Therapeutic Exosomes for Renal Failure
The kidney is an important vital organ of the human body, which has the functions of expelling drugs and toxins from the body, regulating water and acid-base balance, and endocrine functions. Chronic kidney disease caused by various causes, which are painless and itchy at the beginning, will eventually develop into renal failure (RF). Currently, RF can only be maintained with dialysis or treated with a kidney transplant. Studies have found that mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes can improve renal failure. Creative Biolabs has always been committed to exosome drugs research, and can provide customers with a full range of technical services.
Renal Failure (RF)
RF is a pathological state of a partial or total loss of renal function caused by the development of various chronic kidney diseases to the later stage. RF can be divided into acute renal failure (ARF) and chronic renal failure (CRF). ARF is rapidly progressive and usually results from acute tubular necrosis. Most ARFs are reversible. However, the main cause of CRF is long-term kidney disease. With time and disease progression, kidney function gradually declines, leading to the occurrence of RF. Some chronic kidney diseases that cause RF include primary glomerulonephritis, diabetic nephropathy, hypertensive nephropathy, renal interstitial tubular nephropathy, and polycystic kidney disease. The progression of chronic kidney disease usually progressively worsens as the glomerular filtration rate (GFR) decreases. In the end stage, chronic kidney disease progresses to RF. At this time, the patient's renal function was severely decreased, with bilateral renal atrophy, anorexia, and severe anemia.
Therapeutic Exosomes for RF
Renal fibrosis is a critical step toward renal failure. Renal fibrosis is an abnormal buildup of fibrotic material within the kidney that impedes kidney function and may lead to eventual RF. Peritubular capillary (PTC) loss and renal microvascular damage are typical features of renal fibrosis. Studies have shown that mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) may improve RF by paracrine transfer of glial cell-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF). Therefore, a research group transfected GDNF into human adipose-derived MSCs by a lentiviral transfection system and isolated exosomes (GDNF-AMSC-exos). In a unilateral ureteral occlusion (UUO) mouse model, GDNF-AMSC-exos ameliorated tubulointerstitial fibrosis by activating the angiogenic program in PTC via SIRT1/eNOS signaling pathway. This study shows that GDNF-AMSC-exos is promising for the treatment of RF.
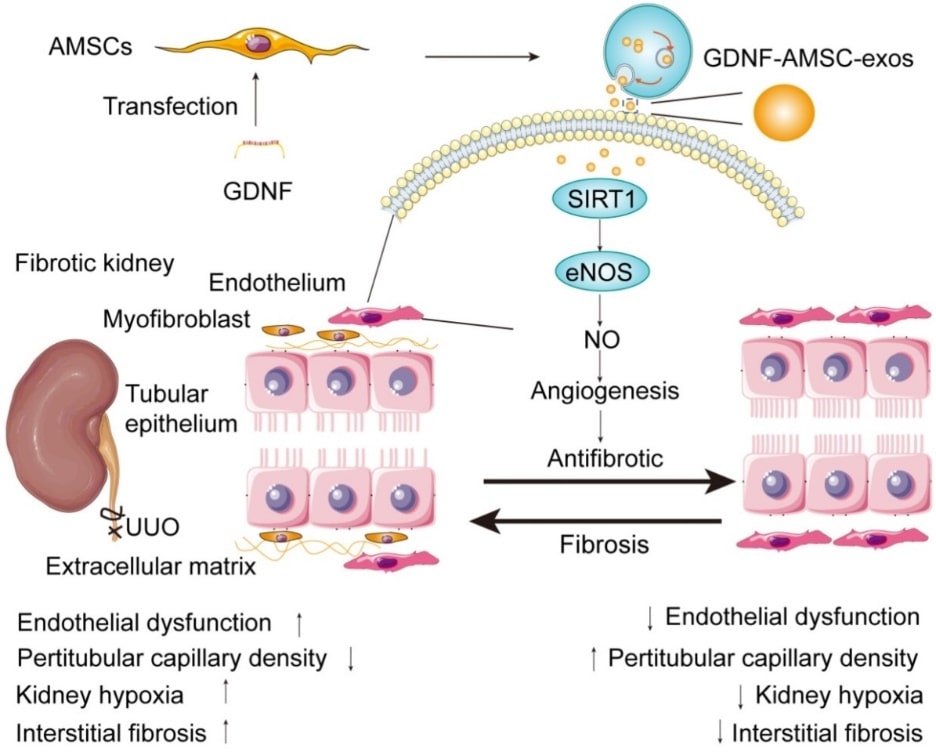 Fig.1 The Proposed mechanism by which GDNF-AMSC-exos ameliorate damage to UUO-treated kidneys by activating the SIRT1/eNOS signaling pathway.1,2
Fig.1 The Proposed mechanism by which GDNF-AMSC-exos ameliorate damage to UUO-treated kidneys by activating the SIRT1/eNOS signaling pathway.1,2
Creative Biolabs has a professional team of scientists and advanced exosome research equipment, which can provide customers with the most comprehensive services and the most detailed experimental data. Please feel free to contact us to further explore exosome therapy ideas for RF.
References
-
Chen, L.; et al. Exosomes derived from GDNF-modified human adipose mesenchymal stem cells ameliorate peritubular capillary loss in tubulointerstitial fibrosis by activating the SIRT1/eNOS signaling pathway. Theranostics. 2020, 10(20):9425-9442.
-
under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only. Cannot be used by patients.
Related Services:

 Fig.1 The Proposed mechanism by which GDNF-AMSC-exos ameliorate damage to UUO-treated kidneys by activating the SIRT1/eNOS signaling pathway.1,2
Fig.1 The Proposed mechanism by which GDNF-AMSC-exos ameliorate damage to UUO-treated kidneys by activating the SIRT1/eNOS signaling pathway.1,2








