Creative Biolabs is a leader in the field of antibody and antibody fragments conjugation, especially the single domain antibody (sdAb) conjugation. We have developed a range of custom sdAb bioconjugation services, including quantum dots conjugation, fluorophores conjugation, PEGylation conjugation, biotins conjugation and so on. We also offer customize bioconjugation service to meet our clients’ specific research programs.
Bioconjugation is a chemical strategy to form a stable covalent link between two molecules. Synthetically modified biomolecules can have diverse functionalities, such as tracking cellular actions, revealing enzyme function, determining protein biodistribution, and specific biomarkers. The common bioconjugations are coupling of a small molecule, such as biotin or fluorescent dye, to antibodies, or protein-protein conjugations, such as the coupling of an antibody to an enzyme. Moreover, antibodies conjugated to oligosaccharides, nucleic acids, and synthetic polymers are widely used in pharmaceutical industry.
Single domain antibodies (sdAbs) are antibody fragment consisting of a single monomeric variable antibody domain, derived from the heavy-chain-only antibodies produced by camelids or sharks, or the specific developed human VH and VL domain. Compared to conventional antibodies, sdAb has advantages that cannot be ignored. The fusion of biological molecular to sdAb targeting proteins allows nanometer spatial resolution and minimal linkage error because of the small size and high affinity of sdAb. Therefore, conjugated sdAbs have been found significant applications for enhanced stability, sensitive and functionalities in diagnostics and therapeutics.
 Fig.1 SdAb Conjugation.
Fig.1 SdAb Conjugation.
Our extensive range of custom sdAb conjugation service including but not limited to:
Table 1. Hot Services of SdAb Conjugation
The applications of sdAb conjugation services including but not limited to:
Based on our deep knowledge and rich experience in biomaterial conjugation, Creative Biolabs offers advanced processes for various sdAb conjugation services. Our services can be tailored to meet our customers’ unique requirements under a fast, reliable and affordable manner. If you are interested in our sdAb conjugation service, please feel free to inquire us to for more details.
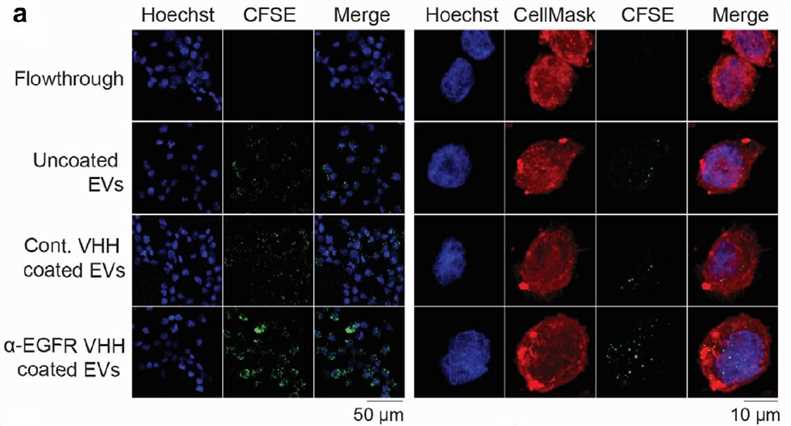 Fig. 2 Conjugation of RBCEVs with EGFR‐targeting peptides increases the uptake of the EVs by EGFR‐positive cells. (Tin Chanh Pham, 2021)
Fig. 2 Conjugation of RBCEVs with EGFR‐targeting peptides increases the uptake of the EVs by EGFR‐positive cells. (Tin Chanh Pham, 2021)
Here, researchers describe a new method of partially covalently combining EV with high copy number targeting. The combination of EV with an epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) targeting peptide or anti-EGFR single domain antibody can promote its accumulation in EGFR positive cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. This method is also suitable for binding EV to peptides and single domain antibodies targeting other receptors (such as HER2 and SIRPα), and the bound EV can deliver RNA in addition to small molecules, supporting the multi-functional application of EV in cancer therapy. This simple, efficient, and universal method allows stable surface modification of EV without genetic or chemical modification, thus helping to deliver the therapeutic payload safely and specifically to the target cells.
The conjugation of single domain antibody refers to the covalent binding of a single antigen binding domain with other biomolecules or chemical molecules to form complexes with new or enhanced functions. This coupling can be achieved by chemical cross-linking, biological covalent, or non-covalent bonds, which can be used to bind single-domain antibodies to drugs, markers, or other carrier proteins to achieve specific biological or pharmacological effects.
Drug delivery: conjugation of single-domain antibodies and drug molecules or toxins can achieve highly selective delivery to specific targets, thereby enhancing the efficacy of drugs and reducing toxicity to non-targeted tissues.
Marker detection: combining single-domain antibodies with markers, such as fluorescent dyes, radioisotopes, or gold nanoparticles, can be used to detect the presence and distribution of specific biomolecules or cells, such as through immunohistochemical analysis or biological imaging.
Immunotherapy: specific killing of tumor cells can be achieved by conjugation of single-domain antibodies with immune stimulators or cytotoxic molecules, such as through the CAR structure in CAR-T cell therapy.
Diagnosis and treatment: conjugation of single-domain antibodies with diagnostic reagents or therapeutic drugs can achieve the integration of simultaneous diagnosis and treatment, for example, through immunotherapy for targeting tumor markers.
Chemical cross-linking: the formation of covalent bonds between single-domain antibodies and target molecules by chemical reactions, such as chemical coupling with reactants using active groups.
Biological covalent binding: the use of specific binding between biomolecules, such as the binding of enzymes to substrates and the binding of affinity ligands to receptors.
Protein engineering: by changing the amino acid sequence of a single domain antibody, a specific binding site or mutant is introduced to enable it to bind specifically to the target molecule.
Nanotechnology: using the special properties of nanomaterials, such as gold nanoparticles, magnetic nanoparticles, etc., to combine single-domain antibodies with target molecules.
Use the resources in our library to help you understand your options and make critical decisions for your study.
All listed services and products are For Research Use Only. Do Not use in any diagnostic or therapeutic applications.
| USA:
Europe: Germany: |
|
|
Call us at: USA: UK: Germany: |
|
|
Fax:
|
|
| Email: info@creative-biolabs.com |
