Chitosan
Introduction Chitosan and its Derivatives Applications
Liposomes' low resilience to stomach pH, enzymatic breakdown, and poor stability all restrict their application. To change the surface properties of liposomes, a variety of synthetic and natural polymers were used. Chitosan (CS) is the most common biopolymer utilized to modify liposomes. Creative Biolabs provides chitosan-based liposome development services, to provide high-quality and efficient solutions to fulfill your unique drug delivery requirements.
Why Choose Chitosan-coated Liposomes?
Chitosan (CS) is a naturally cationic polymer with excellent physicochemical and biological properties, such as biodegradability, antimicrobial activity, biocompatibility, low toxicity, blood compatibility, and adhesiveness. The positively charged amino groups of chitosan interact electrostatically with negatively charged liposomes, and hydrogen bonds form between the hydroxyl groups of chitosan and the liposomes, resulting in a chitosan coating on the liposome surface. These chitosan-coated liposomes, also known as chitosomes, regulate the biological functions of liposomal vesicles by delaying drug release, enhancing liposome stability, half-life, and bioavailability. However, the solubility of chitosan in acidic media and its insolubility in neutral or alkaline media significantly limit its applications. To retain the biological properties of chitosan while extending its solubility across a wide pH range, various derivatives can be synthesized by grafting hydroxyl or amino functional groups.
Chitosan and its Derivatives
Chitosan derivatives are compounds that have undergone chemical modification of chitosan's amino and hydroxyl groups by introducing new functional groups, allowing for the improvement of their solubility, biocompatibility, and functional properties without altering their inherent characteristics. The main chitosan derivatives used for modifying liposomes include glycol chitosan, N-dodecyl chitosan, N-trimethyl chitosan, and thioglycolic acid chitosan, among others.
|
Chitosan Derivatives
|
Chemical Structure
|
Aim of Chitosan Derivatization
|
|
Chitosan
|
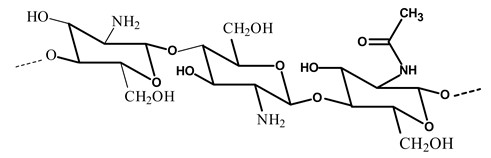
|
-
Improve the chitosan characteristics.
|
|
Glycol chitosan
|
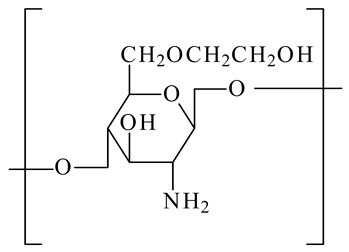
|
-
Focusing on the acidic tumor microenvironment.
-
Boost the potency of anti-cancer medications.
|
|
Methylated N-(4-N,N-dimethylaminobenzyl) chitosan (TMBz-chitosan)
|
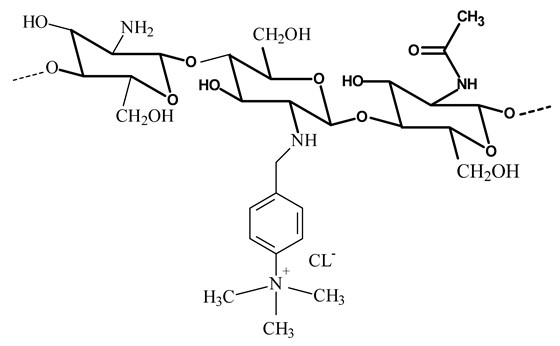
|
-
Enhancing hydrophobic interactions with cell membranes by supplying hydrophobic regions.
|
|
N-dodecyl chitosan
|
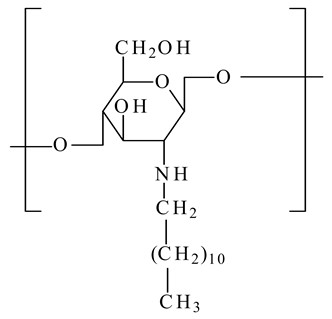
|
-
Long alkyl chains anchor the bilayer of liposomes, increasing their stability.
