Creative Biolabs provides SIAT® antigen presentation assay service to identify potential epitopes from biotherapeutic drugs in complex with HLA molecules by mass spectrometry. The SIAT® antigen presentation assay can be used to measure antigen processing and presentation, which can directly identify the epitopes of a protein antigen that are bound to HLA molecules and displayed to T cells by antigen-presenting cells (APCs). This service offers valuable and accurate information for epitopes from biotherapeutic drug candidates and other proteins of interest to help understand and manage their potential immunogenicity. It can be employed to explore the population bias of responses to the same epitopes by using HLA-typed blood cells from different donors. Also, it can facilitate the profiling and comparison of the immune responses between novel agents or biosimilars and existing safe drugs or proteins. In addition, the efficacy of agents that interfere with antigen presentation process can also be evaluated by SIAT® antigen presentation assay.
 Professional antigen-presenting cells process intracellular and extracellular pathogens. (Roy, 2003)
Professional antigen-presenting cells process intracellular and extracellular pathogens. (Roy, 2003)
Antigen recognition by immune effector cells requires APCs, such as dendritic cells (DCs), to present the epitopes with human leukocyte antigen (HLA, also known as major histocompatibility complex, MHC) class II molecules on the cell surface. DCs process antigens into small peptides consisting of 13-18 amino acids and HLA class II molecules are loaded with these peptides within endosomes and subsequently transported to the plasma membrane of DCs. Peptides in the form of HLA-II:peptide complexes can then lead to T cell activation by interaction with specific T cell receptors (TCRs). The peptides within the complexes are hence termed TCR epitopes. TCR epitopes can be utilized not only for the optimization of biotherapeutic drug candidates in their efficiency and safety but also for the development of novel drugs and basic research.
Despite the fact that there are diverse ways of predicting and identifying this valuable information, it is the most direct approach by analyzing the presented molecules with HLA molecules. SIAT® antigen presentation assay service from Creative Biolabs is able to deliver this information about TCR epitopes through interpretation of what DCs naturally says. Below is a brief description of our workflow of SIAT® antigen presentation assay service.
As a leading life science service provider, Creative Biolabs has extensive experience in the development of biotherapeutic drugs at exploratory, preclinical and clinical stages. The functional relevance of the TCR epitopes identified by SIAT® antigen presentation assay can be confirmed by various other services of the SIAT® platform including in silico, in vitro, ex vivo, in vivo immunogenicity assessments. We are dedicated to providing the best services to help our clients accelerate their new biotherapeutic drug discovery and development.
More SIAT® Immunogenicity Related Services at Creative Biolabs
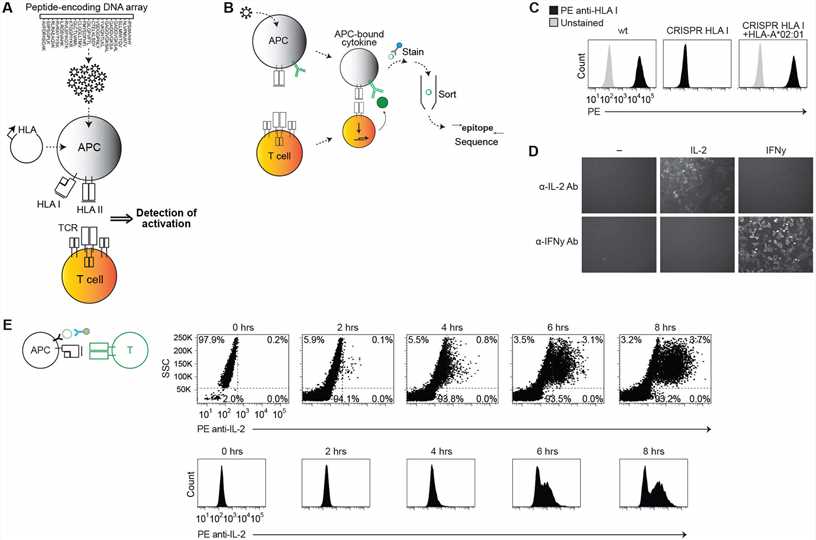 Fig. 2 Establishing a system for epitope identification by APC cytokine capture. (Mark N. Lee, 2021)
Fig. 2 Establishing a system for epitope identification by APC cytokine capture. (Mark N. Lee, 2021)
In the study, researchers developed a high-throughput method using antigen-presenting cells (APCs) engineered to capture cytokines, enabling the identification of epitopes for HLA class I and II-restricted T cell receptors from complex peptide libraries. This approach overcomes traditional limitations by linking T cell activation directly to the DNA encoding the peptide. Key results include the successful identification of specific epitopes for both CD8+ and CD4+ TCRs from highly complex libraries, notably uncovering previously unknown epitopes of human cytomegalovirus. The antigen presentation assay was pivotal, employing engineered APCs that express anti-cytokine antibodies, a library of DNA-encoded peptides, and multiple HLA molecules, facilitating the screening of thousands of potential epitopes and advancing the discovery of T cell targets crucial for disease understanding and therapeutic development.
An antigen presentation assay is a technique used to identify and characterize the peptides presented by HLA molecules on the surface of cells. This assay is crucial for understanding how biotherapeutic drugs interact with the immune system, particularly which parts of the drug are displayed to T cells.
Mass spectrometry is employed to precisely identify the peptide sequences that bind to HLA molecules. This method provides a detailed analysis of the peptide repertoire presented by HLA molecules after exposure to a biotherapeutic drug, helping to pinpoint potential immunogenic epitopes.
HLA molecules are responsible for presenting peptide fragments, including those derived from therapeutic drugs, to T cells. The binding affinity of peptides to HLA molecules greatly influences the immune response, making their study vital for assessing the immunogenic potential of biotherapeutics.
Cells, typically antigen-presenting cells such as dendritic cells or B cells, are cultured with the biotherapeutic drug. The cells process the drug and present its peptides on their surface HLA molecules. These cells are then harvested for analysis by mass spectrometry.
This assay can be applied to a wide range of biotherapeutic drugs, including monoclonal antibodies, vaccines, fusion proteins, and other recombinant proteins. It is particularly useful for drugs where specific epitope identification is crucial for understanding their immunogenicity.
Challenges include the need for highly sensitive mass spectrometry equipment to detect low-abundance peptides, the complexity of data analysis, and the requirement for in-depth knowledge of HLA peptide binding preferences.
By identifying the peptide sequences that bind to HLA molecules, researchers can predict which fragments of the biotherapeutic might be recognized by T cells, potentially leading to an immune response. This insight is critical for modifying drugs to reduce their immunogenicity.
This method offers a high-resolution, unbiased approach to epitope mapping compared to techniques like peptide scanning or computational prediction. It allows for the direct identification of naturally processed and presented peptides, providing a more accurate reflection of potential immunogenic epitopes in vivo.
Use the resources in our library to help you understand your options and make critical decisions for your study.
All listed services and products are For Research Use Only. Do Not use in any diagnostic or therapeutic applications.
| USA:
Europe: Germany: |
|
|
Call us at: USA: UK: Germany: |
|
|
Fax:
|
|
| Email: info@creative-biolabs.com |
