Immunogenicity testing is an important part of the clinical safety assessment of biotech drugs. Drug-induced antibody responses can affect pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, and toxicity. The immunogenicity may be a chimeric biopharmaceutical, or even a humanized molecule and a fully-humanized biopharmaceutical drug. In most cases, immunogenicity is caused by residues in the CDR regions. Creative Biolabs provides you with detailed testing methods and testing techniques in ADA assay sample test and accurate analysis of your samples, in order to enter the clinical trials more quickly, to ensure the safety of a candidate drug.
Screening assays and specificity assays are typically included, and characterization assays typically include antibody titration and neutralization antibody detection. When applied to a specific study sample, the anti-drug antibody analysis experiment requires two key decision parameters, which are the screening critical point of the screening test and the specific critical point of the specific verification test. The screening critical point contributes to the classification of the anti-drug antibody detection results, the active sample is higher than the screening critical point, and the inactive sample is below the critical point. The active sample is tested positive or negative by a specific confirmation test. The specificity critical point is the amount of sample required to suppress signal passage, that is, the drug-resistant antibody of a specific drug, which needs to be determined by experiments.
 Fig.1 ADA assay formats used for cynomolgus monkeys. (Carrasco-Triguero, 2016)
Fig.1 ADA assay formats used for cynomolgus monkeys. (Carrasco-Triguero, 2016)
Validation tests prior to the start of sample bioanalysis in clinical and non-clinical studies are usually known as pre-study validation, which describes the performance characteristics of analytical methods in terms of both mathematical and quantifiable aspects. After a complete method of development and optimization, the analytical method should be qualified for the corresponding verification. For example, the optimized experimental data indicates that the detection method has potential reliability and is suitable for the corresponding testing requirements.
Creative Biolabs owns the most comprehensive testing equipment and testing technology. Please contact us in time about more details and we will be glad to serve you.
Other optional SIAT® Anti-drug Antibodies (ADA) Assays:
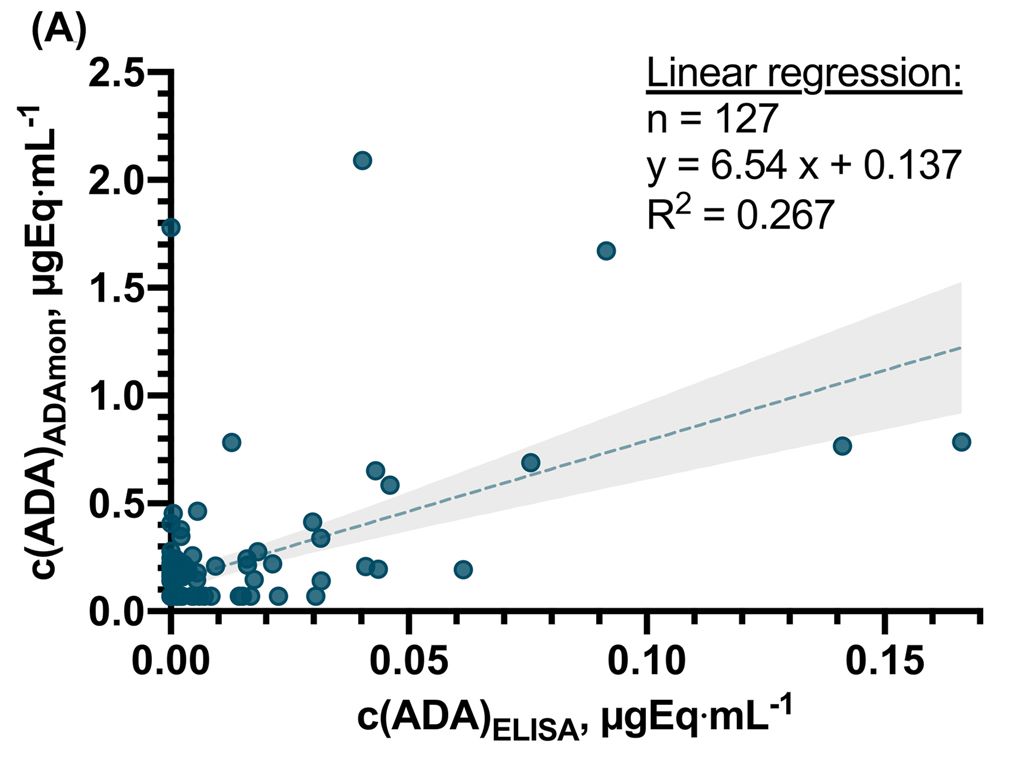 Fig. 2 Method comparison of ADAmon and ELISA for ADA quantification and detection. (Melina K Grasmeier, 2023)
Fig. 2 Method comparison of ADAmon and ELISA for ADA quantification and detection. (Melina K Grasmeier, 2023)
The study evaluates the clinical implications of anti- TNF-α mAb antibody (ADA) detection and quantification using surface plasmon resonance (SPR) assays, introducing a novel approach for therapeutic drug monitoring in patients with inflammatory bowel disease. By confirming the precision of the SPR-based ADA assay (ADAmon) in quantifying ADAs and determining ADA binding stability through dissociation ratios (DissR), even in the presence of anti-TNF-α mAb, the research highlights a significant advancement over traditional ELISA, which showed poor concordance with SPR. This enhanced detection and characterization of ADAs by SPR could facilitate more tailored and effective treatment strategies, indicating its potential to influence future diagnostic and therapeutic protocols in managing autoinflammatory diseases.
ADA assay sample analysis is crucial for determining whether patients develop immune responses against biologic therapies, which can impact drug efficacy and patient safety. It helps in understanding how patients' bodies react to biologic drugs, guiding adjustments to treatment plans to optimize therapeutic outcomes.
Sample preparation for an ADA assay typically involves collecting blood from the patient, separating the serum or plasma, and treating the sample to reduce interference from the drug or other serum components. This may include processes like precipitation, dilution, or specific binding steps to isolate ADAs for accurate detection.
Common techniques in ADA assay sample analysis include enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), radioimmunoassay (RIA), and electrochemiluminescence (ECL). More advanced methods like surface plasmon resonance (SPR) and mass spectrometry are also used for their ability to provide detailed information about ADA characteristics and concentration.
Ensuring specificity in ADA assays involves using specific reagents that only recognize human immunoglobulins bound to the drug, not the drug itself or other serum proteins. Techniques like competitive inhibition or the use of blocking agents can also help reduce non-specific binding and improve assay accuracy.
ADA assays are designed to detect all clinically relevant isotypes of antibodies, including IgG, IgM, and IgA. The assay conditions, such as the choice of detection reagents, are tailored to capture the broad spectrum of ADAs that a patient might develop against a biologic drug.
Drug interference occurs when the presence of the drug in the sample prevents the detection of ADAs. It is managed by designing assays with high drug tolerance, using techniques such as acid dissociation or the use of high-affinity capture reagents that can bind ADAs even in the presence of the drug.
Positive control establishes the assay's capability to detect ADAs if present. A good positive control should reflect the properties of ADAs expected in patient samples, including antibody isotype and affinity, to ensure the assay's relevance and reliability.
Use the resources in our library to help you understand your options and make critical decisions for your study.
All listed services and products are For Research Use Only. Do Not use in any diagnostic or therapeutic applications.
| USA:
Europe: Germany: |
|
|
Call us at: USA: UK: Germany: |
|
|
Fax:
|
|
| Email: info@creative-biolabs.com |
