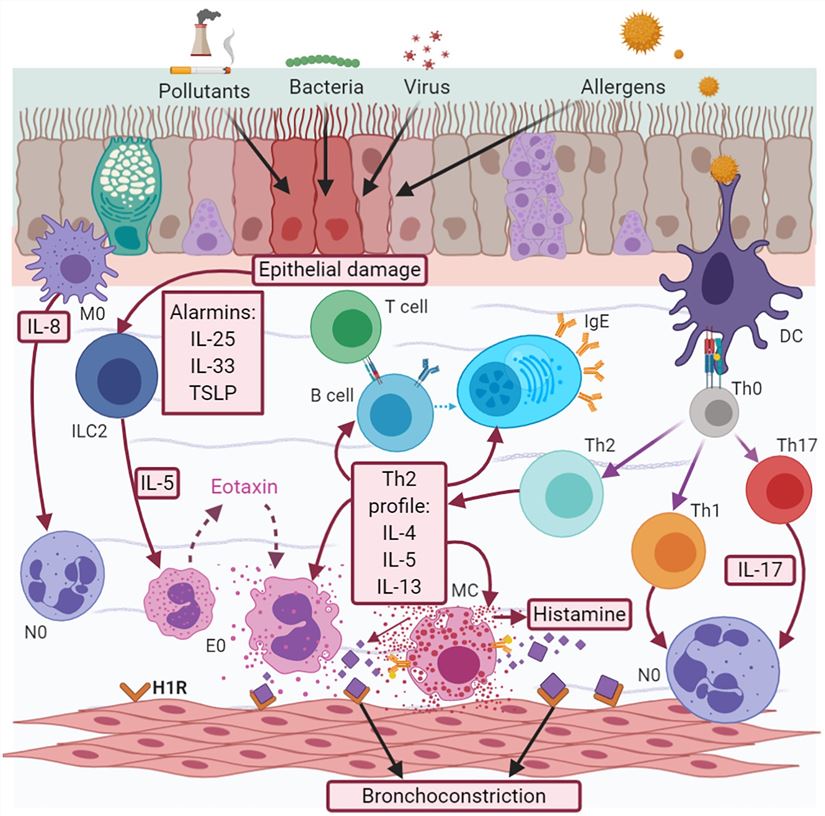 Fig.1 Asthma pathophysiology.1,2
Fig.1 Asthma pathophysiology.1,2
Exosome Therapy for Asthma
At present, the main mechanism of drugs for the treatment of asthma is to directly inhibit the elevated activity of type II cytokines. These drugs can only reduce airway inflammation and cannot accelerate the repair of damaged lungs. Some new studies have shown that mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes (MSC-Exo) can reduce lung inflammation caused by allergic asthma and promote the remodeling of airway structure and function. Intratracheal administration of MSC-Exo in a mouse model of asthma can inhibit tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 1 (TRAF1) by remodeling macrophage polarization, regulating nuclear factor kappa-B (NF-κB) and PI3K/Akt signaling pathways, thereby reducing inflammation and improving asthma. Abnormal proliferation and function of regulatory T cells (Tregs) play an important role in the development of asthma. By treating peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) of asthma patients with MSC-Exo, it has been found that MSC-Exo upregulates the levels of IL-10 and TGF-β1 secreted by PBMCs, thereby promoting the proliferation and immunosuppression of Tregs. This study further demonstrates the potential of MSC-Exo in the treatment of asthma.
Adhering to the rigorous scientific attitude and enthusiastic service attitude, Creative Biolabs has always been a trusted exosome service provider for customers. Our professional scientists can formulate the most rigorous experimental plan for you according to your project needs and escort your exosome drug research and development. Please feel free to contact us to further advance your project.
References
-
Pavón-Romero, GF.; et al. Neuroimmune pathophysiology in asthma. Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology. 2021, 9:663535.
-
under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only. Cannot be used by patients.
Related Services:

 Fig.1 Asthma pathophysiology.1,2
Fig.1 Asthma pathophysiology.1,2








