With the excellent High-Affi™ technology, Creative Biolabs can offer the customers with pan anti-carboxylation and site-specific anti-carboxylation antibodies discovery and production services. It includes lysine and glutamate specific antibodies. These antibodies are produced by optimized immunization and purification, with no cross-react with non-modified lysine and glutamate residues, or other kinds of modified peptides.
Carboxylation is an ancient post-translational modification which takes place in glutamate or lysine residues. It plays a critical role in many functions.
Γ-Carboxylation
Γ-carboxylation is an important post-translational modification which is widely distributed in the animal kingdom, with the conversion of glutamate residues to γ-carboxyglutamate (Gla) residues in proteins. This process is catalyzed by γ-glutamyl carboxylase in the lumen of the endoplasmic reticulum, using vitamin K as a cofactor. Γ-glutamyl carboxylase interacts the substrate with a high-affinity γ-carboxylation recognition sequence and performs multiple modifications of the substrate, and then the product is released.
Substrates and functions of Γ-Carboxylation
It has been shown that γ-carboxylation occurs primarily in proteins involved in the blood clotting cascade, specifically factors II, VII, IX, and X, protein C, and protein S. Γ-carboxylation have also been found in some bone proteins to impact bone growth and extraosseous calcification.
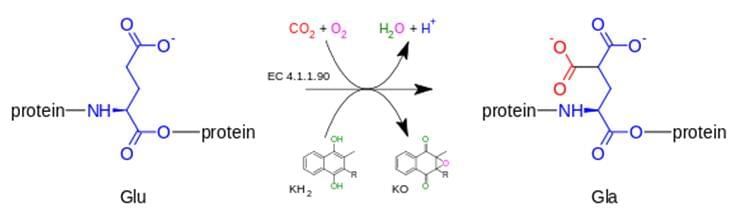 Fig.1 Protein γ-carboxylation.1
Fig.1 Protein γ-carboxylation.1
Lysine carboxylation
Unlike γ-carboxylation, lysine carboxylation occurs spontaneously under basic pH conditions involving carbon dioxide in solution and without the mediation of any other enzyme. It involves the addition of a carboxyl group to the ε-amino group of the lysine.
Substrates and functions of lysine carboxylation
Lysine carboxylation is required for the catalytic function of several important enzymes, as the lysine contains an acidic residue which can perform a direct role in the catalytic reaction. More frequently, lysine carboxylation can be as a co-catalytic determinant of metal ion(s) to trigger conformational and physicochemical changes of proteins. In addition, lysine carboxylation can result in the rearrangement of the active site of a protein by forming strong hydrogen-bonding interactions.
Difficulties in researching of carboxylation
Compared with other modifications, carboxylation has not been fully investigated. The difficulty is mainly from the instability of the modification, as the carboxyl group is spontaneously released in acidic conditions. Therefore, mass spectrometry cannot be used to detect carboxylation. Besides, X-ray crystallography is not exempt for the problems of a labile chemical modification and distinguishing carboxylation from other modifications. In addition, the specific antibodies for carboxylation have not been discovered. All these influence factors and disadvantages have limited the research for carboxylation.
Fortunately, computational methods can be valuable in overcoming the difficulties affecting the detection of spontaneous post-translational modification such as carboxylation. Creative Biolabs has many years of experiences in antibody discovery for post-translational modification based on the excellent High-Affi™ technology. Benefit from computational methods, our scientists can provide the global customers with custom antibody services for post-translational modification specific antibody discovery.
Creative Biolabs can provide a comprehensive list of PTM-specific antibody production services of your choice.
Reference
All listed services and products are For Research Use Only. Do Not use in any diagnostic or therapeutic applications.
| USA:
Europe: Germany: |
|
|
Call us at: USA: UK: Germany: |
|
|
Fax:
|
|
| Email: info@creative-biolabs.com |
