Western Immunoblot Introduction
Western blotting (WB) is a technique that is susceptible to many factors and plays an important role in the field of protein research. After decades of accumulation, Creative Biolabs has established a complete WB detection platform to provide high-quality NAA detection and analysis services to customers around the world.
What is WB?
WB has a wide range of applications in molecular biology, biochemistry and cell biology. WB is a very promising technique for the detection of proteins and post-translational modifications of proteins. Based on the specificity of antigen-antibody interactions, specific information about target proteins can be obtained from complex samples through antibody recognition of specific antigens, thereby providing semi-quantitative data of target proteins. Simply put, WB is a fast and sensitive detection method for the detection and characterization of proteins.
Procedures of WB
WB involves multiple steps, and errors can occur at any step, so each step is critical to obtaining reliable and reproducible results. WB mainly includes the following key steps:
- Homogenize the sample.
- Use gel electrophoresis to separate proteins in a sample based on molecular weight.
- Transfer the resulting protein to a solid support, typically a nitrocellulose or PVDF membrane matrix.
- Add a primary antibody that recognizes the target protein. Secondary antibodies are then added to bind to specific primary antibodies.
- Finally, the bound antibody is detected by developing film. Because the antibody binds to the protein, only one band is shown. The thickness of the band corresponds to the amount of protein present.
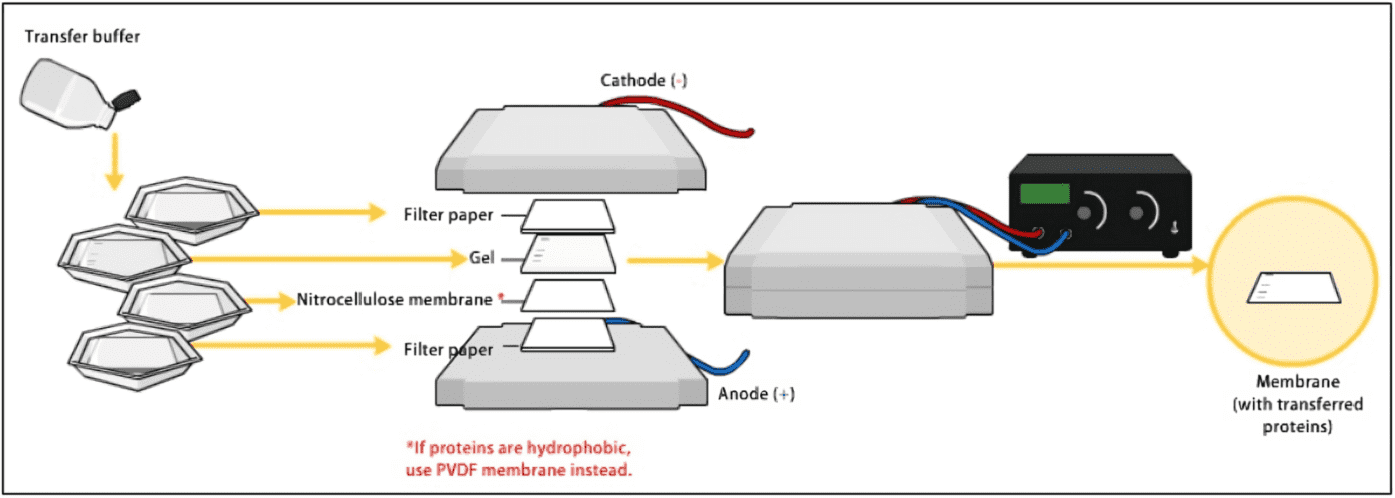 Fig.1 Detailed schematic diagram of western blot transfer technique.1
Fig.1 Detailed schematic diagram of western blot transfer technique.1
Basic Principle of WB
Electrophoresis is an efficient method for separating proteins based on shape, size or charge. Proteins are charged macromolecules that can migrate in the polyacrylamide gel under electric field. The migration speed is related to the molecular weight of the protein. The final result is that mixed protein samples form different bands on the gel. Proteins were subsequently immobilized by transferring them to PVDF membranes. Primary antibodies against proteins or secondary antibodies against primary antibodies can be used to detect proteins on membranes and can be detected and visualized in multiple ways, usually chemiluminescence. Furthermore, WB can be used alone or with other immunoassays.
Applications of WB
- High sensitivity to detect specific proteins even in small amounts.
- Diagnosis of different diseases, such as infectious diseases and non-infectious diseases.
- Immunogenic responses to infectious agents (e.g., viruses, bacteria) are readily detected by this technique.
- Quantify proteins and other gene products in gene expression studies.
- Different biomarkers such as growth factors, cytokines and hormones were also analyzed by WB.
- Detection of different isoforms of proteins.
- Detection of protein-protein, protein-DNA interactions.
- Detection of post-translational modifications.
With our advanced platform and experienced team, we are happy to provide the best service and the most accurate test results to meet the needs of every customer. If you have any questions please contact us for more details.
Reference
- From Wikipedia: By Bensaccount - Own work, CC BY 3.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Western_blot_transfer.png