|
|
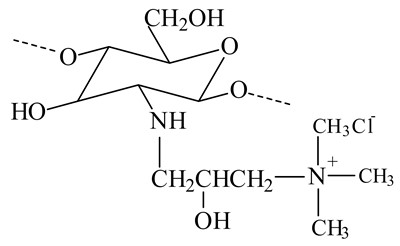
N-[(2-hydroxy-3-trimethylamine) propyl] chitosan chloride (HPTMA-chitosan)
|
|
-
Improve the stability of liposomes
-
Increase the solubility of chitosan.
|
|
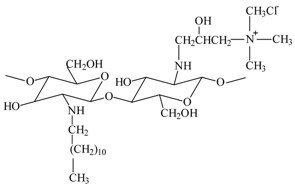
N-dodecyl-chitosan N-[(2-hydroxy-3-trimethylamine) propyl]chloride (N-dodecyl-chitosan-HPTMA)
|
|
-
Improve the stability of liposomes.
-
Increase chitosan solubility
|
|
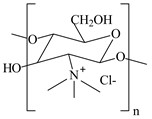
N-trimethyl chitosan
|
|
-
Increasing the solubility of chitosan across a broad pH range.
-
Improve the stability of liposomes.
|
|
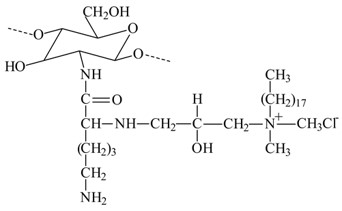
PEGylated octadecyl-quaternized lysine modified chitosan
|
|
-
Offering amphiphilicity and spatial stability.
|
Pelargonic chitosan (n=7)
Lauric chitosan (n=10)
|
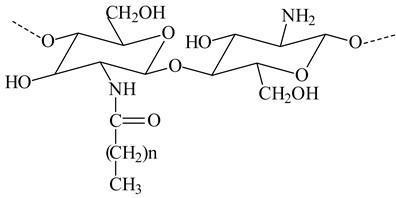
|
-
Mucoadhesive coating is used to encapsulate positively charged liposomes.
-
Liposomes in solutions are further stabilized sterically by the side groups inserted into the polysaccharide chains.
|
|
Thioglycolic acid chitosan (TGA-chitosan)
|
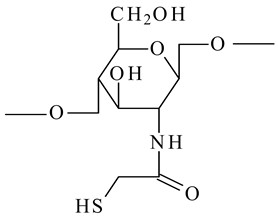
|
-
Boost the peptides' oral bioavailability and mucoadhesive properties.
|
|
Thioglycolic acid 6-mercaptonicotinamide-conjugate chitosan (TGA-MNA-chitosan)
|
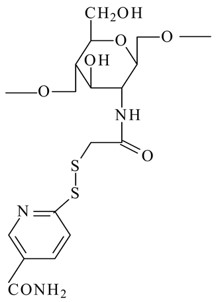
|
-
By conjugating thioglycolic acid chitosan with 6,6′-dithionicotinamide, the resultant derivative showed increased mucoadhesive characteristics and was less susceptible to oxidation.
|
Biomedical Applications of Chitosan-coated Liposomes
-
Vaccine delivery
-
Tumor targeting
-
Gene delivery
-
Antiviral activity
-
Tissue engineering
-
Wound healing drug delivery
As an industry-leading supplier, Creative Biolabs possesses extensive experience in the development of chitosomes, aiming to revolutionize drug delivery with their unique properties. Contact us to explore how our expertise in chitosomes and other chitosan-based delivery systems can be customized to your needs and contribute to a healthier future.
References
-
Sebaaly, Carine, et al. "Chitosan-coating effect on the characteristics of liposomes: A focus on bioactive compounds and essential oils: A review." Processes 9.3 (2021): 445.
-
Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.

For Research Use Only. Not For Clinical Use












 For Research Use Only. Not For Clinical Use
For Research Use Only. Not For Clinical Use
