Malassezia-derived Exosome Research and Application
Malassezia-derived exosomes play a close role in the pathogenesis of inflammatory dermatoses, such as seborrheic dermatitis, Malassezia folliculitis, and atopic dermatitis, induced by Malassezia sympodialis, which parasitizes the skin surface as a common commensal fungus. Creative Biolabs, as a supplier of exosome research services for many years, specializes in providing high-quality services for clients researching Malassezia-derived exosomes.
Isolation of Malassezia-derived Exosomes
-
Inoculate the resuscitated Malassezia sympodialis in modified Dixon agar plates and incubate in a 30 ℃ incubator for about 48-72 h, and then pass on the culture. After 3-4 passages, pick a colony into the liquid modified Dixon medium and incubate it overnight in a 30 ℃ shaking incubator.
-
Remove Malassezia sympodialis bodies, media impurities, dead body fragments, and larger diameter extracellular vesicle components by differential centrifugation.
-
Collect the supernatant from each step of centrifugation and discard the precipitates. Concentrate the supernatant obtained after the last centrifugation by ultrafiltration and filter it to further remove possible impurity components.
-
Ultracentrifuge the Malassezia sympodialis supernatant several times in succession and resuspend the Malassezia-derived exosome precipitate with cold PBS solution.
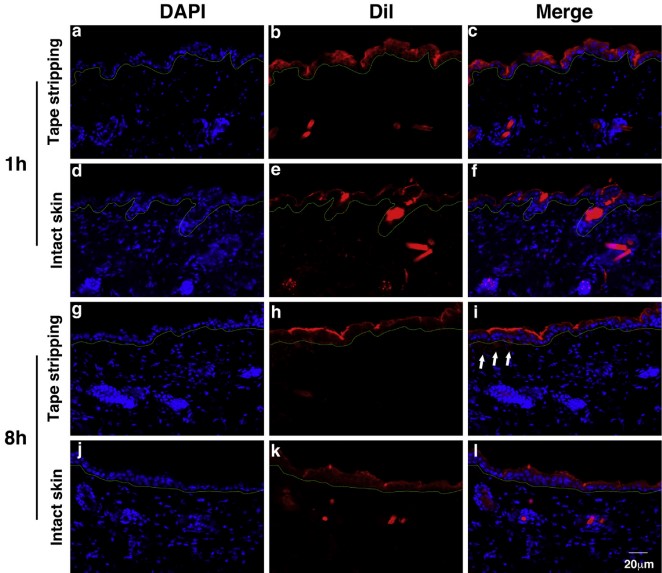 Fig. 1 Fluorescence micrographs of Malassezia-derived exosomes penetrating into mouse epidermis.1
Fig. 1 Fluorescence micrographs of Malassezia-derived exosomes penetrating into mouse epidermis.1
Studies on Malassezia-derived Exosomes
|
Research
|
Conclusion
|
|
Exosomes generated from Malassezia are internalized by the cell.
|
Fluorescence confocal microscopy of keratinocytes incubated with Malassezia-derived exosomes revealed that the distribution of Malassezia-derived exosomes in the perinuclear area of the cells accumulated with increasing incubation time without causing damage.
|
|
Malassezia-derived exosomes regulated IL-6 expression in keratinocytes.
|
qPCR and ELISA assays revealed that human immortalized keratinocytes exposed to Malassezia-derived exosomes strongly secreted IL-6.
The immunohistochemistry experiment further indicated that Malassezia-derived exosomes significantly enhanced IL-6 production in a mouse skin model of epidermal barrier breakdown.
|
|
Malassezia-derived exosomes upregulated IL-6 involving activation of NF-kB.
|
Protein blotting results showed a gradual increase in phosphorylated p65 in human immortalized keratinocytes after Malassezia-derived exosomes treatment. Meanwhile, the strong expression of IL-6 induced by Malassezia-derived exosomes was counteracted by pretreatment with NF-kB inhibitors.
|
|
Malassezia-derived exosomes regulated ICAM-1 expression in primary keratinocytes.
|
Confocal laser scanning imaging of Malassezia-derived exosomes-stimulated human primary keratinocytes suggested that Malassezia-derived exosomes significantly encouraged keratinocytes to express high levels of ICAM-1 as compared to control cells.
|
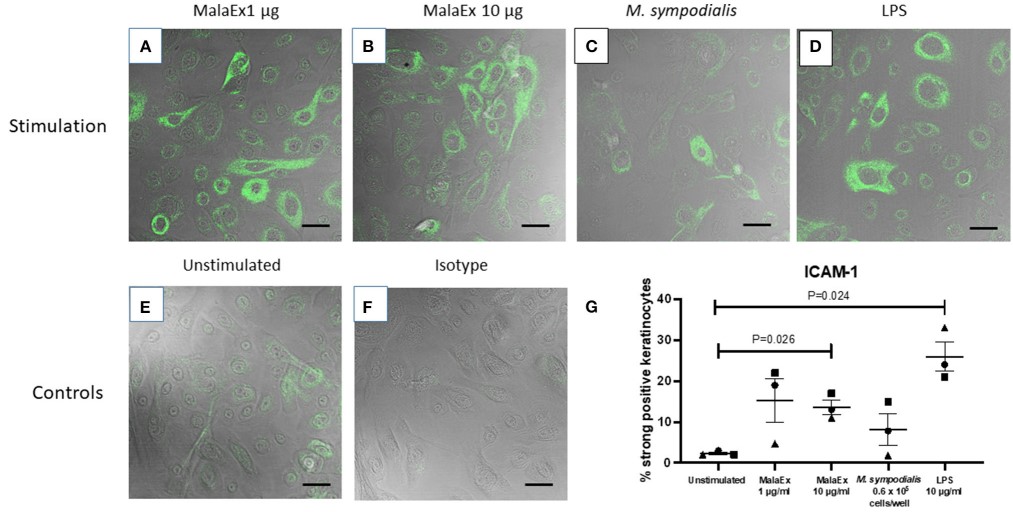 Fig. 2 Malassezia-derived exosomes enhanced ICAM-1 expression.2
Fig. 2 Malassezia-derived exosomes enhanced ICAM-1 expression.2
Malassezia-derived exosomes provide autocrine or paracrine signals in Malassezia sympodialis interaction with the host, involving cross-kingdom regulation present in the cell. Moreover, Malassezia-derived exosomes have been shown to stimulate keratinocytes to produce inflammation-associated factors, exhibiting immunomodulatory effects. Creative Biolabs provides services for characterization, function, and related molecular mechanism studies of the Malassezia-derived exosome, contributing scientific data to Malassezia-associated skin disease projects. Please contact us to discuss your project.
References
-
Zhang, Yu-Jing, et al. "Extracellular vesicles derived from Malassezia furfur stimulate IL-6 production in keratinocytes as demonstrated in in vitro and in vivo models." Journal of Dermatological Science 93.3 (2019): 168-175.
-
Vallhov, Helen, et al. "Extracellular vesicles released from the skin commensal yeast Malassezia sympodialis activate human primary keratinocytes." Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology 10 (2020): 6.
For Research Use Only. Cannot be used by patients.
Related Services:

 Fig. 1 Fluorescence micrographs of Malassezia-derived exosomes penetrating into mouse epidermis.1
Fig. 1 Fluorescence micrographs of Malassezia-derived exosomes penetrating into mouse epidermis.1
 Fig. 2 Malassezia-derived exosomes enhanced ICAM-1 expression.2
Fig. 2 Malassezia-derived exosomes enhanced ICAM-1 expression.2








