Enzyme-responsive Liposome Development Service
Introduction Design Principle Advantages
Enzyme-responsive liposomes are a commonly utilized form of stimuli-responsive liposomes, belonging to the smart drug delivery systems. Creative Biolabs specializes in the development of enzyme-responsive liposomes, tailor-made to revolutionize targeted drug delivery.
What is Enzyme-responsive Liposomes?
Enzymes, biological catalysts produced by living cells, are involved in nearly all biochemical and metabolic processes within biological systems. In areas of tumors or inflammation, changes in the expression of specific enzymes can be observed, such as proteases, phosphatases, and glycosidases. Using these enzymes as triggers for stimuli-responsive liposomes can mediate the targeted accumulation of drugs at the desired biological locations, thereby improving therapeutic efficacy and reducing side effects.
Enzyme-responsive liposomes, also referred to as enzyme-sensitive or enzyme-activated liposomes, undergo degradation, disassembly, or morphological changes when exposed to specific enzymatic environments, leading to drug release. The mechanism of drug release following enzyme exposure involves alterations in the structural integrity of the lipid bilayer; detachment of a protective polymeric layer, enhancing cellular internalization; and cleavage of a lipopeptide or lipopolymer embedded within the bilayer; the activation of a prodrug contained within the liposomes.
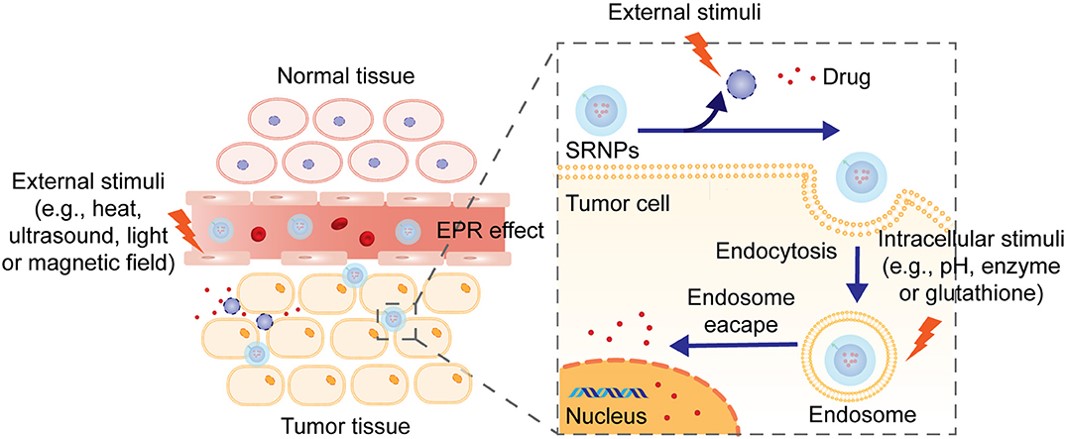 Fig.1 The mechanism of drug release from stimuli-responsive liposomes.1, 2
Fig.1 The mechanism of drug release from stimuli-responsive liposomes.1, 2
Design Principle of Enzyme-responsive Liposomes
The design principle of enzyme-responsive liposomes involves the conjugation of enzyme-substrate fragments to the liposomal structure through covalent bonds, hydrophobic interactions, or electrostatic interactions, thus integrating them as part of the liposome and endowing them with enzyme sensitivity. Various enzymes, such as Cathepsin B, Hyaluronidase, and Matrix Metalloproteinases, have been utilized in the construction of enzyme-sensitive liposomes. By leveraging their substrates, enzyme-responsive liposomes can be developed to target different pathological environments.
|
Enzymes
|
Types of enzymes
|
Enzyme Substrate
|
Pathological Characteristics
|
|
Secreted phospholipase A2 (sPLA2)
|
Extracellular enzymes
|
The acyl chain at sn-2 position in a phospholipid.
|
Highly expressed in inflammatory diseases, atherosclerosis, and cancer.
|
|
Matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs)
|
Extracellular enzymes
|
Short peptide linkers connect TAT liposomes to PEG chains.
|
Elevated expression in inflammatory diseases, cardiovascular diseases, and cancer.
|
|
Urokinase plasminogen activator (uPA)
|
Extracellular enzymes
|
Arg-Ser bond in peptides.
|
Highly expressed in cancers such as colon, breast, bladder, and ovarian tumors.
|
|
Cathepsin B
|
Intracellular enzyme
|
Extracellular matrix proteins and cell adhesion proteins.
|
Highly expressed in various cancers, it is involved in the occurrence, invasion, metastasis, and autophagy of cancers.
|
|
Phospholipase A2 (PLA2)
|
Extracellular and intracellular enzymes
|
Phospholipids.
|
Overexpressed in various cancers such as pancreatic, breast, lung, and prostate
|
|
Hyaluronidase (HAase)
|
Extracellular enzymes
|
Hyaluronan.
|
Elevated expression in various cancers, is associated with tumor angiogenesis and cell migration.
|
|
Prostate-specific antigen (PSA)
|
Extracellular enzymes
|
Spermatin
|
Highly expressed in prostate cancer.
|
|
α-amylase
|
Extracellular and intracellular enzymes
|
α-1,4-glucoside bond
|
Overexpression in breast cancer, lung cancer, and other cancers.
|
Advantages of Enzyme-responsive Liposomes
Compared to other types of stimuli-responsive liposomes, enzyme-responsive liposomes offer the following advantages:
-
Enzymes are endogenous substances that obviate the requirement for external triggers like magnetic fields, ultrasonic waves, or light. They possess inherent biocompatibility and biosafety.
-
Enzymatic reactions are rapid and occur under mild conditions (body temperature, neutral pH, aqueous solutions).
-
Enzymes exhibit substrate specificity, which helps avoid non-specific drug targeting and release.
-
Enzyme expression varies across different stages of tumor development, allowing for personalized dosing based on enzyme levels at the tumor site, achieving precision cancer therapy.
-
The drug release in target tissues is generally proportional to the level of enzymatic activity and the severity of the pathological state.
-
The bioactive molecules generated after enzymatic digestion may have synergistic therapeutic effects or promote drug absorption.
As a pioneer in enzyme-responsive liposome development, Creative Biolabs is at the forefront of advanced drug delivery systems. We are your gateway to the cutting-edge world of enzyme-responsive liposomes. Contact us now to unlock the future of targeted therapeutics and propel your scientific advancements forward.
References
-
Li, Mengqian, et al. "Enzyme-responsive nanoparticles for anti-tumor drug delivery." Frontiers in chemistry 8 (2020): 647.
-
Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.

For Research Use Only. Not For Clinical Use

 Fig.1 The mechanism of drug release from stimuli-responsive liposomes.1, 2
Fig.1 The mechanism of drug release from stimuli-responsive liposomes.1, 2
 For Research Use Only. Not For Clinical Use
For Research Use Only. Not For Clinical Use


