|
Research
|
Conclusion
|
|
Investigation of the ability of Aspergillus flavus to produce exosomes.
|
Aspergillus flavus was cultured to cause spore formation, its spores were inoculated and cultured in a suitable medium, and then the conidium culture was collected. Filtering and concentrating the supernatant of Aspergillus flavus conidium culture by ultrafiltration. Finally, Aspergillus flavus-derived exosomes were obtained by ultracentrifugation. NTA detected that these vesicles had a similar size and distribution as the common bacterial vesicles.
|
|
Assessment of Aspergillus flavus-derived exosomes affecting the host immune response profile.
|
Bone marrow-derived macrophages exposed to Aspergillus flavus-derived exosomes were found to produce important pro-inflammatory mediators, including TNF-α, NO, and IL-1β, in a dose-dependent manner.
|
|
Aspergillus flavus-derived exosomes induced strong bactericidal activity in macrophages.
|
An assay of phagocytosis of macrophages showed that treatment with Aspergillus flavus-derived exosomes stimulated enhanced bactericidal activity of macrophages with more fungal conidia being phagocytosed.
|
|
Aspergillus flavus-derived exosomes induced polarization of the macrophage phenotype.
|
Macrophages co-incubated with Aspergillus flavus-derived exosomes were detected to have significantly increased levels of the polarization marker iNOS transcripts, whereas there were no significant changes in the M2-associated polarization marker transcripts. This suggests that Aspergillus flavus-derived exosomes stimulated macrophage polarization to the M1 phenotype.
|
|
Detection of in vivo effects of Aspergillus flavus-derived exosomes.
|
Galleria mellonella larval models were pretreated with Aspergillus flavus-derived exosomes and subsequently attacked with Aspergillus flavus conidia. It was found that Aspergillus flavus-derived exosomes reduced CFU levels in vivo, showing resistance to fungal infection through activation of the immune system.
|

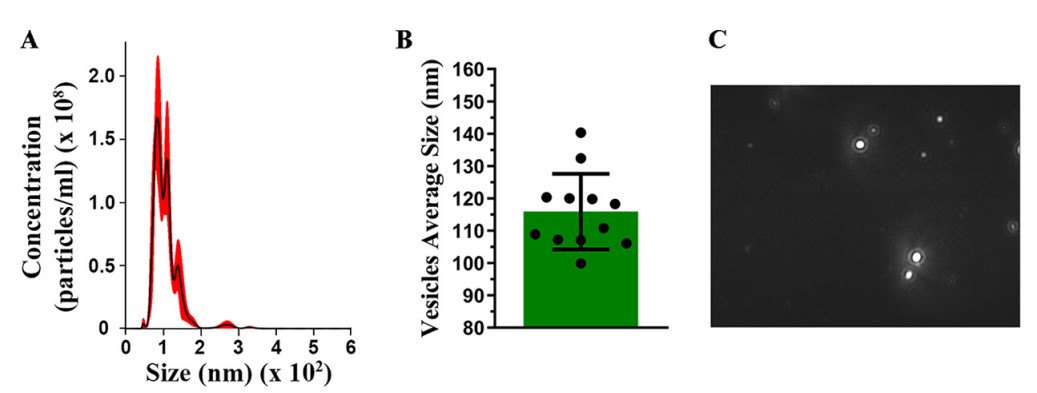 Fig. 1 NTA characterization of Aspergillus flavus-derived Exosome.1
Fig. 1 NTA characterization of Aspergillus flavus-derived Exosome.1








